058.走遍全世界
在国际象棋中,“骑士”这颗棋子的走法很奇特,它只能往前后左右移动一格,然后再往斜向移动一格。
你能用“骑士”在8×8的国际象棋棋盘(见图2-2)上,将每一格都恰好走过,不许重复,也不遗漏,然后再回到出发点吗?该怎么走?
图2-2 国际象棋中“骑士”的走法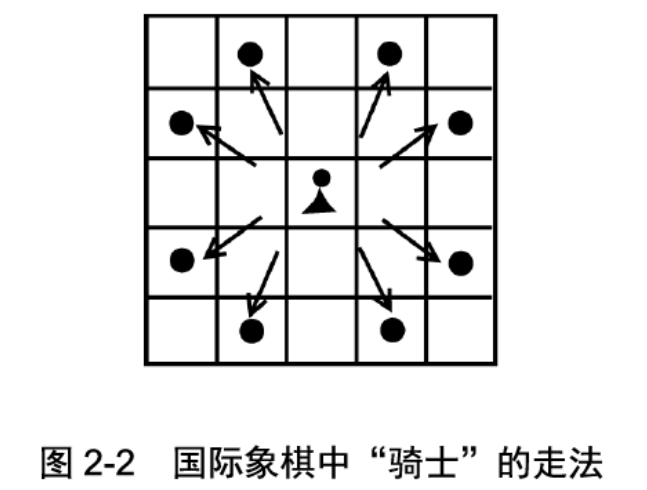
其实就是“骑士巡游”问题,骑士走法就是马走日的步法。下面是一个解决方案,采用多线程+Warnsdorff启发式算法+位掩码,迅速枚举出解,每秒差不多出一万解。可在后台运行,想枚举出所有,是不可能的,没有那么大的存储,估摸着能枚举出上千万的解,顶天一亿多。默认起(0,0),可以在命令行输入起点坐标。
/*
* 用法:gcc -O3 -pthread knigt_tour.c -o knight && ./knight [start_x start_y]
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define N 8 /* 棋盘尺寸,可改为 6,10,12… */
#define NN (N*N)
/* 8 个马步方向 */
static const int dx[8] = { 2, 1,-1,-2,-2,-1, 1, 2 };
static const int dy[8] = { 1, 2, 2, 1,-1,-2,-2,-1 };
/* ================= 全局进度相关 ================= */
static volatile uint64_t g_nodes = 0; /* 已访问节点数 */
static volatile uint64_t g_total_sols = 0; /* 已得解数 */
static volatile bool g_progress_stop = false;
/* 原子递增封装 */
static inline void bump_node(void) {
__atomic_add_fetch(&g_nodes, 1, __ATOMIC_RELAXED);
}
static inline void bump_sol(void) {
__atomic_add_fetch(&g_total_sols, 1, __ATOMIC_RELAXED);
}
/* 进度线程:每秒 stderr 刷新 */
static void *progress_thread(void *dummy) {
uint64_t last_n = 0, last_s = 0;
time_t start = time(NULL);
while (!g_progress_stop) {
sleep(1);
uint64_t n = g_nodes;
uint64_t s = g_total_sols;
double spd = (double)(n - last_n);
fprintf(stderr, "\r节点 %llu 解 %llu 速度 %.0f 节点/s 已用 %ld s",
(unsigned long long)n, (unsigned long long)s, spd, time(NULL)-start);
last_n = n; last_s = s;
}
return NULL;
}
/* ============================================ */
/* 线程私有数据 */
typedef struct {
int tid; /* 线程编号 = 第一跳方向 */
FILE *fp; /* 输出文件句柄 */
uint64_t cnt; /* 本线程解数 */
char buf[1024*1024]; /* 1 MB 缓冲,减少 fwrite 调用 */
int buf_used;
int start_sq; /* 用户指定的起点格子编号 */
} worker_t;
static worker_t g_workers[8];
/* 缓冲刷盘 */
static void flush_buf(worker_t *w) {
if (w->buf_used) {
fwrite(w->buf, 1, w->buf_used, w->fp);
w->buf_used = 0;
}
}
/* 把一条完整回路写入缓冲 */
static void push_solution(worker_t *w, const int path[NN]) {
bump_sol(); /* 全局解数++ */
char tmp[NN*8 + 2];
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < NN; ++i)
len += sprintf(tmp + len, "(%d,%d)", path[i] / N, path[i] % N);
tmp[len++] = '\n';
if (w->buf_used + len > sizeof(w->buf)) flush_buf(w);
memcpy(w->buf + w->buf_used, tmp, len);
w->buf_used += len;
w->cnt++;
}
/* DFS + 位掩码 + Warnsdorff */
static void dfs(int sq, int step, uint64_t mask, int path[NN], worker_t *w) {
bump_node(); /* 每进入一次 = 一个节点 */
path[step] = sq;
/* 到达最后一步,检查能否跳回起点形成闭链 */
if (step == NN - 1) {
int start_sq = w->start_sq;
int x0 = start_sq / N, y0 = start_sq % N;
int x1 = sq / N, y1 = sq % N;
int dx0 = abs(x0 - x1), dy0 = abs(y0 - y1);
if ((dx0 == 1 && dy0 == 2) || (dx0 == 2 && dy0 == 1))
push_solution(w, path);
return;
}
uint64_t next_mask = mask | (1ULL << sq);
int x = sq / N, y = sq % N;
int cand[8], nc = 0;
/* 生成所有可行下一步 */
for (int d = 0; d < 8; ++d) {
int nx = x + dx[d], ny = y + dy[d];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N) continue;
int ns = nx * N + ny;
if (mask & (1ULL << ns)) continue;
cand[nc++] = ns;
}
/* Warnsdorff:优先扩展“后续选择最少”的节点 */
for (int i = 0; i < nc; ++i) {
int min_deg = 99, best = -1;
for (int j = i; j < nc; ++j) {
int s = cand[j], dg = 0;
int sx = s / N, sy = s % N;
for (int d = 0; d < 8; ++d) {
int nx = sx + dx[d], ny = sy + dy[d];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N) continue;
int ns2 = nx * N + ny;
if (next_mask & (1ULL << ns2)) continue;
dg++;
}
if (dg < min_deg) { min_deg = dg; best = j; }
}
/* 交换到当前位置 */
int t = cand[i]; cand[i] = cand[best]; cand[best] = t;
dfs(cand[i], step + 1, next_mask, path, w);
}
}
/* 每个 DFS 线程的入口 */
static void *thread_entry(void *arg) {
worker_t *w = (worker_t *)arg;
int path[NN];
int start_sq = w->start_sq;
uint64_t mask = 1ULL << start_sq;
path[0] = start_sq;
/* 本线程只负责“第一跳”方向 = tid */
int x = start_sq / N, y = start_sq % N;
int d = w->tid;
int nx = x + dx[d], ny = y + dy[d];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N) return NULL;
int ns = nx * N + ny;
dfs(ns, 1, mask | (1ULL << ns), path, w);
flush_buf(w); /* 线程结束把剩余缓冲写盘 */
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
/* 解析起点 */
int start_x = 0, start_y = 0;
if (argc >= 3) { start_x = atoi(argv[1]); start_y = atoi(argv[2]); }
if (start_x < 0 || start_x >= N || start_y < 0 || start_y >= N) {
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid start position (%d,%d)\n", start_x, start_y);
return 1;
}
int start_sq = start_x * N + start_y;
printf("Searching closed tours from (%d,%d) ...\n", start_x, start_y);
FILE *fp = fopen("knight_tour_closed.txt", "w");
if (!fp) { perror("fopen"); return 1; }
/* 启动进度线程 */
pthread_t prog_tid;
pthread_create(&prog_tid, NULL, progress_thread, NULL);
/* 启动 8 个 DFS 线程 */
pthread_t tids[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
worker_t *w = &g_workers[i];
w->tid = i; w->fp = fp; w->cnt = 0; w->buf_used = 0; w->start_sq = start_sq;
pthread_create(&tids[i], NULL, thread_entry, w);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) pthread_join(tids[i], NULL);
g_progress_stop = true; /* 通知进度线程退出 */
pthread_join(prog_tid, NULL);
putchar('\n'); /* 换行覆盖进度条 */
uint64_t total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) total += g_workers[i].cnt;
printf("Total closed tours from (%d,%d): %llu\n", start_x, start_y, (unsigned long long)total);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}























 1922
1922

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








