package cn.itcast.other;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
creatProperties();
}
public static void readProperties() throws IOException{
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileReader("F:\\persons.properties"));
Set<Entry<Object, Object>> entrys = properties.entrySet();
for(Entry<Object, Object> entry :entrys){
System.out.println("键:"+ entry.getKey() +" 值:"+ entry.getValue());
}
properties.setProperty("狗娃", "007");
properties.store(new FileWriter("F:\\persons.properties"), "hehe");
}
public static void creatProperties() throws IOException{
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("狗娃", "123");
properties.setProperty("狗剩","234");
properties.setProperty("铁蛋","345");
properties.store(new FileWriter("F:\\persons.properties"), "hehe");
}
}
package cn.itcast.other;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("F:\\count.properties");
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(file));
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
int count = 0;
String value = properties.getProperty("count");
if(value!=null){
count = Integer.parseInt(value);
}
if(count==3){
System.out.println("你已经超出了试用次数,请购买正版软件!!");
System.exit(0);
}
count++;
System.out.println("你已经使用了本软件第"+count+"次");
properties.setProperty("count",count+"");
properties.store(fileOutputStream,"runtime");
}
}
package cn.itcast.other;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
class Animal{
String name;
String color;
public Animal(String name,String color){
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "名字:"+this.name+ " 颜色:"+ this.color;
}
}
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("F:\\a.txt");
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(file);
File logFile = new File("F:\\2015年1月8日.log");
PrintStream logPrintStream = new PrintStream( new FileOutputStream(logFile,true) );
try{
int c = 4/0;
System.out.println("c="+c);
int[] arr = null;
System.out.println(arr.length);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace(logPrintStream);
}
}
}
package cn.itcast.other;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
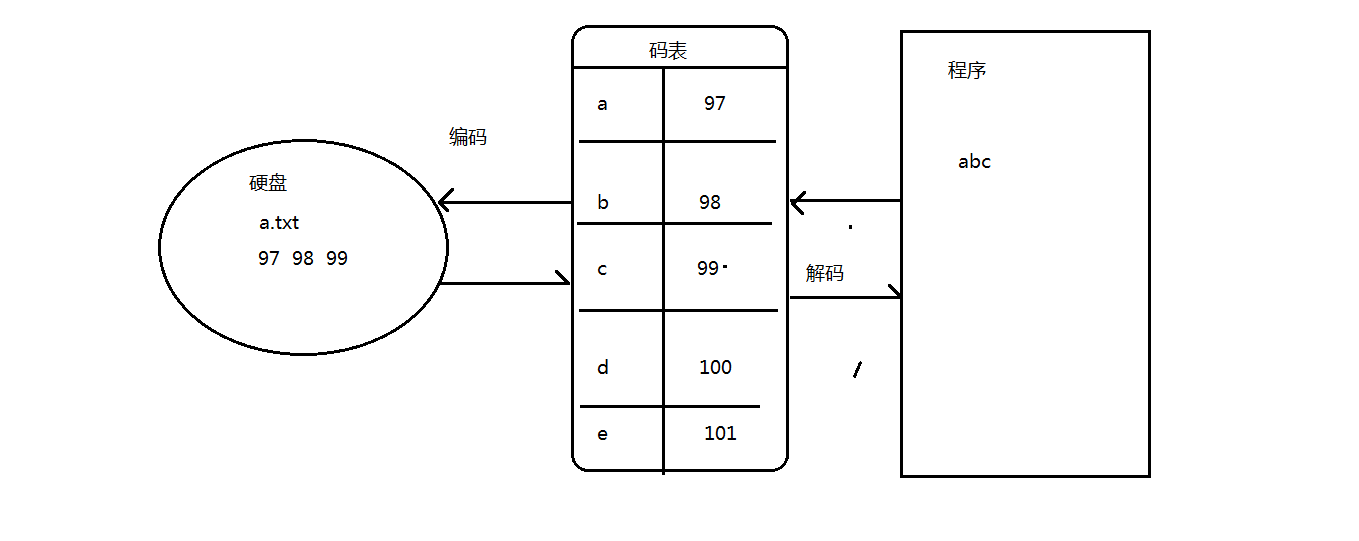
/*
编码与解码
编码: 把看得懂的字符变成看不懂码值这个过程我们称作为编码。
解码: 把码值查找对应的字符,我们把这个过程称作为解码。
注意: 以后编码与解码一般我们都使用统一的码表。否则非常容易出乱码。
*/
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*
String str = "中国";
byte[] buf = str.getBytes("utf-8");
System.out.println("数组的元素:"+Arrays.toString(buf));
str = new String(buf,"utf-8");
System.out.println("解码后的字符串:"+ str);
*/
/*String str = "a中国";
byte[] buf = str.getBytes("unicode");
System.out.println("数组的内容:"+ Arrays.toString(buf));
*/
String str = "大家好";
byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("字节数组:"+ Arrays.toString(buf));
str = new String(buf,"iso8859-1");
byte[] buf2 = str.getBytes("iso8859-1");
str = new String(buf2,"gbk");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
package cn.itcast.other;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
readTest2();
}
public static void readTest2() throws IOException{
File file = new File("F:\\a.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream,"utf-8");
char[] buf = new char[1024];
int length = 0;
while((length = inputStreamReader.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,length));
}
}
public static void writeTest2() throws IOException{
File file = new File("F:\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "utf-8");
outputStreamWriter.write("新中国好啊");
outputStreamWriter.close();
}
public static void writeTest() throws IOException{
File file = new File("F:\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream);
outputStreamWriter.write("大家好");
outputStreamWriter.close();
}
public static void readTest() throws IOException{
InputStream in = System.in;
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(in);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String line = null;
while((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println("内容:"+ line);
}
}
}























 311
311

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








