Summary of Course
如题,后天上午期末考试,因课表冲突不得不突击复习,以下内容包括教材信息以及重点分析 (本科学过图论算法,简单的概念和证明以及本人熟悉的部分一带而过)
刚刚考完,附上回忆版试题
Textbook
《Introduction to Algorithm (Third Edition)》by Thomas H. Cormen,Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest and Clifford Stein
Temporary Link:download PDF
Selected Solutions for《Introduction to Algorithm》
Temporary Link:download PDF
Key Points
Chapter 22 Basic Graph Algorithm
- Graph Basics
Graph (Edge&Vertex)
Undirected Graph&Directed Graph
Adjacency
Repeated edge, Self-loop & Simple graph
Degree, Isolated vertex
Cycle, Sub-graph,
Connected (connected component, strongly connected, strongly connected component)
Special Graph (complete, bipartite, forest, tree, sparse, dense)
Theorem 1.1
Given an undirected graph G = ( V , E ) G = (V, E) G=(V,E), ∑ v ∈ V d ( v ) = 2 ∣ E ∣ \sum_{v\in V}d(v)=2\lvert E\rvert ∑v∈Vd(v)=2∣E∣
Copollary 1.2
Given an undirected graph G = ( V , E ) G = (V, E) G=(V,E), the number of vertices with odd degrees is even.
- Representations of graphs
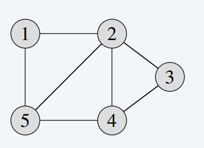
For an undirected graph G = ( V , E ) G = (V, E) G=(V,E),
-
Adjacency-list:
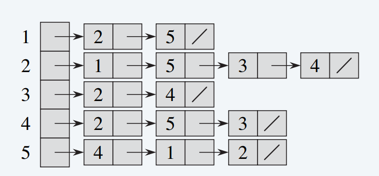
Advantage:
When the graph is sparse, uses only O( ∣ V ∣ + ∣ E ∣ |V|+|E| ∣V∣+∣E∣) memory.
Disvantage:
No quicker way to determine if a given edge ( u , v ) (u, v) (u,v) is present in the graph than to search for v in the adjacency list A d j [ u ] Adj[u] Adj[u]. O( ∣ V ∣ | V | ∣V∣) -
Adjacency matrix
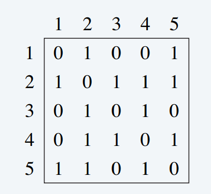
Advantage:
Easily or quickly to determine if an edge is in the graph or not. O(1)
Disvantage:
Uses more memory to store a graph. O( ∣ V ∣ | V | ∣V∣2)
- Elementary graph algorithms
-
BFS(Breadth-First Search)

-
DFS(Deep-First Search)

-
White Path Theorem

-
Topological Sort

-
Strongly connected components

Chapter 23 Minimum spanning tree
- Kruskal algorithm
- Prim algorithm
Chapter 24 Single-Source Shortest Path
- Bellman-Ford algorithm
- Dijkstra Algorithm
- Proof of Dijkstra algorithm
Chapter 15 Dynamic programming
- Shortest path in DAGs
- Knapsack problem
- Bellman-Ford algorithm
Chapter 26 Maximum Flow
- Capacity-scaling algorithm
- Bipartite matching
试题(回忆版)
1.证明BFS生成的是最短路径树
2.证明一个图上的两颗最小生成树的边集的递增序列相同
3.设计O(VE)算法判断有向图是否有负圈,若没有,输出每个顶点的最短可达距离
(顶点v的最短可达距离:对于任意定点u∈V,dis=min{δ(u,v)}) 并证明算法正确性
4.设计DP算法,对于树T=(V,E),去掉最少的点,使得没有边剩下
5.证明在ford-fulkerson算法求s→t最大流时,在残留网络求增广路径时,对于任意u,v∈V,s到u的最短路径长度都不比上一次短,v到t也是
6.形式化描述最大独立集和最小顶点覆盖问题,并证明其等价
























 884
884











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








