场景:
有时候我们会遇到根据用户不同的定位为用户推荐不同的信息内容
或者,根据用户位置不同 是否提供相应的服务
那么如何判断一个坐标是否在一组坐标所围成的地理围栏内呢?
以下代码作为参考
经纬坐标类:代码
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package util;
public class GeoPoint implements Cloneable {
private double latitude;
private double longitude;
public GeoPoint(double latitude, double longitude) {
this();
this.setLatitude(latitude);
this.setLongitude(longitude);
}
public GeoPoint() {
this.latitude = 0.0D;
this.longitude = 0.0D;
}
public void setLatitude(double lat) {
this.latitude = lat;
}
public void setLongitude(double lon) {
this.longitude = lon;
}
public double getLatitude() {
return this.latitude;
}
public double getY() {
return this.latitude;
}
public double getLongitude() {
return this.longitude;
}
public double getX() {
return this.longitude;
}
public boolean equals(Object other, double epsilon) {
if (!(other instanceof GeoPoint)) {
return false;
} else {
GeoPoint gp = (GeoPoint)other;
double deltaLat = Math.abs(gp.getLatitude() - this.getLatitude());
double deltaLon = Math.abs(gp.getLongitude() - this.getLongitude());
return deltaLat < epsilon && deltaLon < epsilon;
}
}
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return this.equals(other, 1.0E-7D);
}
public int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
}
定位计算类:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package util;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class GeoPolygon implements Cloneable {
private GeoPoint[] boundary;
public GeoPolygon(List<GeoPoint> gpList) {
this.boundary = gpList.toArray(getGeoPointArray(gpList.size()));
}
public static GeoPoint[] getGeoPointArray(int size) {
return (GeoPoint[]) Array.newInstance(GeoPoint.class, size);
}
public static GeoPoint[] closePolygon(GeoPoint[] gp) {
if (isEmpty(gp)) {
return gp;
} else if (gp.length < 3) {
return gp;
} else {
GeoPoint gp0 = gp[0];
GeoPoint gpN = gp[gp.length - 1];
if(gp0.equals(gpN)){
return gp;
}else{
ArrayList<GeoPoint> resultList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(gp)) ;
resultList.add(gp0);
return resultList.toArray(getGeoPointArray(resultList.size()));
}
}
}
public static <T> boolean isEmpty(T[] A) {
return A == null || A.length == 0;
}
public GeoPoint[] getGeoPoints() {
return this.boundary;
}
public boolean isPointInside(GeoPoint gp) {
return isPointInside(gp, this.getGeoPoints());
}
public static boolean isPointInside(GeoPoint gp, GeoPoint... pp) {
if (gp != null && pp != null) {
pp = closePolygon(pp);
int wn = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pp.length - 1; ++i) {
if (pp[i].getY() <= gp.getY()) {
if (pp[i + 1].getY() > gp.getY() && _isLeft(pp[i], pp[i + 1], gp) > 0.0D) {
++wn;
}
} else if (pp[i + 1].getY() <= gp.getY() && _isLeft(pp[i], pp[i + 1], gp) < 0.0D) {
--wn;
}
}
return wn != 0;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private static double _isLeft(GeoPoint gp0, GeoPoint gp1, GeoPoint gpC) {
double val = (gp1.getX() - gp0.getX()) * (gpC.getY() - gp0.getY()) - (gpC.getX() - gp0.getX()) * (gp1.getY() - gp0.getY());
return val;
}
}
测试
package util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GeoPoint testgp1 = new GeoPoint(Double.parseDouble("36.8"), Double.parseDouble("112.7"));// Point1 inside
List<GeoPoint> geoPointList = new ArrayList<>();
geoPointList.add(new GeoPoint(37.6, 111.3));
geoPointList.add(new GeoPoint(37.5, 115.6));
geoPointList.add(new GeoPoint(35.25, 113.2));
GeoPolygon fence = new GeoPolygon(geoPointList);
boolean inzone = fence.isPointInside(testgp1);
System.out.println("testGp1是否在范围内:"+inzone);
}
}
结果
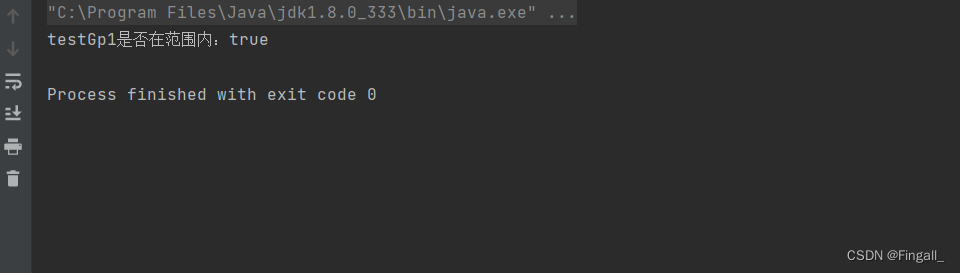
以上就是全部代码了是不是非常简单呢

























 604
604











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








