Description
There is an apple tree outside of kaka's house. Every autumn, a lot of apples will grow in the tree. Kaka likes apple very much, so he has been carefully nurturing the big apple tree.
The tree has N forks which are connected by branches. Kaka numbers the forks by 1 to N and the root is always numbered by 1. Apples will grow on the forks and two apple won't grow on the same fork. kaka wants to know how many apples are there in a sub-tree, for his study of the produce ability of the apple tree.
The trouble is that a new apple may grow on an empty fork some time and kaka may pick an apple from the tree for his dessert. Can you help kaka?

Input
The first line contains an integer N (N ≤ 100,000) , which is the number of the forks in the tree.
The following N - 1 lines each contain two integers u and v, which means fork u and fork v are connected by a branch.
The next line contains an integer M (M ≤ 100,000).
The following M lines each contain a message which is either
"C x" which means the existence of the apple on fork x has been changed. i.e. if there is an apple on the fork, then Kaka pick it; otherwise a new apple has grown on the empty fork.
or
"Q x" which means an inquiry for the number of apples in the sub-tree above the fork x, including the apple (if exists) on the fork x
Note the tree is full of apples at the beginning
Output
Sample Input
3 1 2 1 3 3 Q 1 C 2 Q 1
Sample Output
3 2
原文链接:POJ 3321 Apple Tree (树状数组)
题目大意:给出一棵树,最初每个节点上都有一个苹果。有两种操作,修改(即修改某一个节点,修改时这一个节点苹果从有到无,或从无到有)和查询(查询某一个节点他的子树上有多少个苹果)。
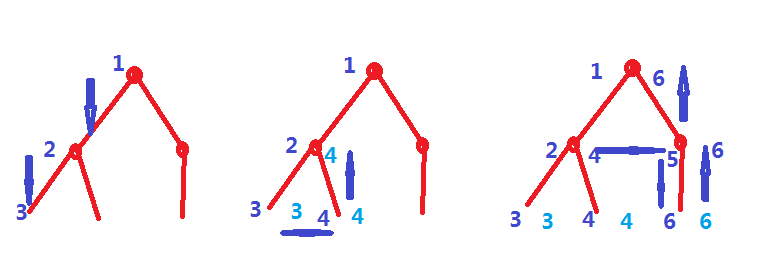
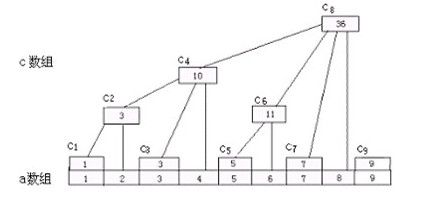
解题思路:由于此题数据比较大(N<=10^5),而且不是标准的二叉树,所以这里我们队每一个节点重新编号,另外为每一个节点赋一个左值和一个右值,表示这个节点的管辖范围。
上图也就是DFS搜索的时候做标记的过程,这样新的编号为1~6的节点所管辖的范围分别就是[1,6] [2,4] [3,3] [4,4] [5,6] [6,6],其中左边的是左值,右边的是右值,节点1的区间是[1,6],正好这棵子树有6个节点,其他的情况也一样。
我们求出每一个节点从1~左值的和1~右值的和,他们的差就是这个节点的子树的所有的和(即这棵子树苹果数目)
最后每输入一组数据就进行依次操作就可以了
代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#define MAXN 100005
#define mem(a) memset(a, 0, sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
int TreeArray[MAXN], Left[MAXN], Right[MAXN], Fork[MAXN];
typedef vector<int> Ve;
vector<Ve>Edge(MAXN);
int N,M;
int key;
void init()//初始化数组和
{
mem(Left); mem(Right);
mem(Fork); mem(TreeArray);
for(int i=0;i<MAXN;i++)Edge[i].clear();
}
void DFS(int node)//为每一个node添加一个左值和右值,表示这个节点所
{
Left[node] = key;
for(int i=0;i<Edge[node].size();i++)
{
key+=1;
DFS(Edge[node][i]);
}
Right[node] = key;
}
int LowBit(int x)//返回的是2^k
{
return x & (x ^ (x-1));
}
void Edit(int k, int num)//修改节点k,如果是添加一个,代入1,删除一个代入-1
{
while(k <= N)
{
TreeArray[k] += num;
k += LowBit(k);
}
}
int GetSum(int k)//得到1...k的和
{
int sum = 0;
while(k>=1)
{
sum += TreeArray[k];
k -= LowBit(k);
}
return sum;
}
void ReadDataAndDo()
{
int a,b;
char ch;
for(int i=1;i<N;i++)//输入a,b把边存放在容器里面
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
Edge[a].push_back(b);
}
key = 1; DFS(1);//为每一个节点对应一个左边界和右边界,他自己就存放在左边界里面,而它的管辖范围就是左边界到右边界
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
Fork[i] = 1;//最初每个Fork上都有一个苹果
Edit(i,1);//同时更新树状数组的值
}
scanf("%d%*c", &M);
for(int i=0;i<M;i++)
{
scanf("%c %d%*c", &ch, &b);
if(ch == 'Q')//b的子树就是[Left[b], right[b]]
{
printf("%d\n", GetSum(Right[b]) - GetSum(Left[b]-1));
}
else
{
if(Fork[b]) Edit(Left[b],-1);//由于每个节点的编号就是它的左值,所以直接修改左节点
else Edit(Left[b],1);
Fork[b] = !Fork[b];//变为相反的状态
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d", &N))
{
init();
ReadDataAndDo();
}
return 0;
}























 525
525

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








