Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
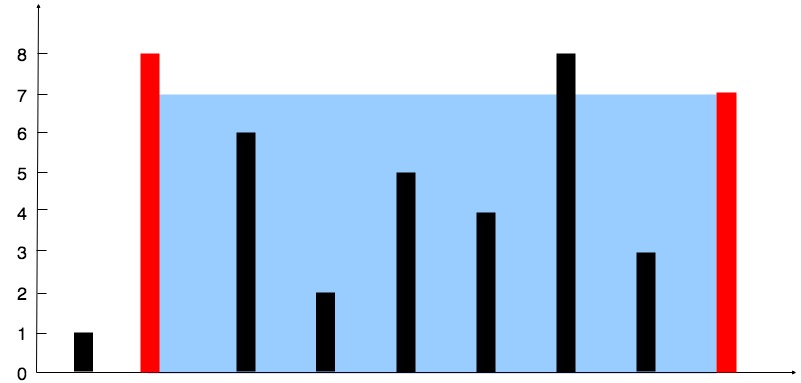
The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example:
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49
Solutions:
//利用双指针移动,时间复杂度为O(n)
/*原理为 area = (end - start) * shortHeight;
例如start<end时,面积最小值不可能出现在以start为起点,
end往中间移动所围成的边。
理由由下:preArea = (end - start) * preShortHeight,
backArea = (end-start-i) * backShortHeight,
i为继续往中间移动次数,由(end-start-i)<end-start,
preShortHeight<=backShortHeight,则preArea<backArea。
则面积出现最大只可能出现在较短者继续往中间移动,因为靠近中间移动时,
shortHeight增大幅度可能远远大于(end-start),可能出现面积更大处。
*/
int maxArea(int* height, int heightSize){
int maxArea = 0,shortHeight = 0;
int start = 0, end = heightSize - 1;
while(start<end){
shortHeight = height[start]>height[end]?height[end]:height[start];
if (maxArea<(end - start)*shortHeight) {
maxArea = (end - start)*shortHeight;
}
if(height[start]<height[end]){
start++;
}else{
end--;
}
}
return maxArea;
}
//暴力破解,时间复杂度为O(n^2)
int maxArea(int* height, int heightSize){
int maxArea = 0,shortHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<heightSize; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j<heightSize; j++) {
shortHeight = height[i]>height[j]?height[j]:height[i];
if((j-i)*shortHeight>maxArea){
maxArea = (j-i)*shortHeight;
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}```

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








