结合视频第二集和笔记:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/20894041?refer=intelligentunit
Nearest Neighbor分类器
图像分类数据集:CIFAR-10。一个非常流行的图像分类数据集是CIFAR-10。这个数据集包含了60000张32X32的小图像。每张图像都有10种分类标签中的一种。这60000张图像被分为包含50000张图像的训练集和包含10000张图像的测试集。
用代码实现:
我们将CIFAR-10的数据加载到内存中,并分成4个数组:训练数据(Xtr)和标签(Ytr),测试数据(Xte)和标签(Yte)。Xtr(大小是50000x32x32x3)存有训练集中所有的图像,Ytr是对应的长度为50000的1维数组,存有图像对应的分类标签(从0到9):
Xtr, Ytr, Xte, Yte = load_CIFAR10('data/cifar10/') # a magic function we provide
# flatten out all images to be one-dimensional
Xtr_rows = Xtr.reshape(Xtr.shape[0], 32 * 32 * 3) # Xtr_rows becomes 50000 x 3072
Xte_rows = Xte.reshape(Xte.shape[0], 32 * 32 * 3) # Xte_rows becomes 10000 x 3072现在我们得到所有的图像数据,并且把他们拉长成为行向量了。接下来展示如何训练并评价一个分类器:
nn = NearestNeighbor() # create a Nearest Neighbor classifier class
nn.train(Xtr_rows, Ytr) # train the classifier on the training images and labels
Yte_predict = nn.predict(Xte_rows) # predict labels on the test images
# and now print the classification accuracy, which is the average number
# of examples that are correctly predicted (i.e. label matches)
print 'accuracy: %f' % ( np.mean(Yte_predict == Yte) )作为评价标准,我们常常使用准确率,它描述了我们预测正确的得分。
import numpy as np
class NearestNeighbor(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def train(self, X, y):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example. Y is 1-dimension of size N """
# the nearest neighbor classifier simply remembers all the training data
self.Xtr = X
self.ytr = y
def predict(self, X):
""" X is N x D where each row is an example we wish to predict label for """
num_test = X.shape[0]
# lets make sure that the output type matches the input type
Ypred = np.zeros(num_test, dtype = self.ytr.dtype)
# loop over all test rows
for i in xrange(num_test):
# find the nearest training image to the i'th test image
# using the L1 distance (sum of absolute value differences)
distances = np.sum(np.abs(self.Xtr - X[i,:]), axis = 1)
min_index = np.argmin(distances) # get the index with smallest distance
Ypred[i] = self.ytr[min_index] # predict the label of the nearest example
return Ypredk-Nearest Neighbor分类器
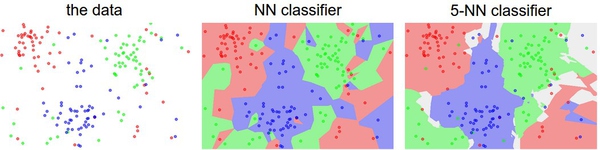
它的思想很简单:与其只找最相近的那1个图片的标签,我们找最相似的k个图片的标签,然后让他们针对测试图片进行投票,最后把票数最高的标签作为对测试图片的预测。所以当k=1的时候,k-Nearest Neighbor分类器就是Nearest Neighbor分类器。从直观感受上就可以看到,更高的k值可以让分类的效果更平滑,使得分类器对于异常值更有抵抗力。
- 为了确定超参数k,可以用尝试的方法,但决不能使用测试集来进行调优。当你在设计机器学习算法的时候,应该把测试集看做非常珍贵的资源,不到最后一步,绝不使用它。如果你使用测试集来调优,而且算法看起来效果不错,那么真正的危险在于:算法实际部署后,性能可能会远低于预期。这种情况,称之为算法对测试集过拟合。
- 从另一个角度来说,如果使用测试集来调优,实际上就是把测试集当做训练集,由测试集训练出来的算法再跑测试集,自然性能看起来会很好。这其实是过于乐观了,实际部署起来效果就会差很多。所以,最终测试的时候再使用测试集,可以很好地近似度量你所设计的分类器的泛化性能
好在我们有不用测试集调优的方法。其思路是:从训练集中取出一部分数据用来调优,我们称之为验证集(validation set)。以CIFAR-10为例,我们可以用49000个图像作为训练集,用1000个图像作为验证集。验证集其实就是作为假的测试集来调优。下面就是代码:
# assume we have Xtr_rows, Ytr, Xte_rows, Yte as before
# recall Xtr_rows is 50,000 x 3072 matrix
Xval_rows = Xtr_rows[:1000, :] # take first 1000 for validation
Yval = Ytr[:1000]
Xtr_rows = Xtr_rows[1000:, :] # keep last 49,000 for train
Ytr = Ytr[1000:]
# find hyperparameters that work best on the validation set
validation_accuracies = []
for k in [1, 3, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100]:
# use a particular value of k and evaluation on validation data
nn = NearestNeighbor()
nn.train(Xtr_rows, Ytr)
# here we assume a modified NearestNeighbor class that can take a k as input
Yval_predict = nn.predict(Xval_rows, k = k)
acc = np.mean(Yval_predict == Yval)
print 'accuracy: %f' % (acc,)
# keep track of what works on the validation set
validation_accuracies.append((k, acc))交叉验证。有时候,训练集数量较小(因此验证集的数量更小),人们会使用一种被称为交叉验证的方法,这种方法更加复杂些。还是用刚才的例子,如果是交叉验证集,我们就不是取1000个图像,而是将训练集平均分成5份,其中4份用来训练,1份用来验证。然后我们循环着取其中4份来训练,其中1份来验证,最后取所有5次验证结果的平均值作为算法验证结果。
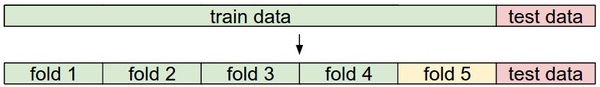
常用的数据分割模式。给出训练集和测试集后,训练集一般会被均分。这里是分成5份。前面4份用来训练,黄色那份用作验证集调优。如果采取交叉验证,那就各份轮流作为验证集。最后模型训练完毕,超参数都定好了,让模型跑一次(而且只跑一次)测试集,以此测试结果评价算法。








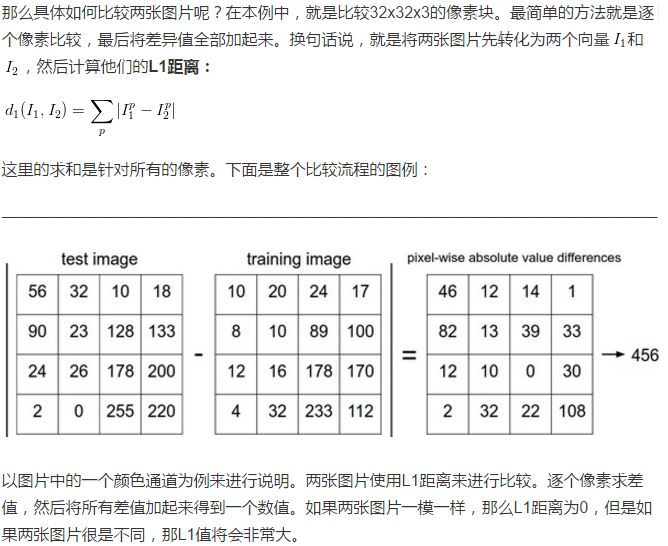














 2638
2638

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








