今天我想讲一下最长公共子序列的问题,希望会对读者有很大的帮助。(我希望读者可以坚持看完)
首先我们来一个最简单(相对于最长公共子序列的题来说)的题目:
最长公共子序列问题
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory limit: 65536K
题目描述
输入
输出
示例输入
ABCBDAB BDCABA
示例输出
4
提示
来源
示例程序
答案是ACAB,或ACBA都可以。当然长度为4啦。
那怎么做呢?
这里我们就用到了我们学过的动态规划的方法了(LCS),
/*转载
考虑最长公共子序列问题如何分解成子问题,设A=“a0,a1,…,am-1”,B=“b0,b1,…,bm-1”,并Z=“z0,z1,…,zk-1”为它们的最长公共子序列。不难证明有以下性质:
(1) 如果am-1=bn-1,则zk-1=am-1=bn-1,且“z0,z1,…,zk-2”是“a0,a1,…,am-2”和“b0,b1,…,bn-2”的一个最长公共子序列;
(2) 如果am-1!=bn-1,则若zk-1!=am-1,蕴涵“z0,z1,…,zk-1”是“a0,a1,…,am-2”和“b0,b1,…,bn-1”的一个最长公共子序列;
(3) 如果am-1!=bn-1,则若zk-1!=bn-1,蕴涵“z0,z1,…,zk-1”是“a0,a1,…,am-1”和“b0,b1,…,bn-2”的一个最长公共子序列。
这样,在找A和B的公共子序列时,如有am-1=bn-1,则进一步解决一个子问题,找“a0,a1,…,am-2”和“b0,b1,…,bm-2”的一个最长公共子序列;如果am-1!=bn-1,则要解决两个子问题,找出“a0,a1,…,am-2”和“b0,b1,…,bn-1”的一个最长公共子序列和找出“a0,a1,…,am-1”和“b0,b1,…,bn-2”的一个最长公共子序列,再取两者中较长者作为A和B的最长公共子序列。
求解:
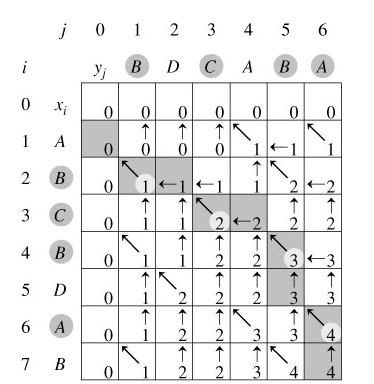
引进一个二维数组c[][],用c[i][j]记录X[i]与Y[j] 的LCS 的长度,b[i][j]记录c[i][j]是通过哪一个子问题的值求得的,以决定搜索的方向。
我们是自底向上进行递推计算,那么在计算c[i,j]之前,c[i-1][j-1],c[i-1][j]与c[i][j-1]均已计算出来。此时我们根据X[i] = Y[j]还是X[i] != Y[j],就可以计算出c[i][j]。
问题的递归式写成:
回溯输出最长公共子序列过程:
算法分析:
由于每次调用至少向上或向左(或向上向左同时)移动一步,故最多调用(m + n)次就会遇到i = 0或j = 0的情况,此时开始返回。返回时与递归调用时方向相反,步数相同,故算法时间复杂度为Θ(m + n)。
*/
不知道大家是否看明白?
这里主要就是一点一点的找,从一个串的第一个开始找与之匹配的另一个串的所有字符,一点一点的加就可以了
下面是这个题的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXLEN 600
int main()
{
int i, j;
char x[MAXLEN];
char y[MAXLEN];
int c[MAXLEN][MAXLEN];
int m, n;
while ( ~scanf ( "%s %s", x, y ) )
{
m = strlen(x);
n = strlen(y);
for(i = 0; i <= m; i++)
c[i][0] = 0;
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
c[0][j] = 0;
for(i = 1; i<= m; i++)
{
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(x[i-1] == y[j-1])
{
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}
else if(c[i-1][j] >= c[i][j-1])
{
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j];
}
else
{
c[i][j] = c[i][j-1];
}
}
}
printf ( "%d\n", c[m][n] );
}
return 0;
}
那如何打印最开始的(也就是最先来到的)最长公共子序列呢?
上面的题解已经告诉我们了,我们只要用一个数组储存来时的回路就可以了。
我先上传代码了
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXLEN 600
void LCSLength(char *x, char *y, int m, int n, int c[][MAXLEN], int b[][MAXLEN])
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i <= m; i++)
c[i][0] = 0;
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
c[0][j] = 0;
for(i = 1; i<= m; i++)
{
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(x[i-1] == y[j-1])
{
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1] + 1;
b[i][j] = 0;
}
else if(c[i-1][j] >= c[i][j-1])
{
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j];
b[i][j] = 1;
}
else
{
c[i][j] = c[i][j-1];
b[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
}
void PrintLCS(int b[][MAXLEN], char *x, int i, int j)
{
if(i == 0 || j == 0)
return;
if(b[i][j] == 0)
{
PrintLCS(b, x, i-1, j-1);
printf("%c ", x[i-1]);
}
else if(b[i][j] == 1)
PrintLCS(b, x, i-1, j);
else
PrintLCS(b, x, i, j-1);
}
int main()
{
char x[MAXLEN] ;
char y[MAXLEN] ;
int b[MAXLEN][MAXLEN];
int c[MAXLEN][MAXLEN];
int m, n;
scanf ( "%s %s", x, y );
m = strlen(x);
n = strlen(y);
LCSLength(x, y, m, n, c, b);
PrintLCS(b, x, m, n);
return 0;
}
我们会发现出现0的地方都是两个字符串可以对应的地方。
这样我们就可以慢慢的回溯就行了。明白吗?
然后我们就来做一个稍微变形的题目:
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 19018 | Accepted: 10598 |
Description
A human gene can be identified through a series of time-consuming biological experiments, often with the help of computer programs. Once a sequence of a gene is obtained, the next job is to determine its function.
One of the methods for biologists to use in determining the function of a new gene sequence that they have just identified is to search a database with the new gene as a query. The database to be searched stores many gene sequences and their functions – many researchers have been submitting their genes and functions to the database and the database is freely accessible through the Internet.
A database search will return a list of gene sequences from the database that are similar to the query gene.
Biologists assume that sequence similarity often implies functional similarity. So, the function of the new gene might be one of the functions that the genes from the list have. To exactly determine which one is the right one another series of biological experiments will be needed.
Your job is to make a program that compares two genes and determines their similarity as explained below. Your program may be used as a part of the database search if you can provide an efficient one.
Given two genes AGTGATG and GTTAG, how similar are they? One of the methods to measure the similarity
of two genes is called alignment. In an alignment, spaces are inserted, if necessary, in appropriate positions of
the genes to make them equally long and score the resulting genes according to a scoring matrix.
For example, one space is inserted into AGTGATG to result in AGTGAT-G, and three spaces are inserted into GTTAG to result in –GT--TAG. A space is denoted by a minus sign (-). The two genes are now of equal
length. These two strings are aligned:
AGTGAT-G
-GT--TAG
In this alignment, there are four matches, namely, G in the second position, T in the third, T in the sixth, and G in the eighth. Each pair of aligned characters is assigned a score according to the following scoring matrix.

denotes that a space-space match is not allowed. The score of the alignment above is (-3)+5+5+(-2)+(-3)+5+(-3)+5=9.
Of course, many other alignments are possible. One is shown below (a different number of spaces are inserted into different positions):
AGTGATG
-GTTA-G
This alignment gives a score of (-3)+5+5+(-2)+5+(-1) +5=14. So, this one is better than the previous one. As a matter of fact, this one is optimal since no other alignment can have a higher score. So, it is said that the
similarity of the two genes is 14.
Input
Output
Sample Input
2 7 AGTGATG 5 GTTAG 7 AGCTATT 9 AGCTTTAAA
Sample Output
14 21
Source
Memory: 744K Time: 0MS
Language: G++ Result: Accepted
Source Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 120;
char ch1[MAX], ch2[MAX];
int Ich1[MAX], Ich2[MAX];
int len_ch1, len_ch2;
int c[MAX][MAX];
int dist[5][5]={
5, -1, -2, -1, -3,
-1, 5, -3, -2, -4,
-2, -3, 5, -2, -2,
-1, -2, -2, 5, -1,
-3, -4, -2, -1, -MAX
};
int max2(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
x = y;
if (x < z)
x = z;
return x;
}
void init()
{
int i;
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
for ( i = 0;i < len_ch1; i++ )
{
if (ch1[i] == 'A')
Ich1[i+1] = 0;
else if (ch1[i] == 'C')
Ich1[i+1] = 1;
else if (ch1[i] == 'G')
Ich1[i+1] = 2;
else if (ch1[i] == 'T')
Ich1[i+1] = 3;
}
for ( i = 0;i < len_ch2; i++ )
{
if (ch2[i] == 'A')
Ich2[i+1] = 0;
else if (ch2[i] == 'C')
Ich2[i+1] = 1;
else if (ch2[i] == 'G')
Ich2[i+1] = 2;
else if (ch2[i] == 'T')
Ich2[i+1] = 3;
}
}
int MaxNum()
{
int i, j;
c[0][0] = 0;
for ( i = 1;i <= len_ch1; i++ )
{
c[i][0] = dist[Ich1[i]][4]+c[i-1][0];
}
for ( i = 1;i <= len_ch2; i++ )
{
c[0][i] = dist[4][Ich2[i]]+c[0][i-1];
}
for ( i = 1;i <= len_ch1; i++ )
{
for ( j = 1;j <= len_ch2; j++ )
{
c[i][j] = max2(c[i-1][j-1]+dist[Ich1[i]][Ich2[j]], c[i][j-1]+dist[4][Ich2[j]], c[i-1][j]+dist[Ich1[i]][4]);
}
}
return c[len_ch1][len_ch2];
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf ( "%d", &t );
while ( t-- )
{
scanf ( "%d %s", &len_ch1, ch1 );
scanf ( "%d %s", &len_ch2, ch2 );
init();
int sum = MaxNum();
printf ( "%d\n", sum );
}
}|
Palindrome
Description
A palindrome is a symmetrical string, that is, a string read identically from left to right as well as from right to left. You are to write a program which, given a string, determines the minimal number of characters to be inserted into the string in order to obtain a palindrome.
As an example, by inserting 2 characters, the string " Ab3bd" can be transformed into a palindrome (" dAb3bAd" or "Adb3bdA"). However, inserting fewer than 2 characters does not produce a palindrome. Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The first line contains one integer: the length of the input string N, 3 <= N <= 5000. The second line contains one string with length N. The string is formed from uppercase letters from 'A' to 'Z', lowercase letters from 'a' to 'z' and digits from '0' to '9'. Uppercase and lowercase letters are to be considered distinct.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. The first line contains one integer, which is the desired minimal number.
Sample Input 5 Ab3bd Sample Output 2 Source |
题意就是: 给你一个字符串,问最少添加多少个字符就能使其成为一个回文串。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 5005;
char str[MAX], str1[MAX];
short c[MAX][MAX];
int n;
int BigLeight()
{
int i, j;
int len_str = strlen(str);
for ( i = 0; i <= len_str; i++ )
{
c[i][0] = 0;
c[0][i] = 0;
}
for ( i = 1;i <= len_str; i++ )
{
for ( j = 1;j <= len_str; j++ )
{
if (str[i-1] == str1[j-1])
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1]+1;
else
{
c[i][j] = max(c[i-1][j], c[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
return c[len_str][len_str];
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
scanf ( "%d", &n );
scanf ( "%s", str );
int len_str = strlen(str);
j = 0;
for ( i = len_str-1; i >= 0; i-- )
{
str1[j++] = str[i];
}
str1[j] = '/0';
int sum = BigLeight();
printf ( "%d", n-sum );
}
代码菜鸟,如有错误,请多包涵!!!










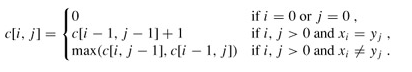

















 11万+
11万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








