LinkedHashSet的图表如下:
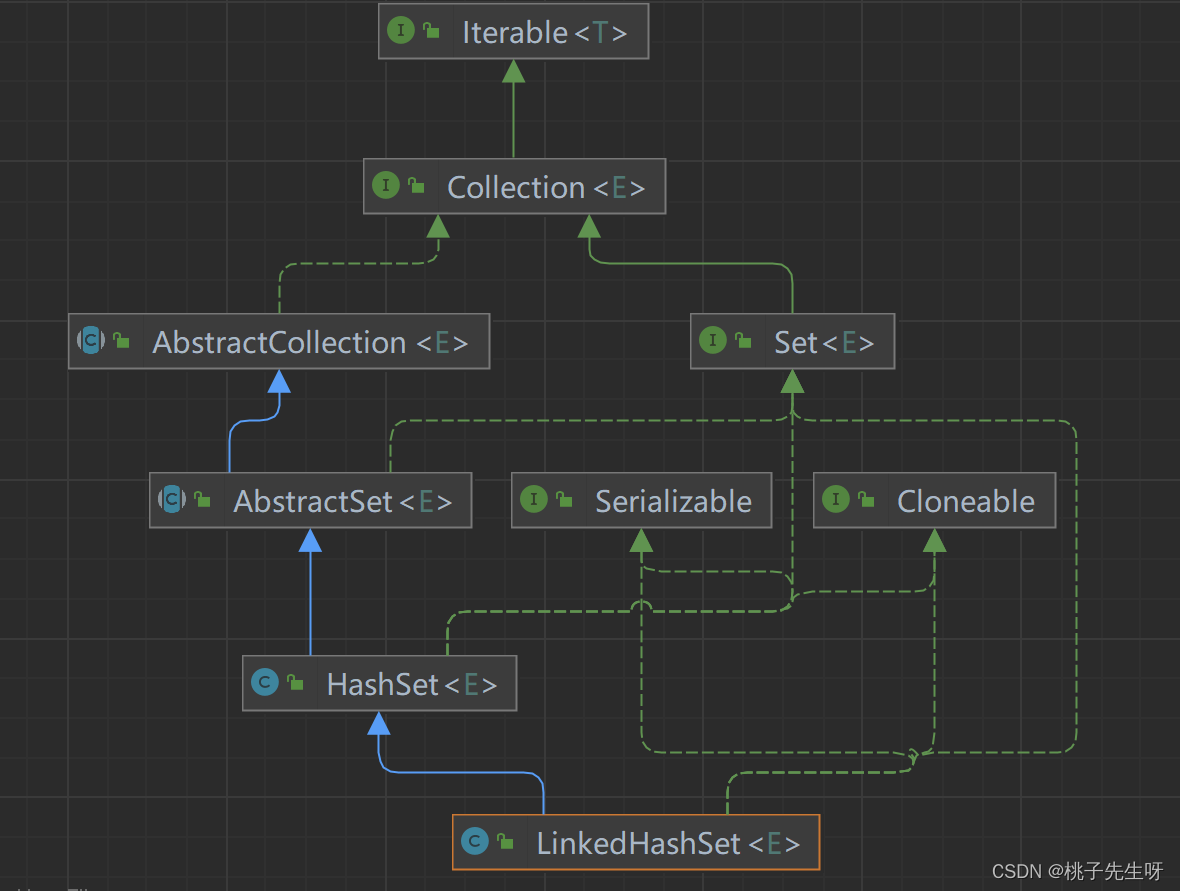
LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类,底层实现为:数组+双向链表。
LinkedHashSet也具有去重功能,并且元素是有序的。
构造方法如下:

执行空构造
LinkedHashSet<Object> hashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();分析:
/**
* Constructs a new, empty linked hash set with the default initial
* capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public LinkedHashSet() {
super(16, .75f, true); //调用父类(HashSet)的构造器
}
创建了一个LinkedHashMap,初始容量16,加载因子0.75
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); //这里计算出来=16
}调用 hashSet.add(123); 添加元素,会执行以下方法,底层也是走的hashMap的put方法
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
// 以下方法的添加逻辑同上一篇博客,这里略过
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
// 注意这里创建结点,走的是子类的逻辑,后面说明
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
主要这里的扩容方法有点差异
oldThr = threshold = 16(调用构造方法的时候通过以下逻辑赋值
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity)
)
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr; // ① oldThr = 16,newCap初始容量 = 16
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; // hashSet是走的这个逻辑
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) { // ② 条件成立
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; //ft = 12.0
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); // newThr = 12
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; // 创建16容量的结点数组
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
扩容完成后,后面的添加逻辑不再赘述。
注意创建结点的时候走的是子类的方法,如下
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
// 创建了一个LinkedHashMap的静态内部类对象Entry<K,V>
// 其中Entry<K,V> 构成如下,before:前指向 after:后指向 形成双向链表
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
} LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
// 方法逻辑如下,将tail指向刚创建的结点,如果last = null
// 将head也指向刚创建的结点
// 否则,刚创建的结点的[前指向:before]指向之前添加的结点,
// 之前添加结点的[后指向:after]指向新创建的结点,形成双向列表
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}// 指向结束后,返回创建的新结点
return p;
}
前篇博客提到过这个方法afterNodeInsertion(evict),是供子类实现的,这里就有实现如下:
子类LinkedHashMap重写了该方法,逻辑如下:
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
// 主要负责在节点插入到哈希表结构后,进一步调整其在维护插入顺序的链表中的位置,确保链表能够准确反映元素的插入顺序,后面详细作用补足
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
到此,添加完成,继续添加元素
当添加的元素重复时,会进入此逻辑
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); // 这个实现逻辑后面补足
return oldValue;
}主要是这里有点区别,afterNodeAccess(e) 后面补足,如果hash位置计算相同,元素比较是不同元素时,添加到链表尾部,即 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null)
到此,添加的底层机制大概如上所述,底层模板走的也是HashMap那一套,具体有些区别在于子类重写了其中的一些方法。




















 2075
2075











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








