原文链接: TensorFlow infogan 生成 mnist 数据集
上一篇: TensorFlow 使用 slim 模块搭建复杂网络
下一篇: TensorFlow aegan 对mnist 数据集压缩特征及重建
建立两个噪声数据,一般噪声和隐含信息,与label结合放入生成器中,生成器模拟样0本,然后将模拟样0本和真实样0本分别输入到判别器中,生成判别结果,重构的隐含信息,以及样0本标签。
做优化时,让判别器对真实的样0本判别结果为1,对模拟数据的判别结果为0来做损失值计算,对生成器让判别结果为1来做损失计算
classes_dim = 10 # 10 classes
con_dim = 2 # 隐含信息变量维度
rand_dim = 38 # 噪声
z_con = tf.random_normal((batch_size, con_dim)) # 2列
z_rand = tf.random_normal((batch_size, rand_dim)) # 38列
z = tf.concat(axis=1, values=[tf.one_hot(y, depth=classes_dim), z_con, z_rand]) # 50列
gen = generator(z)
从模拟噪声来回复样0本,需要使用反卷积函数,并且要做批量归一化处理。
生成器处理,以及每一次的shape,将(batch,50) ----> (batch,28,28,1)
def generator(x):
reuse = len([t for t in tf.global_variables() if t.name.startswith('generator')]) > 0
print(x.get_shape()) # (10, 50)
with tf.variable_scope('generator', reuse=reuse):
x = slim.fully_connected(x, 1024)
print(x.shape) # (10, 1024)
x = slim.batch_norm(x, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 1024)
x = slim.fully_connected(x, 7 * 7 * 128)
print(x.shape) # (10, 6272)
x = slim.batch_norm(x, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 6272)
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 7, 7, 128])
print(x.shape) # (10, 7, 7, 128)
x = slim.conv2d_transpose(x, 64, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=None)
print(x.shape) # (10, 14, 14, 64)
x = slim.batch_norm(x, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 14, 14, 64)
z = slim.conv2d_transpose(x, 1, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=tf.nn.sigmoid)
print('z---', z.shape) # z--- (10, 28, 28, 1)
return z
判别器经过两次卷积,再接两次全连接,生成的数据可以分别连接不同的输出层产生不同的结果,其中一维的输出层产生判别结果,1或0
10维的输出层产生分类结果,2维输出层产生隐含维度信息
在生成器和判别器中,都会使用各自的命名空间,这是在多网络模型定义变量的一个好习惯,在指定训练参数,获取以及显示训练参数时,都可以通过指定的命名空间拿到对应的变量,不至于混乱。
判别器网络和各层shape
def discriminator(x, num_classes=10, num_cont=2):
reuse = len([t for t in tf.global_variables() if t.name.startswith('discriminator')]) > 0
print(x.get_shape()) # (10, 28, 28, 1)
with tf.variable_scope('discriminator', reuse=reuse):
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
print(x.shape) # (10, 28, 28, 1)
x = slim.conv2d(x, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 14, 14, 64)
x = slim.conv2d(x, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 7, 7, 128)
x = slim.flatten(x)
print(x.shape) # (10, 6272)
shared_tensor = slim.fully_connected(x, num_outputs=1024, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(shared_tensor.shape) # (10, 1024)
recog_shared = slim.fully_connected(shared_tensor, num_outputs=128, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(recog_shared.shape) # (10, 128)
disc = slim.fully_connected(shared_tensor, num_outputs=1, activation_fn=None)
print(disc.shape) # (10, 1)
disc = tf.squeeze(disc, -1)
print(disc.shape) # (10,)
recog_cat = slim.fully_connected(recog_shared, num_outputs=num_classes, activation_fn=None)
print(recog_cat.shape) # (10, 10)
recog_cont = slim.fully_connected(recog_shared, num_outputs=num_cont, activation_fn=tf.nn.sigmoid)
print(recog_cont.shape) # (10, 2)
return disc, recog_cat, recog_cont
判别器中,判别结果的loss有两个:真实输入的结果与模拟输入的结果,将两个结合在一起生成loss_d,生成器的loss为自己输出的模拟数据,让他在判别器中为真,定义为loss_g
定义网络中共有的loss,真实的标签与输入真实样0本判别出的标签,真实的标签与输入模拟样0本判别出的标签,隐含信息的重构误差,然后创建两个优化器,将他们放到对应的优化器中
小技巧: 将判别器的学习率设小,将生成器的学习率设大,这么做是为了 让生成器有更快的进化速度来模拟真实数据,优化同样是adam。
所谓的AC-GAN就是将loss_cr加入到loss_c中,如果没有loss_cr,令loss_c=loss_cf,对于网络生成的模拟数据是不影响的,但是会损失真实分类与模拟数据间的对应关系。
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/") # , one_hot=True)
tf.reset_default_graph()
def generator(x):
reuse = len([t for t in tf.global_variables() if t.name.startswith('generator')]) > 0
print(x.get_shape()) # (10, 50)
with tf.variable_scope('generator', reuse=reuse):
x = slim.fully_connected(x, 1024)
print(x.shape) # (10, 1024)
x = slim.batch_norm(x, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 1024)
x = slim.fully_connected(x, 7 * 7 * 128)
print(x.shape) # (10, 6272)
x = slim.batch_norm(x, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 6272)
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 7, 7, 128])
print(x.shape) # (10, 7, 7, 128)
x = slim.conv2d_transpose(x, 64, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=None)
print(x.shape) # (10, 14, 14, 64)
x = slim.batch_norm(x, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 14, 14, 64)
z = slim.conv2d_transpose(x, 1, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=tf.nn.sigmoid)
print('z---', z.shape) # z--- (10, 28, 28, 1)
return z
def discriminator(x, num_classes=10, num_cont=2):
reuse = len([t for t in tf.global_variables() if t.name.startswith('discriminator')]) > 0
print(x.get_shape()) # (10, 28, 28, 1)
with tf.variable_scope('discriminator', reuse=reuse):
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
print(x.shape) # (10, 28, 28, 1)
x = slim.conv2d(x, num_outputs=64, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 14, 14, 64)
x = slim.conv2d(x, num_outputs=128, kernel_size=[4, 4], stride=2, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(x.shape) # (10, 7, 7, 128)
x = slim.flatten(x)
print(x.shape) # (10, 6272)
shared_tensor = slim.fully_connected(x, num_outputs=1024, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(shared_tensor.shape) # (10, 1024)
recog_shared = slim.fully_connected(shared_tensor, num_outputs=128, activation_fn=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
print(recog_shared.shape) # (10, 128)
disc = slim.fully_connected(shared_tensor, num_outputs=1, activation_fn=None)
print(disc.shape) # (10, 1)
disc = tf.squeeze(disc, -1)
print(disc.shape) # (10,)
recog_cat = slim.fully_connected(recog_shared, num_outputs=num_classes, activation_fn=None)
print(recog_cat.shape) # (10, 10)
recog_cont = slim.fully_connected(recog_shared, num_outputs=num_cont, activation_fn=tf.nn.sigmoid)
print(recog_cont.shape) # (10, 2)
return disc, recog_cat, recog_cont
batch_size = 10 # 获取样0本的批次大小32
classes_dim = 10 # 10 classes
con_dim = 2 # 隐含信息变量维度
rand_dim = 38 # 噪声
n_input = 784
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None])
z_con = tf.random_normal((batch_size, con_dim)) # 2列
z_rand = tf.random_normal((batch_size, rand_dim)) # 38列
z = tf.concat(axis=1, values=[tf.one_hot(y, depth=classes_dim), z_con, z_rand]) # 50列
gen = generator(z)
genout = tf.squeeze(gen, -1)
# labels for discriminator
y_real = tf.ones(batch_size) # 真
y_fake = tf.zeros(batch_size) # 假
# 判别器
disc_real, class_real, _ = discriminator(x)
disc_fake, class_fake, con_fake = discriminator(gen)
pred_class = tf.argmax(class_fake, dimension=1)
# 判别器 loss
loss_d_r = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=disc_real, labels=y_real))
loss_d_f = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=disc_fake, labels=y_fake))
loss_d = (loss_d_r + loss_d_f) / 2
# generator loss
loss_g = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=disc_fake, labels=y_real))
# categorical factor loss
loss_cf = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=class_fake, labels=y)) # class ok 图片对不上
loss_cr = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=class_real, labels=y)) # 生成的图片与class ok 与输入的class对不上
loss_c = (loss_cf + loss_cr) / 2
# continuous factor loss
loss_con = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(con_fake - z_con))
# 获得各个网络中各自的训练参数
t_vars = tf.trainable_variables()
d_vars = [var for var in t_vars if 'discriminator' in var.name]
g_vars = [var for var in t_vars if 'generator' in var.name]
disc_global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
gen_global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
train_disc = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(loss_d + loss_c + loss_con, var_list=d_vars,
global_step=disc_global_step)
train_gen = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss_g + loss_c + loss_con, var_list=g_vars,
global_step=gen_global_step)
training_epochs = 3
display_step = 1
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0.
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
# 遍历全部数据集
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) # 取数据
feeds = {x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys}
# Fit training using batch data
l_disc, _, l_d_step = sess.run([loss_d, train_disc, disc_global_step], feeds)
l_gen, _, l_g_step = sess.run([loss_g, train_gen, gen_global_step], feeds)
# 显示训练中的详细信息
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch + 1), "cost=", "{:.9f} ".format(l_disc), l_gen)
print("完成!")
# 测试
print("Result:", loss_d.eval({x: mnist.test.images[:batch_size], y: mnist.test.labels[:batch_size]})
, loss_g.eval({x: mnist.test.images[:batch_size], y: mnist.test.labels[:batch_size]}))
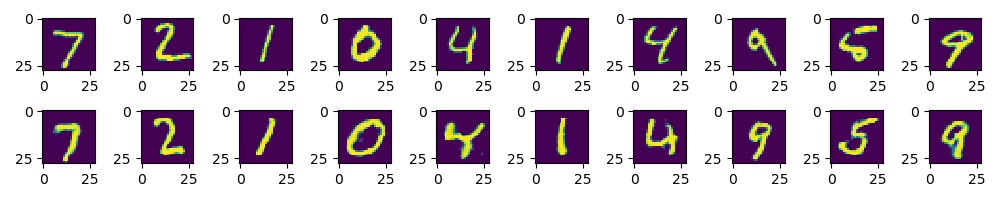
# 根据图片模拟生成图片
show_num = 10
gensimple, d_class, inputx, inputy, con_out = sess.run(
[genout, pred_class, x, y, con_fake],
feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images[:batch_size], y: mnist.test.labels[:batch_size]})
f, a = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(10, 2))
for i in range(show_num):
a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(inputx[i], (28, 28)))
a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(gensimple[i], (28, 28)))
print("d_class", d_class[i], "inputy", inputy[i], "con_out", con_out[i])
plt.draw()
plt.show()
my_con = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 2])
myz = tf.concat(axis=1, values=[tf.one_hot(y, depth=classes_dim), my_con, z_rand])
mygen = generator(myz)
mygenout = tf.squeeze(mygen, -1)
my_con1 = np.ones([10, 2])
a = np.linspace(0.0001, 0.99999, 10)
y_input = np.ones([10])
figure = np.zeros((28 * 10, 28 * 10))
my_rand = tf.random_normal((10, rand_dim))
for i in range(10):
for j in range(10):
my_con1[j][0] = a[i]
my_con1[j][1] = a[j]
y_input[j] = j
mygenoutv = sess.run(mygenout, feed_dict={y: y_input, my_con: my_con1})
for jj in range(10):
digit = mygenoutv[jj].reshape(28, 28)
figure[i * 28: (i + 1) * 28,
jj * 28: (jj + 1) * 28] = digit
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(figure, cmap='Greys_r')
plt.show()






















 2449
2449

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








