我在学习Android第一行代码的时候按照书上第四章的代码练习的时候遇到一些疑惑。首先贴上主布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/left_fragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:name="com.example.leslie.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<!--<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/right_layout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
>-->
<fragment
android:id="@+id/right_fragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:name="com.example.leslie.fragmenttest.RightFragment" />
</LinearLayout>可以看出主布局很简单,就是一个线性布局下2个Fragment.下面贴出主活动中的代码:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void onClick(View view){
switch (view.getId()){
case R.id.button:
AnotherRightFragment fragment=new AnotherRightFragment();
FragmentManager fragmentManager=getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction=fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.right_fragment,fragment);
transaction.commit();
break;
default:break;
}代码的逻辑也很简单,就是希望点击左边的fragment中的按钮,能够更换右边的fragment。为此制作了右边的2个fragment布局文件如下
这是right_fragment布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#00ff00">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="This is right fragment"/>
</LinearLayout>
这是another_right_fragment布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ffff00"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:text="This is another right fragment"/>
</LinearLayout>
两者并无太大不同。仅仅显示的text不同而已,运行结果并没有像我想象的那样右边的fragment完全覆盖住,而是仅仅覆盖了非TextView部分。
如图所示: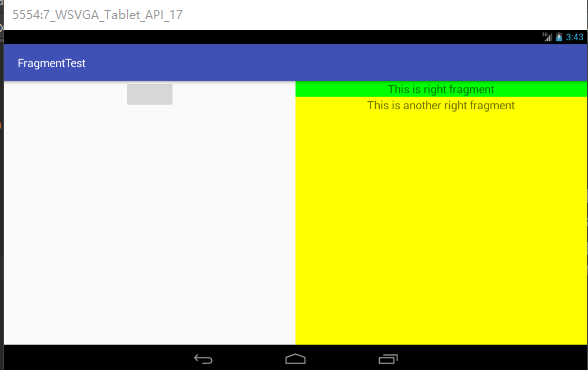
这让我百思不得其解。
网上搜索到的答案是用FrameLayout做被替代的fragment的父容器就可以了。我自己暂时还不知道为什么要这么做。为什么不用FrameLayout只能替代一部分导致还有一部分可见。





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








