说明:
1、简单点说明,就是不断的修饰,不断加东西在一个实体上,比如:游戏里面人物不断的添加装备。原来的东西都在,让其更加的完美
2、常常是对旧功能的添加一些新的功能,不改变旧的功能
1、装饰模式
案例说明:类似虚拟人物换装,对人装饰不同的衣服
1、创建人物形象接口
在这里就是对特性的抽离
//人物形象接口
public interface ICharacter {
public void show();
}
2、人实现接口初始化
类似于游戏新创建的人物什么装备都没有,初始化状态
//具体人类
public class Person implements ICharacter {
private String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("装扮的"+name);
}
}
3、服饰类的抽象(重点)
也就是针对一类的统称,通过该类去获取具体的装饰的内容
public class Finery implements ICharacter {
protected ICharacter component;
public void decorate(ICharacter component) {
this.component=component;
}
public void show() {
if (this.component != null){
this.component.show();
}
}
}4、服饰类抽象具体化
对于本案例就是针对人进行穿着装饰,实现的类似,简单看一个就可以了,可以看到将其父类的show方法进行了调用
public class BigTrouser extends Finery {
public void show(){
System.out.print(" 垮裤");
super.show();
}
}
public class LeatherShoes extends Finery {
public void show(){
System.out.print(" 皮鞋");
super.show();
}
}
public class Sneakers extends Finery {
public void show(){
System.out.print(" 球鞋");
super.show();
}
}
public class Strawhat extends Finery {
public void show(){
System.out.print(" 草帽");
super.show();
}
}
public class Suit extends Finery {
public void show(){
System.out.print(" 西装");
super.show();
}
}
public class Tie extends Finery {
public void show(){
System.out.print(" 领带");
super.show();
}
}
public class TShirts extends Finery {
public void show(){
System.out.print(" 大T恤");
super.show();
}
}
5、测试和结果
解释:
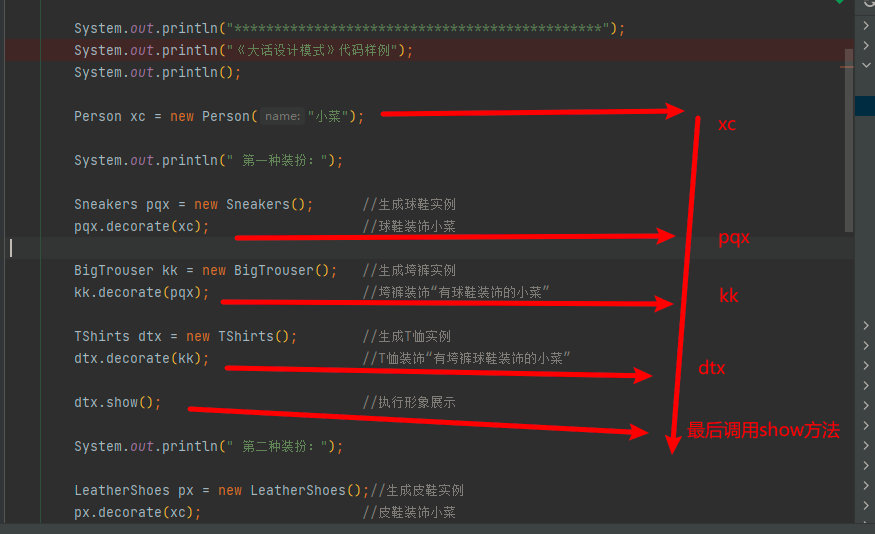
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("**********************************************");
System.out.println("《大话设计模式》代码样例");
System.out.println();
Person xc = new Person("小菜");
System.out.println(" 第一种装扮:");
Sneakers pqx = new Sneakers(); //生成球鞋实例
pqx.decorate(xc); //球鞋装饰小菜
BigTrouser kk = new BigTrouser(); //生成垮裤实例
kk.decorate(pqx); //垮裤装饰“有球鞋装饰的小菜”
TShirts dtx = new TShirts(); //生成T恤实例
dtx.decorate(kk); //T恤装饰“有垮裤球鞋装饰的小菜”
dtx.show(); //执行形象展示
System.out.println(" 第二种装扮:");
LeatherShoes px = new LeatherShoes();//生成皮鞋实例
px.decorate(xc); //皮鞋装饰小菜
Tie ld = new Tie(); //生成领带实例
ld.decorate(px); //领带装饰“有皮鞋装饰的小菜”
Suit xz = new Suit(); //生成西装实例
xz.decorate(ld); //西装装饰“有领带皮鞋装饰的小菜”
xz.show(); //执行形象展示
System.out.println(" 第三种装扮:");
Sneakers pqx2 = new Sneakers(); //生成球鞋实例
pqx2.decorate(xc); //球鞋装饰小菜
LeatherShoes px2 = new LeatherShoes();//生成皮鞋实例
px2.decorate(pqx2); //皮鞋装饰“有球鞋装饰的小菜”
BigTrouser kk2 = new BigTrouser(); //生成垮裤实例
kk2.decorate(px2); //垮裤装饰“有皮鞋球鞋装饰的小菜”
Tie ld2 = new Tie(); //生成领带实例
ld2.decorate(kk2); //领带装饰“有垮裤皮鞋球鞋装饰的小菜”
Strawhat cm2 = new Strawhat(); //生成草帽实例
cm2.decorate(ld2); //草帽装饰“有领带垮裤皮鞋球鞋装饰的小菜”
cm2.show(); //执行形象展示
System.out.println();
System.out.println("**********************************************");
}
}结果
2、简单工厂+策略+装饰模式
说明:该案例是对第二章,策略模式收银员买商品和数量,优惠问题在进行展开的,这里增加的是在优惠八折的基础上有进行一个满300减100,这里就关系到装饰模式
1、创建销售接口
public interface ISale {
public double acceptCash(double price,int num);
}2、优惠类型的抽象(重点)
public class CashSuper implements ISale {
protected ISale component;
//装饰对象
public void decorate(ISale component) {
this.component=component;
}
public double acceptCash(double price,int num){
double result = 0d;
if (this.component != null){
//若装饰对象存在,则执行装饰的算法运算
result = this.component.acceptCash(price,num);
}
return result;
}
}
3、优惠类型抽象具体化
public class CashNormal implements ISale {
//正常收费,原价返回
public double acceptCash(double price,int num){
return price * num;
}
}
public class CashRebate extends CashSuper {
private double moneyRebate = 1d;
//打折收费。初始化时必需输入折扣率。八折就输入0.8
public CashRebate(double moneyRebate){
this.moneyRebate = moneyRebate;
}
//计算收费时需要在原价基础上乘以折扣率
public double acceptCash(double price,int num){
double result = price * num * this.moneyRebate;
return super.acceptCash(result,1);
}
}
public class CashReturn extends CashSuper {
private double moneyCondition = 0d; //返利条件
private double moneyReturn = 0d; //返利值
//返利收费。初始化时需要输入返利条件和返利值。
//比如“满300返100”,就是moneyCondition=300,moneyReturn=100
public CashReturn(double moneyCondition,double moneyReturn){
this.moneyCondition = moneyCondition;
this.moneyReturn = moneyReturn;
}
//计算收费时,当达到返利条件,就原价减去返利值
public double acceptCash(double price,int num){
double result = price * num;
if (moneyCondition>0 && result >= moneyCondition)
result = result - Math.floor(result / moneyCondition) * moneyReturn;
return super.acceptCash(result,1);
}
}
4、简单工厂使用
public class CashContext {
private ISale cs; //声明一个ISale接口对象
//通过构造方法,传入具体的收费策略
public CashContext(int cashType){
switch(cashType){
case 1:
this.cs = new CashNormal();
break;
case 2:
this.cs = new CashRebate(0.8d);
break;
case 3:
this.cs = new CashRebate(0.7d);
break;
case 4:
this.cs = new CashReturn(300d,100d);
break;
case 5:
//先打8折,再满300返100
CashNormal cn = new CashNormal();
CashReturn cr1 = new CashReturn(300d,100d);
CashRebate cr2 = new CashRebate(0.8d);
cr1.decorate(cn); //用满300返100算法包装基本的原价算法
cr2.decorate(cr1); //打8折算法装饰满300返100算法
this.cs = cr2; //将包装好的算法组合引用传递给cs对象
break;
case 6:
//先满200返50,再打7折
CashNormal cn2 = new CashNormal();
CashRebate cr3 = new CashRebate(0.7d);
CashReturn cr4 = new CashReturn(200d,50d);
cr3.decorate(cn2); //用打7折算法包装基本的原价算法
cr4.decorate(cr3); //满200返50算法装饰打7折算法
this.cs = cr4; //将包装好的算法组合引用传递给cs对象
break;
}
}
public double getResult(double price,int num){
//根据收费策略的不同,获得计算结果
return this.cs.acceptCash(price,num);
}
}
5、测试和结果
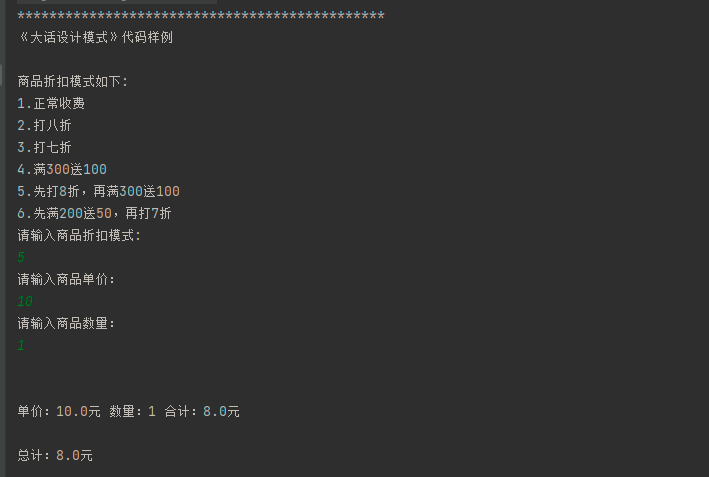
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("**********************************************");
System.out.println("《大话设计模式》代码样例");
System.out.println();
int discount = 0; //商品折扣模式
double price = 0d; //商品单价
int num = 0; //商品购买数量
double totalPrices = 0d;//当前商品合计费用
double total = 0d; //总计所有商品费用
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println("商品折扣模式如下:");
System.out.println("1.正常收费");
System.out.println("2.打八折");
System.out.println("3.打七折");
System.out.println("4.满300送100");
System.out.println("5.先打8折,再满300送100");
System.out.println("6.先满200送50,再打7折");
System.out.println("请输入商品折扣模式:");
discount = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("请输入商品单价:");
price = Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("请输入商品数量:");
num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println();
if (price>0 && num>0){
//根据用户输入,将对应的策略对象作为参数传入CashContext对象中
CashContext cc = new CashContext(discount);
//通过Context的getResult方法的调用,可以得到收取费用的结果
//让具体算法与客户进行了隔离
totalPrices = cc.getResult(price,num);
total = total + totalPrices;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("单价:"+ price + "元 数量:"+ num +" 合计:"+ totalPrices +"元");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("总计:"+ total+"元");
System.out.println();
}
}
while(price>0 && num>0);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("**********************************************");
}
}
结果























 2373
2373

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










