Okabe likes to take walks but knows that spies from the Organization could be anywhere; that's why he wants to know how many different walks he can take in his city safely. Okabe's city can be represented as all points (x, y) such that x and y are non-negative. Okabe starts at the origin (point (0, 0)), and needs to reach the point (k, 0). If Okabe is currently at the point (x, y), in one step he can Go to (x + 1, y + 1), (x + 1, y), or (x + 1, y - 1).
Additionally, there are n horizontal line segments, the i-th of which goes from x = ai to x = bi inclusive, and is at y = ci. It is guaranteed that a1 = 0, an ≤ k ≤ bn, and ai = bi - 1 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n. The i-th line segment forces Okabe to walk with y-value in the range 0 ≤ y ≤ ciwhen his x value satisfies ai ≤ x ≤ bi, or else he might be spied on. This also means he is required to be under two line segments when one segment ends and another begins.
Okabe now wants to know how many walks there are from the origin to the point (k, 0) satisfying these conditions, modulo 109 + 7.
The first line of input contains the integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ k ≤ 1018) — the number of segments and the destination xcoordinate.
The next n lines contain three space-separated integers ai, bi, and ci (0 ≤ ai < bi ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ ci ≤ 15) — the left and right ends of a segment, and its y coordinate.
It is guaranteed that a1 = 0, an ≤ k ≤ bn, and ai = bi - 1 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n.
Print the number of walks satisfying the conditions, modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
1 3 0 3 3
4
2 6 0 3 0 3 10 2
4
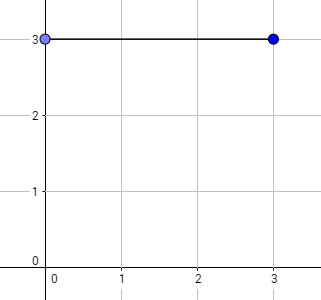
The graph above corresponds to sample 1. The possible walks are:
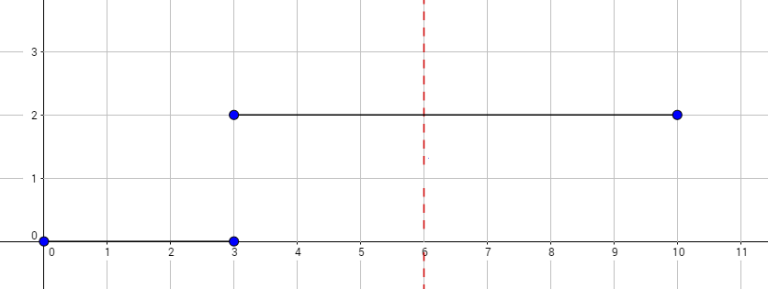
The graph above corresponds to sample 2. There is only one walk for Okabe to reach (3, 0). After this, the possible walks are:
Source
Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2)
My Solution
题意:从(0,0)走到(k,0)(1 ≤ k ≤ 1e18),每次可以从(x, y) 走到 (x+1, y+1) 或 (x+1, y) 或 (x+1, y-1),然后必须在很多个y == ci的线段下面走,
(相邻的线段,前一个的结束x坐标bi和后一个线段的开始x坐标ai+1 相同,且y = ci可能不同)
dp+矩阵快速幂
比较裸的dp+矩阵快速幂,因为这里k为1e18,所以几乎只能用矩阵快速幂来做了。
朴素的dp,dpij表示走到(i, j)时的方案数,
则 状态方程为,if(j+1 <= b[k]) dp[i+1][j+1] += dp[i][j];
if(j-1 >= 0) dp[i+1][j-1] += dp[i][j];
dp[i+1][j] += dp[i][j];
然后可以构造出15*15(ci<=15)的矩阵,把状态转移到矩阵上,然后对于每个a[k]、b[k]、c[k]跑一次快速幂即可。
此外注意a[k],b[k],以及快速幂的参数到是LL。
复杂度 O(n*(15)^3*log(k))
//china no.1
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <list>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cctype>
#include <sstream>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define endl '\n'
#define rand() srand(time(0));
#define me(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x));
#define foreach(it,a) for(__typeof((a).begin()) it=(a).begin();it!=(a).end();it++)
#define close() ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LINF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
const int dx[]={-1,0,1,0,-1,-1,1,1};
const int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,1,-1,1,-1};
const int maxn=1e3+5;
const int maxx=1e5+100;
const double EPS=1e-7;
const int MOD=10000007;
#define mod(x) ((x)%MOD);
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c) { return min(min(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c) { return max(max(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return min(min(a,b),min(c,d));}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return max(max(a,b),max(c,d));}
//typedef tree<pt,null_type,less< pt >,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> rbtree;
long long gcd(long long a , long long b){if(b==0) return a;a%=b;return gcd(b,a);}
#define FOR(x,n,i) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define FOr(x,n,i) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define W while
inline int Scan()
{
int res=0,ch,flag=0;
if((ch=getchar())=='-')flag=1;
else if(ch>='0' && ch<='9')res=ch-'0';
while((ch=getchar())>='0'&&ch<='9')res=res*10+ch-'0';
return flag ? -res : res;
}
LL a[maxx],bb[maxx],c[maxx],n,k,mod=1e9+7,t;
int ssize = 15;
struct Matrix
{
LL m[25][25];
void init(){
memset(m, 0, sizeof m);
}
void setOne()
{
init();
for(int i = 0; i <=ssize; i++) m[i][i] = 1;
}
void print()
{
for(int i = 0; i <= ssize; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= ssize; j++)
cout << m[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
} I,A,B,T,b,res;
Matrix Mul(Matrix a,Matrix b) //
{
int i,j,k;
Matrix c;
for (i = 0; i <= ssize; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j <= ssize; j++)
{
c.m[i][j]=0;
for(k = 0; k <= ssize; k++)
{
c.m[i][j]+=(a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j]);
c.m[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
}
return c;
}
void quickPow(LL n)
{
while(n)
{
if(n&1) res=Mul(res,b);
n>>=1;
b=Mul(b,b);
}
}
int main()
{
close();
cin>>t>>k;
FOR(1,t,i)
cin>>a[i]>>bb[i]>>c[i];
res.init();
res.setOne();
FOR(1,t,i)
{
b.init();
for(int j = 0; j <= c[i]; j++)
{
if(j+1 <= c[i]) b.m[j][j+1]++;
if(j-1 >=0) b.m[j][j-1]++;
b.m[j][j]++;
}
//b.print();
// cout<<"**********"<<endl;
// res.print();
if(bb[i] >= k) quickPow(k - a[i]);
else quickPow(bb[i] - a[i]);
}
LL ans = res.m[0][0];
cout << ans << endl;
}






























 1289
1289











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








