Write a program that takes as input a rooted tree and a list of pairs of vertices. For each pair (u,v) the program determines the closest common ancestor of u and v in the tree. The closest common ancestor of two nodes u and v is the node w that is an ancestor of both u and v and has the greatest depth in the tree. A node can be its own ancestor (for example in Figure 1 the ancestors of node 2 are 2 and 5)
Input
The data set, which is read from a the std input, starts with the tree description, in the form:
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 … successorn
…
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) …
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For each common ancestor the program prints the ancestor and the number of pair for which it is an ancestor. The results are printed on the standard output on separate lines, in to the ascending order of the vertices, in the format: ancestor:times
For example, for the following tree:
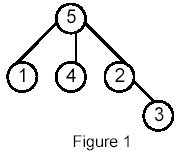
Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1
5:5
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
代码一 LCA转RMQ
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAXN 1000+100
using namespace std;
struct Edge
{
int from, to, next;
};
Edge edge[MAXN<<1];
int head[MAXN], edgenum;
int vs[MAXN<<1], depth[MAXN<<1];
int id[MAXN];
int dfs_clock;
int pre[MAXN];//存储父节点
int N;
int root;//树的根
map<int,int>mp; // 来存结果 还是蛮方便的
void init()
{
edgenum = 0;
mp.clear();
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
pre[i] = i;
}
void addedge(int u, int v)
{
Edge E = {u, v, head[u]};
edge[edgenum] = E;
head[u] = edgenum++;
}
void getMap()
{
int a,b;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
int num;
scanf("%d:(%d)",&a,&num);
while(num--)
{
scanf("%d",&b);
pre[b]=a;
addedge(a,b);
addedge(b,a);
}
}
}
void DFS(int u, int fa, int d)
{
id[u] = dfs_clock;
vs[dfs_clock] = u;
depth[dfs_clock++] = d;
for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if(v == fa) continue;
DFS(v, u, d+1);
vs[dfs_clock] = u;
depth[dfs_clock++] = d;
}
}
void find_depth()
{
dfs_clock = 1;
memset(vs, 0, sizeof(vs));
memset(depth, 0, sizeof(depth));
memset(id, 0, sizeof(id));
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
if(pre[i] == i) root = i;//找根节点
DFS(root, -1, 0);
}
int dp[MAXN<<1][30];
void RMQ_init(int NN)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= NN; i++)
dp[i][0] = i;
for(int j = 1; (1<<j) <= NN; j++)
{
for(int i = 1; i + (1<<j) - 1 <= NN; i++)
{
int a = dp[i][j-1];
int b = dp[i + (1<<(j-1))][j-1];
if(depth[a] < depth[b])
dp[i][j] = a;
else
dp[i][j] = b;
}
}
}
int query(int L, int R)
{
int k = 0;
while(1<<(k+1) <= R-L+1) k++;
int a = dp[L][k];
int b = dp[R-(1<<k)+1][k];
if(depth[a] < depth[b])
return a;
else
return b;
}
int lca(int u, int v)
{
int x = id[u];
int y = id[v];
if(x < y)
return vs[query(x, y)];
else
return vs[query(y, x)];
}
void solve()
{
int q;
scanf("%d",&q);
for(int i=0;i<q;i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf(" (%d %d)",&a,&b); // 这里注意 ,输入到时候前面要加空格
mp[lca(a,b)]++;
}
map<int,int>::iterator it=mp.begin();
for(;it!=mp.end();it++)
printf("%d:%d\n", it->first,it->second); //输出
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d", &N))
{
init();
getMap();
find_depth();
RMQ_init(dfs_clock - 1);
solve();
}
return 0;
}在线 步近法
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define MAXN 1000+1000
#define MAXM 1000000+10
using namespace std;
struct Edge{
int from,to,nexts;
}edge[MAXN<<1];
int head[MAXN],top;
int dis[MAXN];
int par[MAXN];
int n,m;
map<int,int >mp;
void addedge(int a,int b)
{
Edge e={a,b,head[a]};
edge[top]=e;head[a]=top++;
}
void init()
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
memset(par,-1,sizeof(par));
top=0; mp.clear();
}
void getmap()
{
int a,b;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int num;
scanf("%d:(%d)",&a,&num);
while(num--)
{
scanf("%d",&b);
par[b]=a;
addedge(a,b);
addedge(b,a);
}
}
}
void bfs(int st)
{
queue<int>Q;
memset(dis,-1,sizeof(dis));
memset(par,-1,sizeof(par));
dis[st]=0;Q.push(st);par[st]=-1;
while(!Q.empty())
{
int now=Q.front();Q.pop();
for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nexts)
{
int nexts=edge[i].to;
if(dis[nexts]==-1)
{
dis[nexts]=dis[now]+1;
par[nexts]=now;
Q.push(nexts);
}
}
}
}
int lca(int le,int ri)
{
while(dis[le]>dis[ri]) le=par[le];
while(dis[ri]>dis[le]) ri=par[ri];
while(le!=ri)
{
le=par[le];
ri=par[ri];
}
return le;
}
void solve()
{
int q;
scanf("%d",&q);
for(int i=0;i<q;i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf(" (%d %d)",&a,&b);
mp[lca(a,b)]++;
}
map<int,int>::iterator it=mp.begin();
for(;it!=mp.end();it++)
printf("%d:%d\n", it->first,it->second);
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
init();
getmap();int st;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(par[i]==-1) st=i;
bfs(st);
solve();
}
return 0;
}






















 1559
1559











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








