Title of Content
1 冒泡排序 Bubble sort:两两交换,大的冒到最后
概念
解释:
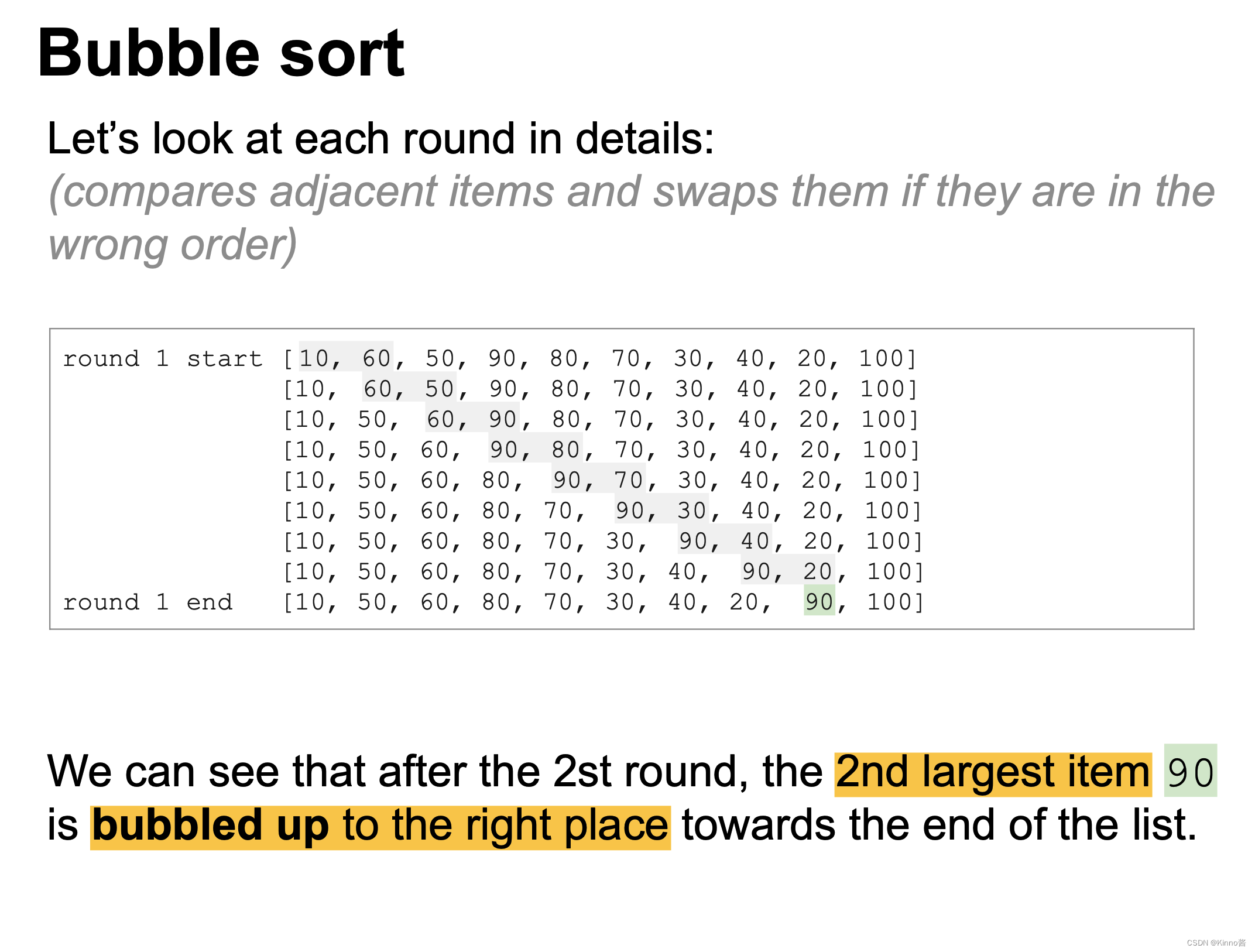
compares adjacent items and swaps them if they are in the wrong order
每轮遍历后的效果:
最大/最小的元素到达数字末尾
口诀:
(对于一个升序序列)两两交换,大的冒到最后


优化实现: 当外层循环(对整个数组的一次遍历)的这一轮遍历时没有进行交换,意味着整个数组已经有序,迭代没有必要再进行。

排序可视化
https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/algorithms/sorting/bubble-sort/visualize/
代码实现
Python - 基础实现
def bubbleSort(intList, sort="asc"):
"""
对整数列表进行冒泡排序。
:param intList: 需要排序的整数列表。
:param sort: 排序方式,"asc" 表示升序(默认),"desc" 表示降序。
如果提供了除 "asc" 或 "desc" 之外的 sort 参数,将默认采用升序排序。
:return: None。函数直接对输入的列表进行排序,不返回任何值。
"""
n = len(intList)
# 如果 sort 参数不是 "asc" 或 "desc",默认为升序
if sort not in ["asc", "desc"]:
sort = "asc"
for i in range(n):
# inner sort
# n-i-1 外层每循环i次,得到i个最大值在末尾,因此这i个位置不用比,-1是因为防止j+1越界
for j in range(n - i - 1):
if (sort == "asc" and intList[j] > intList[j + 1]) or \
(sort == "desc" and intList[j] < intList[j + 1]):
temp = intList[j + 1]
intList[j + 1] = intList[j]
intList[j] = temp
# 测试代码
sample_intList = [60, 10, 90, 50, 100, 80, 70, 30, 40, 20]
bubbleSort(sample_intList, "desc")
print(sample_intList)
bubbleSort(sample_intList, "asc")
print(sample_intList)
排序结果:

Python - 优化实现
增加判断这轮迭代有无进行元素交换的标记swapped
def bubbleSort(intList, sort="asc"):
"""
对整数列表进行冒泡排序。
:param intList: 需要排序的整数列表。
:param sort: 排序方式,"asc" 表示升序(默认),"desc" 表示降序。
如果提供了除 "asc" 或 "desc" 之外的 sort 参数,将默认采用升序排序。
:return: None。函数直接对输入的列表进行排序,不返回任何值。
"""
n = len(intList)
# 如果 sort 参数不是 "asc" 或 "desc",默认为升序
if sort not in ["asc", "desc"]:
sort = "asc"
for i in range(n):
# inner sort
# n-i-1 外层每循环i次,得到i个最大值在末尾,因此这i个位置不用比,-1是因为防止j+1越界
for j in range(n - i - 1):
swapped = False # 这轮循环有无进行交换
if (sort == "asc" and intList[j] > intList[j + 1]) or \
(sort == "desc" and intList[j] < intList[j + 1]):
intList[j], intList[j + 1] = intList[j + 1], intList[j]
swapped = True
# 如果刚刚那轮内层的遍历没有进行过交换,意味着数组已经有序,没有必要再进行后续的遍历
if not swapped:
break
Java - 优化实现
public class Sort {
/**
* 对整数数组进行冒泡排序。
*
* @param array 需要排序的整数数组。
* @param sort 指定排序的类型,"asc" 表示升序,"desc" 表示降序。
* 如果提供的 sort 参数不是 "asc" 或 "desc",将默认使用升序排序。
*/
public static void BubbleSort(int [] array, String sort){
int n = array.length;
if (!(sort.equals("asc")||sort.equals("desc")))
{
sort="asc";
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
boolean swapped=false;
for (int j=0;j<n-i-1;j++)
{
if((sort.equals("asc")&&array[j]>array[j+1])||(sort.equals("desc")&& array[j]<array[j+1])){
swapped=true;
int temp=array[j+1];
array[j+1]=array[j];
array[j]=temp;
}
}
if (!swapped){
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={60, 10, 90, 50, 100, 80, 70, 30, 40, 20};
BubbleSort(array, "asc");
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
System.out.printf("%d ",array[i]);
}
System.out.println();
BubbleSort(array, "desc");
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
System.out.printf("%d ",array[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
C - 优化实现
C++ - 优化实现
2 选择排序 Selection sort:第i轮遍历时,将未排序序列中最小/大的数放到位置i。
概念
解释:
At each round i: find the minimum in {item i, item i+1, … } and swap it to the position i
每一轮迭代,找到一个最小的值,将它和这第i轮迭代对应的数组中位置i的原数字位置对调。
每轮遍历后的效果:
For each pass, we will move left to right looking for the next largest value. Once that is found, it will be swapped into its final position .
口诀:
第i轮遍历时,将未排序序列中最小/大的数放到位置i。


初始化时,选择数组中第一个值为最大值:

排序可视化
https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/algorithms/sorting/selection-sort/visualize/
代码实现
Python
def selectionSort(intList, sort="asc"):
# 升序序列找的是最小值,降序序列找的是最大值
if not (sort == "asc" or sort == "desc"):
sort = "asc"
for i in range(len(intList) - 1):
# 每轮循环开始时,重置 min_or_max_i 为当前轮的起始位置
min_or_max_i = i
# 每一轮内层迭代的目的是找到带排序序列中最小/大值的下标j,并将它赋值给minItem_i记录下来
for j in range(i + 1, len(intList)):
if (sort == "asc" and intList[j] < intList[min_or_max_i]) or \
(sort == "desc" and intList[j] > intList[min_or_max_i]):
min_or_max_i = j
# 找到带排序序列中的最小值后,将它赋值给数组的位置i,表示他是序列中第i小的元素
# 这轮交换后得到的位置i,就是它的最终位置,因此外层循环只需要遍历len-1遍,前len-1个元素有序,整体有序
if min_or_max_i != i:
intList[i], intList[min_or_max_i] = intList[min_or_max_i], intList[i]
Java
3 插入排序 Insertion sort:每轮将未排序元素插入已排序序列(插入方法:在已排序序列中从后往前交换位置,最终找到应插入的位置)
概念
解释:
它的工作原理是通过构建有序序列,对于未排序元素,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入。
每轮遍历后的效果:
At each round i: {item 0, item 1, …, item i} are sorted
得到一个从0-i的有序序列
口诀:
每轮将未排序元素插入已排序序列




排序可视化
https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/algorithms/sorting/insertion-sort/visualize/
代码实现
Python
def insertionSort(intList):
# 外层循环每一轮迭代,i的位置指向的都是本轮未排序的元素
for i in range(1, len(intList)):
# 内存循环的每一轮迭代,从[0,i),是本轮已排序的序列
# 目标就是将未排序元素,插入已排序序列
j = i
while j - 1 >= 0: # 从小到大排序
if intList[j] < intList[j - 1]:
intList[j], intList[j - 1] = intList[j - 1], intList[j]
j -= 1
Java
public static void insertionSort(int[] array, String sort){
if(!(sort.equals("asc")||sort.equals("desc")))
{
sort="asc";
}
//第0轮排序时,第0个元素默认是以有序序列,而a[1]是待排序元素
//所以从i=1开始遍历
for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++)
{
int j = i;
while (j>0)
{
if((sort.equals("asc")&&array[j]<array[j-1])||(sort.equals("desc")&&array[j]>array[j-1])){
int temp=array[j];
array[j]=array[j-1];
array[j-1]=temp;
}
j--;
}
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








