放假这几天搞了一个基于uniapp+rk3588实现了一版yolo检测
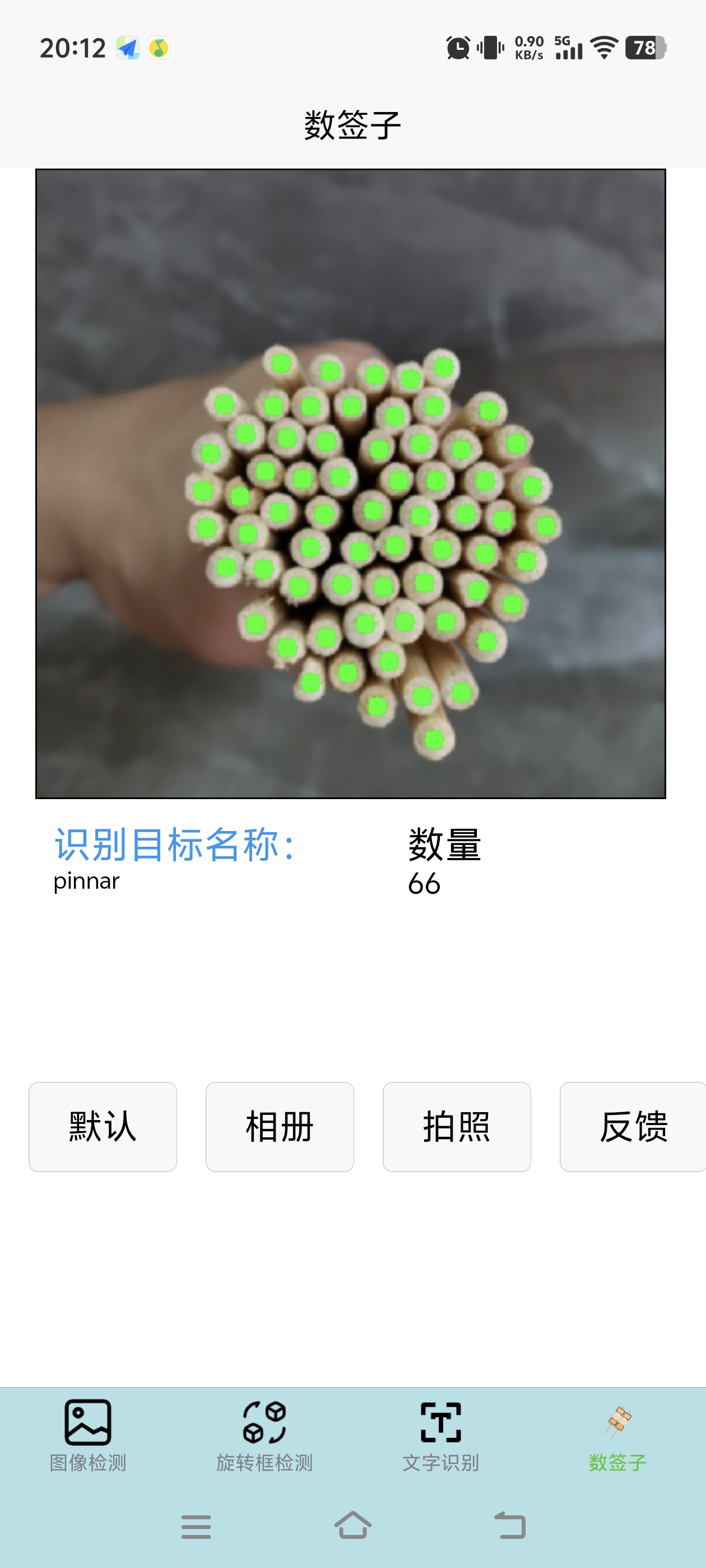
这个是基于前端调用后端api来实现,感觉还可以,但是需要有网络才能进行图像检测,网络不稳定就会出现等待时间会比较久的问题,然后有做了一个在做了一个Android版本的图像检测,我也是参考别人的实现来弄了。
记录一下大概步骤:
1.先安装Android Studio工具
2.下载检测代码yolov8安卓端识别代码
3.配置项目环境,项目下载下来只要环境配置好就可以运行,运行不起来不要怀疑是代码问题,大概下图中的都配置好没报错就可以连接手机,开始真机运行了



4.项目中默认运行项目中自带模型,如果想换其他模型,可以自己训练后转换进行替换
4.1替换默认模型大概步骤
先去拉取yolov8的训练代码 目前我使用yolov8-8.0.50版本,注意训练和导出onnx模型代码要分开,也就是说可以分成两套,下载好yolov8-8.0.50版本代码多复制一份出来,修改其中一套出来用于模型转换(pt转onnx)
具体修改:替换ultralytics-8.0.50\ultralytics-8.0.50\ultralytics\nn\modules.py中的内容,可以直接复制粘贴替换,替换完这个项目用于pt转onnx
转换还需要安装 onnx-simplifier
pip install onnx-simplifier #用于简化onnx模型
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, GPL-3.0 license
"""
Common modules
"""
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.tal import dist2bbox, make_anchors
def autopad(k, p=None, d=1): # kernel, padding, dilation
# Pad to 'same' shape outputs
if d > 1:
k = d * (k - 1) + 1 if isinstance(k, int) else [d * (x - 1) + 1 for x in k] # actual kernel-size
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution with args(ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups, dilation, activation)
default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activation
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, d=1, act=True):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p, d), groups=g, dilation=d, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
class DWConv(Conv):
# Depth-wise convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, d=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, dilation, activation
super().__init__(c1, c2, k, s, g=math.gcd(c1, c2), d=d, act=act)
class DWConvTranspose2d(nn.ConvTranspose2d):
# Depth-wise transpose convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p1=0, p2=0): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, padding_out
super().__init__(c1, c2, k, s, p1, p2, groups=math.gcd(c1, c2))
class ConvTranspose(nn.Module):
# Convolution transpose 2d layer
default_act = nn.SiLU() # default activation
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=2, s=2, p=0, bn=True, act=True):
super().__init__()
self.conv_transpose = nn.ConvTranspose2d(c1, c2, k, s, p, bias=not bn)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2) if bn else nn.Identity()
self.act = self.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv_transpose(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv_transpose(x))
class DFL(nn.Module):
# Integral module of Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) proposed in Generalized Focal Loss https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9792391
def __init__(self, c1=16):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, 1, 1, bias=False).requires_grad_(False)
x = torch.arange(c1, dtype=torch.float)
self.conv.weight.data[:] = nn.Parameter(x.view(1, c1, 1, 1))
self.c1 = c1
def forward(self, x):
b, c, a = x.shape # batch, channels, anchors
return self.conv(x.view(b, 4, self.c1, a).transpose(2, 1).softmax(1)).view(b, 4, a)
# return self.conv(x.view(b, self.c1, 4, a).softmax(1)).view(b, 4, a)
class TransformerLayer(nn.Module):
# Transformer layer https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929 (LayerNorm layers removed for better performance)
def __init__(self, c, num_heads):
super().__init__()
self.q = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
self.k = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
self.v = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
self.ma = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=c, num_heads=num_heads)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.ma(self.q(x), self.k(x), self.v(x))[0] + x
x = self.fc2(self.fc1(x)) + x
return x
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):
# Vision Transformer https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
def __init__(self, c1, c2, num_heads, num_layers):
super().__init__()
self.conv = None
if c1 != c2:
self.conv = Conv(c1, c2)
self.linear = nn.Linear(c2, c2) # learnable position embedding
self.tr = nn.Sequential(*(TransformerLayer(c2, num_heads) for _ in range(num_layers)))
self.c2 = c2
def forward(self, x):
if self.conv is not None:
x = self.conv(x)
b, _, w, h = x.shape
p = x.flatten(2).permute(2, 0, 1)
return self.tr(p + self.linear(p)).permute(1, 2, 0).reshape(b, self.c2, w, h)
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, kernels, expand
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class BottleneckCSP(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = nn.Conv2d(c1, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv3 = nn.Conv2d(c_, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv4 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * c_) # applied to cat(cv2, cv3)
self.act = nn.SiLU()
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
y1 = self.cv3(self.m(self.cv1(x)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv4(self.act(self.bn(torch.cat((y1, y2), 1))))
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, k=((1, 1), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), 1))
class C2(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(2 * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
# self.attention = ChannelAttention(2 * self.c) # or SpatialAttention()
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
a, b = self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat((self.m(a), b), 1))
class C2f(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(Bottleneck(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))
def forward(self, x):
# y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1))
# y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
# return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
print('forward C2f')
x = self.cv1(x)
x = [x, x[:, self.c:, ...]]
x.extend(m(x[-1]) for m in self.m)
x.pop(1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat(x, 1))
def forward_split(self, x):
y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
# Channel-attention module https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/tree/v3.0.0rc1/configs/rtmdet
def __init__(self, channels: int) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return x * self.act(self.fc(self.pool(x)))
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
# Spatial-attention module
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super().__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.cv1 = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.act = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.act(self.cv1(torch.cat([torch.mean(x, 1, keepdim=True), torch.max(x, 1, keepdim=True)[0]], 1)))
class CBAM(nn.Module):
# Convolutional Block Attention Module
def __init__(self, c1, kernel_size=7): # ch_in, kernels
super().__init__()
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(c1)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention(kernel_size)
def forward(self, x):
return self.spatial_attention(self.channel_attention(x))
class C1(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 1 convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1): # ch_in, ch_out, number
super().__init__()
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Conv(c2, c2, 3) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
y = self.cv1(x)
return self.m(y) + y
class C3x(C3):
# C3 module with cross-convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
self.c_ = int(c2 * e)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(self.c_, self.c_, shortcut, g, k=((1, 3), (3, 1)), e=1) for _ in range(n)))
class C3TR(C3):
# C3 module with TransformerBlock()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e)
self.m = TransformerBlock(c_, c_, 4, n)
class C3Ghost(C3):
# C3 module with GhostBottleneck()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(GhostBottleneck(c_, c_) for _ in range(n)))
class SPP(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) layer https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.4729
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * (len(k) + 1), c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1))
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat((x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)), 1))
class Focus(nn.Module):
# Focus wh information into c-space
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = Conv(c1 * 4, c2, k, s, p, g, act=act)
# self.contract = Contract(gain=2)
def forward(self, x): # x(b,c,w,h) -> y(b,4c,w/2,h/2)
return self.conv(torch.cat((x[..., ::2, ::2], x[..., 1::2, ::2], x[..., ::2, 1::2], x[..., 1::2, 1::2]), 1))
# return self.conv(self.contract(x))
class GhostConv(nn.Module):
# Ghost Convolution https://github.com/huawei-noah/ghostnet
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, groups
super().__init__()
c_ = c2 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k, s, None, g, act=act)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c_, 5, 1, None, c_, act=act)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.cv1(x)
return torch.cat((y, self.cv2(y)), 1)
class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):
# Ghost Bottleneck https://github.com/huawei-noah/ghostnet
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=3, s=1): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride
super().__init__()
c_ = c2 // 2
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
GhostConv(c1, c_, 1, 1), # pw
DWConv(c_, c_, k, s, act=False) if s == 2 else nn.Identity(), # dw
GhostConv(c_, c2, 1, 1, act=False)) # pw-linear
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(DWConv(c1, c1, k, s, act=False), Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1,
act=False)) if s == 2 else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x) + self.shortcut(x)
class Concat(nn.Module):
# Concatenate a list of tensors along dimension
def __init__(self, dimension=1):
super().__init__()
self.d = dimension
def forward(self, x):
return torch.cat(x, self.d)
class Proto(nn.Module):
# YOLOv8 mask Proto module for segmentation models
def __init__(self, c1, c_=256, c2=32): # ch_in, number of protos, number of masks
super().__init__()
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k=3)
self.upsample = nn.ConvTranspose2d(c_, c_, 2, 2, 0, bias=True) # nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c_, k=3)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c2)
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(self.cv2(self.upsample(self.cv1(x))))
class Ensemble(nn.ModuleList):
# Ensemble of models
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x, augment=False, profile=False, visualize=False):
y = [module(x, augment, profile, visualize)[0] for module in self]
# y = torch.stack(y).max(0)[0] # max ensemble
# y = torch.stack(y).mean(0) # mean ensemble
y = torch.cat(y, 1) # nms ensemble
return y, None # inference, train output
# heads
class Detect(nn.Module):
# YOLOv8 Detect head for detection models
dynamic = False # force grid reconstruction
export = False # export mode
shape = None
anchors = torch.empty(0) # init
strides = torch.empty(0) # init
def __init__(self, nc=80, ch=()): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.nl = len(ch) # number of detection layers
self.reg_max = 16 # DFL channels (ch[0] // 16 to scale 4/8/12/16/20 for n/s/m/l/x)
self.no = nc + self.reg_max * 4 # number of outputs per anchor
self.stride = torch.zeros(self.nl) # strides computed during build
c2, c3 = max((16, ch[0] // 4, self.reg_max * 4)), max(ch[0], self.nc) # channels
self.cv2 = nn.ModuleList(
nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c2, 3), Conv(c2, c2, 3), nn.Conv2d(c2, 4 * self.reg_max, 1)) for x in ch)
self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c3, 3), Conv(c3, c3, 3), nn.Conv2d(c3, self.nc, 1)) for x in ch)
self.dfl = DFL(self.reg_max) if self.reg_max > 1 else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
shape = x[0].shape # BCHW
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = torch.cat((self.cv2[i](x[i]), self.cv3[i](x[i])), 1)
if self.training:
return x
elif self.dynamic or self.shape != shape:
self.anchors, self.strides = (x.transpose(0, 1) for x in make_anchors(x, self.stride, 0.5))
self.shape = shape
# if self.export and self.format == 'edgetpu': # FlexSplitV ops issue
# x_cat = torch.cat([xi.view(shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in x], 2)
# box = x_cat[:, :self.reg_max * 4]
# cls = x_cat[:, self.reg_max * 4:]
# else:
# box, cls = torch.cat([xi.view(shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in x], 2).split((self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1)
# dbox = dist2bbox(self.dfl(box), self.anchors.unsqueeze(0), xywh=True, dim=1) * self.strides
# y = torch.cat((dbox, cls.sigmoid()), 1)
# return y if self.export else (y, x)
print('forward Detect')
pred = torch.cat([xi.view(shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in x], 2).permute(0, 2, 1)
return pred
def bias_init(self):
# Initialize Detect() biases, WARNING: requires stride availability
m = self # self.model[-1] # Detect() module
# cf = torch.bincount(torch.tensor(np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0]).long(), minlength=nc) + 1
# ncf = math.log(0.6 / (m.nc - 0.999999)) if cf is None else torch.log(cf / cf.sum()) # nominal class frequency
for a, b, s in zip(m.cv2, m.cv3, m.stride): # from
a[-1].bias.data[:] = 1.0 # box
b[-1].bias.data[:m.nc] = math.log(5 / m.nc / (640 / s) ** 2) # cls (.01 objects, 80 classes, 640 img)
class Segment(Detect):
# YOLOv8 Segment head for segmentation models
def __init__(self, nc=80, nm=32, npr=256, ch=()):
super().__init__(nc, ch)
self.nm = nm # number of masks
self.npr = npr # number of protos
self.proto = Proto(ch[0], self.npr, self.nm) # protos
self.detect = Detect.forward
c4 = max(ch[0] // 4, self.nm)
self.cv4 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c4, 3), Conv(c4, c4, 3), nn.Conv2d(c4, self.nm, 1)) for x in ch)
def forward(self, x):
p = self.proto(x[0]) # mask protos
bs = p.shape[0] # batch size
mc = torch.cat([self.cv4[i](x[i]).view(bs, self.nm, -1) for i in range(self.nl)], 2) # mask coefficients
x = self.detect(self, x)
if self.training:
return x, mc, p
return (torch.cat([x, mc], 1), p) if self.export else (torch.cat([x[0], mc], 1), (x[1], mc, p))
class Classify(nn.Module):
# YOLOv8 classification head, i.e. x(b,c1,20,20) to x(b,c2)
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
c_ = 1280 # efficientnet_b0 size
self.conv = Conv(c1, c_, k, s, autopad(k, p), g)
self.pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) # to x(b,c_,1,1)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=True)
self.linear = nn.Linear(c_, c2) # to x(b,c2)
def forward(self, x):
if isinstance(x, list):
x = torch.cat(x, 1)
x = self.linear(self.drop(self.pool(self.conv(x)).flatten(1)))
return x if self.training else x.softmax(1)
5.onnx转ncnn
去官网下载ncnn转换工具

下载完成后打开进入到ncnn-20241226-windows-vs2019\ncnn-20241226-windows-vs2019\x86\bin下面

打开cmd终端执行下面命令 后面的onnx填自己转换的模型
onnx2ncnn.exe yolo.onnx

转换完后会产生两个 bin结尾和param结尾的文件
打开param文件修改最后一行,把output0改成output,这个里面的内容不一定要完全和ncnn-android-yolov8项目中的模型内容一样,刚开始我产生了误区是转换出来必须和项目中的模型内容一样,其实不一样也可以,修改完后就可以拿去替换项目中的模型了

注意:项目中的模型默认是80类别的 如果替换会自己训练的模型一定要对应修改,类别数量
可以下载我上传的android-yolov8检测资源文件,已经测试过没问题























 5373
5373

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








