#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#define BUFSIZE 100
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Tan xujia");
static int irq = 20;
module_param(irq , int, 0660);
static int mode = 1;
module_param(mode , int, 0660);
static struct proc_dir_entry *ent;
static
ssize_t proc_write(struct file *file, const char __user *ubuf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
int num, ret, index, m;
char buf[BUFSIZE];
if(*ppos > 0 || count > BUFSIZE)
return -EFAULT;
if(copy_from_user(buf, ubuf, count))
return -EFAULT;
num = sscanf(buf, "%d %d",&index, &m);
if(num != 2)
return -EFAULT;
irq = index;
mode = m;
ret = strlen(buf);
*ppos = ret;
return ret;
}
static
ssize_t proc_read(struct file *file, char __user *ubuf,size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int len = 0;
if(*ppos > 0 || count < BUFSIZE)
return 0;
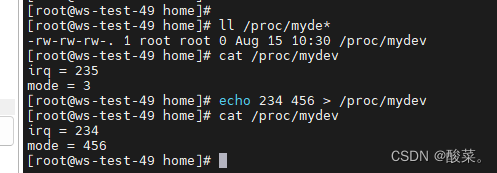
len += sprintf(buf,"irq = %d\n",irq);
len += sprintf(buf + len,"mode = %d\n",mode);
if(copy_to_user(ubuf,buf,len))
return -EFAULT;
*ppos = len;
return len;
}
static struct file_operations proc_ops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = proc_read,
.write = proc_write,
};
static int proc_init(void)
{
ent = proc_create("mydev", 0666, NULL, &proc_ops);
if(!ent)
printk("proc_create fail\n");
printk("proc_init\n");
return 0;
}
static
void proc_cleanup(void)
{
if(ent)
proc_remove(ent);
printk("proc_cleanup\n");
}
module_init(proc_init);
module_exit(proc_cleanup);
obj-m := proc.o
proc-objs := proc_dev.o
all:
make -C /usr/src/kernels/$(shell uname -r) M=$(shell pwd) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(shell pwd) clean
























 1433
1433











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








