数组学习
1 数组定义,元素访问与遍历
1.1 数组的作用
如果存储一个数据可以定义一个变量, 如果存储100个数据呢 可以使用数组
数组就是用来存储一组相同类型若干数据的容器
1.2 如何定义数组
1、数据类型 [] 数组名 = new 数据类型[数组长度] ;
2、数据类型 数组名[] = new 数据类型[数组长度] ;
如:
定义一个数组,存储10个int类型数据
int [] data = new int[10];
说明:
1) int表示数组中存储数据的类型是int整数类型
2) [] 表示正在定义一个数组
3) data是数组名, 数组名其实就是一个变量名,
4) 在Java中数组也是一种引用数据类型, data是变量名, 它的数据类型是: int []
5) new运算符在堆中分配一块连续的存储空间, 这块连续的存储空间可以存储10个int类型数据, 把这块存储空间的引用(起始地址)赋值给data,
6) 数组本质上就是内存中一块连续的存储空间
1.3 如何访问数组元素
为数组的每个元素指定一个索引值(下标),
索引值是从0开始的, 即data数组的索引值分别是: 0~9
为什么通过索引值可以访问数组元素?

/**
* 演示数组的定义与元素的访问
*
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1)数组的定义
//1.1 定义一个数组,存储5个int数据
int [] data = new int[5];
//1.2 定义数组,存储10个double数据
double[] data2 = new double[10];
//1.3 定义数组,存储20个String字符串
String [] data3 = new String[20];
//1.4 定义数组,存储100个char数据
char [] data4 = new char[100];
//2 数组元素的访问
//2.1 给data数组的每个元素赋值, data数组长度是5,表示存储5个int数据, 数组索引值是从0开始的
data[0] = 55;
data[1] = 55;
data[2] = 55;
data[3] = 55;
data[4] = 55;
//使用的数组时,避免数组下标越界异常java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5
// data[5] = 55;
//2.2 打印每个数组元素的值
System.out.println( data[0] );
System.out.println( data[1] );
System.out.println( data[2] );
System.out.println( data[3] );
System.out.println( data[4] );
//2.3 使用for循环打印
//每个数组都有一个length属性,表示数组的长度
for( int i = 0 ; i < data.length; i++){
System.out.println( data[i] );
}
}
}
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1)定义数组,存储5个int数据
int [] data = new int[5];
//2)数组元素的遍历, 遍历就是依次访问数组的每个元素
for( int i = 0 ; i < data.length; i++){
System.out.print( data[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
/*
* 3)数组元素的默认初始化
* 整数数组,元素默认初始化为0
* 小数数组,元素默认初始化为0.0
* 布尔数组,元素默认初始化为false
* 字符数组,元素默认初始化为码值为0的字符, '\u0000'
* 引用数组,元素默认初始化为null
*/
//4)数组的静态初始化, 在定义数组时,给数组的每个元素赋值
//数组静态初始化时, 不需要指定数组的长度,数组长度由初始化元素的个数决定
int [] data2 = new int[]{ 213,45,76,89,12};
//静态初始化,可以简化为
int [] data3 = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
//5)如果仅仅是遍历数组的元素, 可以使用增强的for循环,也叫foreach循环
for (int xx : data3) {
//依次把data3数组的每个元素赋值给局部变量xx
System.out.print( xx + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
//6)数组名之间也可以相互赋值
data3 = data2; //把data2变量的值赋值给data3, 现在data2/data3都保存同一个数组的引用
//7)打印数组的元素时, 可以使用java.util.Arrays工具类toString()方法
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data2));
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data3));
//8)注意, 这种简化的形式仅用于数组的静态初始化,不能进行数组的赋值
// data3 = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
}
}
0 0 0 0 0
1 2 3 4 5 6
[213, 45, 76, 89, 12]
[213, 45, 76, 89, 12]
Process finished with exit code 0
2 数组是一种引用数据类型
/**
* 数组是引用数据类型,可以作为方法的返回值类型,方法的参数类型
*
*/
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//调用getArray()方法, 该方法返回一个数组,
int [] mydata = getArray();
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(mydata ));
//调用方法,交换第一个和最后一个元素的位置
swap(mydata, 0, mydata.length-1 );
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(mydata ));
}
//1)定义一个方法, 返回一个整数数组, 数组的元素从键盘输入
public static int[] getArray() {
int [] data = new int [5];
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for( int i = 0 ; i < data.length; i++){
System.out.println("请输入一个整数");
data[i] = sc.nextInt(); //把键盘上输入的数保存到数组中
}
return data; //方法的返回值类型是数组, 通过return返回一个数组
}
//2)定义方法, 交换数组中指定位置的两个元素, 把array数组中i和j两个位置的元素进行交换
public static void swap( int [] array, int i , int j ) {
int t = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = t;
}
}
1
请输入一个整数
2
请输入一个整数
3
请输入一个整数
4
请输入一个整数
5
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[5, 2, 3, 4, 1]
Process finished with exit code 0
3 可变长参数
package chapter03.demo01;
/**
* 可变长参数
*
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在调用方法, 可以传递任意个数据
sum();
sum(1,2);
sum(1,2,3,4,5);
int [] data = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
sum(data);
}
//定义方法, 可以计算任意个整数的和
public static void sum( int ... num) {
//在方法体中, 把可变长参数当作数组使用
int sum = 0 ; //保存累加和
for( int i = 0 ; i < num.length; i++ ){
sum += num[i];
}
System.out.println("sum=" + sum);
}
}
sum=0
sum=3
sum=15
sum=55
Process finished with exit code 0
4 数组扩容

**
* 数组扩容
*
*/
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
m1(); //手动数组扩容
m2(); //调用系统方法实现数组的复制
m3(); //调用Arrays.copyOf()实现复制
}
private static void m3() {
int [] data = {65,342,786,21,89};
//Arrays.copyOf( 源数组, 新数组的长度 )
data = Arrays.copyOf(data, data.length + 2);
data[5] = 666;
data[6] = 888;
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
private static void m2() {
int [] data = {65,342,786,21,89};
// 1) 定义更大的数组
int [] newdata = new int[data.length + 2 ]; //多存储2个数据
// 2) 把原来数组的内容复制到新数组中
//把src数组中从Srcpos开始的length元素复制到dest数组的destPos开始的位置
// System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length);
System.arraycopy(data, 0, newdata, 0, data.length );
//JNI, Java Native Interface, 通过JNI技术,可以在Java中调用其他语言编写的代码
// 3) 让原来的数组名指向新的数组
data = newdata ;
//4)把数组保存到数组中
data[5] = 666;
data[6] = 888;
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
private static void m1() {
int [] data = {65,342,786,21,89};
// 1) 定义更大的数组
int [] newdata = new int[data.length + 2 ]; //多存储2个数据
// 2) 把原来数组的内容复制到新数组中
for( int i = 0 ; i<data.length; i++){
newdata[i] = data[i];
}
// 3) 让原来的数组名指向新的数组
data = newdata ;
//4)把数组保存到数组中
data[5] = 666;
data[6] = 888;
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
[65, 342, 786, 21, 89, 666, 888]
[65, 342, 786, 21, 89, 666, 888]
[65, 342, 786, 21, 89, 666, 888]
Process finished with exit code 0
5 在数组中插入元素
/**
* 在数组中插入/删除元素
*
*/
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] data = {54,12,76,98,34,59};
data = insert(data, 2, 666);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
data = delete(data, 2);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
//定义方法,在数组中指定的位置插入元素, 在array数组的i位置插入元素key
public static int[] insert( int [] array, int i , int key) {
//1)定义更大的数组
int [] newArray = new int[array.length + 1]; //长度加1
//2) 把array数组中[0,i)范围内的元素复制到新数组中
for( int x = 0; x < i ; x++){
newArray[x] = array[x];
}
//3) 把key存储到新数组的i位置
newArray[i] = key;
//4) 把array数组[i, length)范围内的元素复制到新数组i+1开始的位置
for( int x = i ; x < array.length; x++){
newArray[x+1] = array[x];
}
// System.out.println( Arrays.toString(newArray));
// array = newArray;
// System.out.println( Arrays.toString(array));
//5)返回新的数组
return newArray;
}
//定义方法, 删除数组中指定位置的元素, 把array数组中i位置的元素删除
public static int [] delete (int [] array, int i ) {
//1)定义一个较小的数组
int [] newArray = new int[array.length - 1 ];
//2)把array数组中[0,i)范围的元素复制到新数组中
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, i);
//3)把 array数组中[i+1, length)范围的元素复制到新数组i开始的位置
System.arraycopy(array, i+1, newArray, i, array.length - i - 1);
//4)返回新 的数组
return newArray;
}
}
--------------------------------------
[54, 12, 666, 76, 98, 34, 59]
[54, 12, 76, 98, 34, 59]
Process finished with exit code 0
6 数组的特点
优点:
通过索引值可以快速访问数组的每个元素, 实现数组元素的随机访问
缺点:
向数组中插入/删除元素时, 效率比较低,因为可能需要扩容,复制/移动大量的元素
数组的应用场景:
数组适应于以查询访问为主, 很少进行插入/删除的情况
7 对象数组
public class Student {
String name;
public int age;
public int score;
public Student(String name, int age, int score) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + "]";
}
}
/**
* 定义班级类
*/
public class MyClass {
//定义一个数组,存储Student学生对象
Student [] studentss;
int size; //保存数组中学生对象的个数
//在无参构造方法中,给studentss数组进行默认的初始化
public MyClass() {
studentss = new Student[5]; //默认数组初始化大小为5,实际开发初始化大小要进行估算
}
//定义方法,在班级中添加一个学生,就是把学生对象保存到数组中
public void add(Student stu) {
//向数组中 添加元素,如果数组已满, 数组需要扩容, 按2倍大小扩容
if (size >= studentss.length ) {
studentss = Arrays.copyOf(studentss, studentss.length*2 );
}
//把学生对象保存到数组中
studentss[size] = stu;
size++; //学生个数加1
}
//显示班级中的学生
public void show() {
//遍历数组中已有的学生,打印
for( int i = 0 ; i<size ; i++){
System.out.println( studentss[i] );
}
}
//定义方法,判断班级中是否存在指定姓名的同学
public boolean exist(String stuname) {
//遍历已有的学生, 如果该学生的姓名与指定的参数姓名相同就返回true
for(int i = 0 ; i<size ; i++){
if ( stuname.equals(studentss[i].name)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* 对象数组
*
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1)定义一个数组,存储5个Student对象
Student [] stuss = new Student[5];
//2)给对象数组元素赋值, 实际上是把对象的引用保存到数组元素中
stuss[0] = new Student("lisi", 18, 90);
stuss[1] = new Student("wang", 28, 70);
stuss[2] = new Student("zhao", 38, 60);
Student lisi = new Student("lisi", 48, 40);
stuss[3] = lisi;
//3)遍历打印
for(int i = 0 ; i<stuss.length; i++){
System.out.println( stuss[i] );
}
}
}
[name=lisi, age=18, score=90]
[name=wang, age=28, score=70]
[name=zhao, age=38, score=60]
[name=lisi, age=48, score=40]
null
Process finished with exit code 0
/**
* 测试班级类
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建班级
MyClass class737 = new MyClass();
//添加学生
class737.add( new Student("lu", 22, 85) );
class737.add( new Student("huo", 18, 100) );
class737.add( new Student("wang", 23, 75) );
//显示班级学生信息
class737.show();
//判断是否存在指定姓名的同学
System.out.println( class737.exist("lu"));
System.out.println( class737.exist("chen"));
}
}
[name=lu, age=22, score=85]
[name=huo, age=18, score=100]
[name=wang, age=23, score=75]
true
false
Process finished with exit code 0
8 二维数组
/**
* 演示二维数组
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一维数组
int [] data1 = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
int [] data2 = {4,5,6,7};
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
int [] data3 = {x, y};
/*
* data1/data2/data3分别是一维数组名, 其实就是一个变量名, 它的数据类型是int []
* 在定义数组时,int表示数组中元素的类型, [] 表示正在定义数组
*/
//需求: 定义一个数组, 保存data1/data2/data3三个变量值
int[] [] mydata = { data1 , data2, data3 };
//mydata就是一个二维数组, 它的每个元素又是一个一维数组
//遍历二维数组存储的数据
for( int i = 0 ; i<mydata.length; i++){
// mydata[0]是data1, mydata[i]是一个 一维数组名
for(int j = 0 ; j < mydata[i].length; j++){
System.out.print( mydata[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
//二维数组的动态初始化,
//定义一个长度为5的二维数组, 每个元素是int[]类型的数组
int [][] mydata2 = new int[5][];
for( int i = 0 ; i < mydata2.length ; i++){
System.out.println( mydata2[i] );
}
//在定义二维数组时,也可以指定一维数组的长度,系统会给一维数组默认初始化
int [][] mydata3 = new int[5][4]; //5是二维数组元素的个数, 4是一维数组的长度
//Arrays.deepToString() 可以把多维数组中的元素转换为字符串
System.out.println( Arrays.deepToString(mydata3));
//给二维数组的元素赋值, 只要是int[]类型的数据就可以赋值
mydata3[0] = data1;
mydata3[1] = data3;
System.out.println( Arrays.deepToString(mydata3));
//二维数组的静态初始化, 在 定义二维数组时,给二维数组的元素赋值
int [][] mydata4 = new int[][]{data1, data2, new int[5] , new int[]{6,6,6,6} };
int [][] mydata5 = {data1, data2, data3};
int [][] mydata6 = {data1, {4,4,4,4,4} , {8,8,8}};
System.out.println( Arrays.deepToString(mydata6));
}
}
1 2 3 4 5
4 5 6 7
10 20
null
null
null
null
null
[[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [10, 20], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]
[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [4, 4, 4, 4, 4], [8, 8, 8]]
Process finished with exit code 0
9 数组的相关算法
9.1 冒泡排序
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] data = {12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63};
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
System.out.println("---------------------------");
//第1轮, 可以把最大的交换到后面
for(int i = 0 ; i<data.length - 1; i++){
if (data[i] > data[i+1] ) {
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[i+1];
data[i+1] = t;
}
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
//第2轮, 可以把第二大的交换到后面
for(int i = 0 ; i<data.length - 1 - 1; i++){
if (data[i] > data[i+1] ) {
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[i+1];
data[i+1] = t;
}
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
//第3轮, 可以把第3大的交换到后面
for(int i = 0 ; i<data.length - 1 - 2; i++){
if (data[i] > data[i+1] ) {
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[i+1];
data[i+1] = t;
}
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
//第4轮, 可以把第4大的交换到后面
for(int i = 0 ; i<data.length - 1 - 3; i++){
if (data[i] > data[i+1] ) {
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[i+1];
data[i+1] = t;
}
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
//第5轮, 可以把第5大的交换到后面
for(int i = 0 ; i<data.length - 1 - 4; i++){
if (data[i] > data[i+1] ) {
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[i+1];
data[i+1] = t;
}
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
System.out.println("---------------------------");
}
}
[12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63]
---------------------------
[12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63]
[12, 82, 93, 5, 70, 63]
[12, 82, 5, 93, 70, 63]
[12, 82, 5, 70, 93, 63]
[12, 82, 5, 70, 63, 93]
---------------------------
[12, 82, 5, 70, 63, 93]
[12, 5, 82, 70, 63, 93]
[12, 5, 70, 82, 63, 93]
[12, 5, 70, 63, 82, 93]
---------------------------
[5, 12, 70, 63, 82, 93]
[5, 12, 70, 63, 82, 93]
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93]
---------------------------
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93]
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93]
---------------------------
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93]
---------------------------
Process finished with exit code 0

/**
* 冒泡排序(由小到大)
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] data = {12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63};
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
System.out.println("---------------------------");
for( int x = 0 ; x < data.length - 1; x++){
//第1轮, 可以把最大的交换到后面
for(int i = 0 ; i<data.length - 1 - x; i++){
if (data[i] > data[i+1] ) {
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[i+1];
data[i+1] = t;
}
// System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
// System.out.println("---------------------------");
}
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
[12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63]
---------------------------
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93]
Process finished with exit code 0
9.2 选择排序

/**
* 选择排序
* 与冒泡排序相比, 比较的次数减少, 交换的次数变少了
*
*/
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] data = {12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63};
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
System.out.println("---------------------------");
for(int x = 0 ; x < data.length - 1; x++){
//找当前最小元素的下标
int min = x; //保存最小元素的下标
for( int i = min+1 ; i < data.length ; i++){
if ( data[i] < data[min]) {
min = i;
}
}
//把min标识的元素 交换到前面
int t = data[x];
data[x] = data[min];
data[min] = t;
// System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
// System.out.println("---------------------------");
}
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
[12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63]
---------------------------
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93]
Process finished with exit code 0
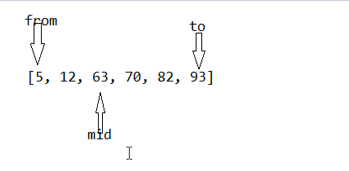
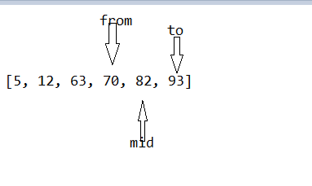
9.3 二分查找
/**
* 二分查
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] data = {5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93};
System.out.println( indexOf(data, 5));
System.out.println( indexOf(data, 93));
System.out.println( indexOf(data, 50));
}
//定义方法,二分查找 , 返回数组中指定元素的索引值
public static int indexOf(int [] array, int key) {
int from = 0 ;
int to = array.length - 1;
int mide = (from+to)/2;
while( from <= to ){
if ( array[mide] == key ) { //先和中间的元素比较
return mide;
}else if ( array[mide] > key) { //比中间的元素小,说明在左一半
to = mide - 1;
mide = (from+to)/2;
}else { //在右一半
from = mide + 1;
mide = (from+to)/2;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
0
5
-1
Process finished with exit code 0
10 Arrays工具类
| 返回值类型 | 方法名 |
|---|---|
| static List | asList(T… a) 把数组转换为List列表 |
| static int | binarySearch(int[] a, int key) 采用二分查找算法在a数组中查找key元素,返回元素在数组中的索引值, 如果不存在key元素返回负数 |
| static int[] | copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) 数组的复制 |
| static String | deepToString(Object[] a) 把数组中的元素转换为字符串 |
| static void | fill(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int val)把a数组[fromindex, toIndex)范围的元素全用Val代替 |
| static void | parallelSort(int[] a) 并行排序,适用于数据非常多的情况 |
| static void | sort(int[] a) 排序 |
| static String | toString(int[] a) 把数组a中的元素转换为字符串 |
/**
* Arrays工具类
*/
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] data = {12, 93, 82, 5, 70, 63};
//1)排序
Arrays.sort(data);
//2)打印
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
//3)扩容
data = Arrays.copyOf(data, data.length * 3 / 2);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
//4)填充
Arrays.fill(data, 6, 9, 666);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(data));
//5)二分查找
System.out.println( Arrays.binarySearch(data, 5));
System.out.println( Arrays.binarySearch(data, 50));
System.out.println( Arrays.binarySearch(data, 666));
}
}
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93]
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93, 0, 0, 0]
[5, 12, 63, 70, 82, 93, 666, 666, 666]
0
-3
6
Process finished with exit code 0
11 对象数组排序
/**
* 对象数组排序
*
*/
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义对象数组
Student[] stuss = new Student[5];
//给对象数组赋值
stuss[0] = new Student("lisi", 28, 80);
stuss[1] = new Student("wang", 18, 90);
stuss[2] = new Student("zhao", 58, 20);
stuss[3] = new Student("chen", 38, 40);
stuss[4] = new Student("zhu", 8, 60);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(stuss ));
//对象数组排序, 可以通过sort方法的第二个参数指定一个比较规则
//Comparator接口后面的<T>是 一个泛型, 指定比较对象的 数据类型
Arrays.sort(stuss, new Comparator<Student>() {
//在匿名内部类中重写接口抽象方法, 通过compare指定一个比较规则
//如果第一个对象大返回正数就是升序排序, 如果第二个对象大返回正数就是降序排序
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.age - o2.age; //根据年龄升序
}
});
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(stuss ));
Arrays.sort(stuss, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o2.score - o1.score;
}
});
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(stuss ));
}
}
[[name=lisi, age=28, score=80], [name=wang, age=18, score=90], [name=zhao, age=58, score=20], [name=chen, age=38, score=40], [name=zhu, age=8, score=60]]
[[name=zhu, age=8, score=60], [name=wang, age=18, score=90], [name=lisi, age=28, score=80], [name=chen, age=38, score=40], [name=zhao, age=58, score=20]]
[[name=wang, age=18, score=90], [name=lisi, age=28, score=80], [name=zhu, age=8, score=60], [name=chen, age=38, score=40], [name=zhao, age=58, score=20]]
Process finished with exit code 0
12 练习
/**
* 定义一个方法, 返回一个整数数组, 要求对数组元素进行随机的初始化[0,100)范围内的数据,
* Math.random() 产生[0,1) 范围内的随机小数
定义第二个方法, 实现数组的逆序
定义第三个方法, 返回指定数组中最大元素的索引值
*
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] myarray = getArray();
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(myarray));
System.out.println( getMaxIndex(myarray));
reverse(myarray);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(myarray));
System.out.println( getMaxIndex(myarray));
xxxx(myarray);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(myarray));
}
//定义一个方法, 返回一个整数数组, 要求对数组元素进行随机的初始化[0,100)范围内的数据
public static int[] getArray() {
int [] data = new int[10];
for(int i = 0 ; i<data.length; i++){
int xxx = (int)(Math.random()*100);
data[i] = xxx;
}
return data;
}
//实现数组的逆序
public static void reverse( int [] array) {
for( int i = 0 ; i < array.length/2; i++){
int t = array[i];;
array[i] = array[array.length-1 - i];
array[array.length-1 - i] = t;
}
}
//返回指定数组中最大元素的索引值
public static int getMaxIndex( int [] array) {
int max = 0 ; //保存最大元素的下标, 假设第0个元素最大
//遍历数组后面的元素,依次与data[max]比较,
for(int i = 1; i < array.length; i++){
//如果有某个元素大于 data[max] 就让max保存该元素的下标
if (array[i] > array[max]) {
max = i;
}
}
return max;
}
//定义方法, 把数组中的最小元素,交换到索引值为0的位置
public static void xxxx(int [] array) {
//在array数组中找出最小元素的索引值, min
int min = 0 ; //保存最小元素的索引值
for( int i = min +1 ; i < array.length; i++){
if ( array[i] < array[min]) {
min = i;
}
}
//索引值为min的元素与索引值为0的元素进行交换
int t = array[min];
array[min]= array[0];
array[0] = t;
}
}
[29, 92, 68, 73, 34, 69, 23, 52, 29, 36]
1
[36, 29, 52, 23, 69, 34, 73, 68, 92, 29]
8
[23, 29, 52, 36, 69, 34, 73, 68, 92, 29]
Process finished with exit code 0






















 182
182











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








