(一)学习总结
1.用思维导图对本周的学习内容进行总结。

2.当程序中出现异常时,JVM会依据方法调用顺序依次查找有关的错误处理程序。可使用printStackTrace 和getMessage方法了解异常发生的情况。阅读下面的程序,说明printStackTrace方法和getMessage 方法的输出结果分别是什么?并分析异常的传播过程。
public class PrintExceptionStack {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
try {
method1();
} catch ( Exception e ) {
System.err.println( e.getMessage() + "\n" );
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void method1() throws Exception
{
method2();
}
public static void method2() throws Exception
{
method3();
}
public static void method3() throws Exception
{
throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" );
}
}printStackTrace()的输出结果:
at PrintExceptionStack.method3(PrintExceptionStack.java:22)
at PrintExceptionStack.method2(PrintExceptionStack.java:18)
at PrintExceptionStack.method1(PrintExceptionStack.java:14)
at PrintExceptionStack.main(PrintExceptionStack.java:6)getMessage()的输出结果:
Exception thrown in method3getMessage()只会获得具体的异常名称.
printStackTrace()会打出详细异常,异常名称,出错位置,便于调试用。
3.阅读下面程序,分析程序的运行结果,解释产生错误的原因,如果删除的是books集合的最后一个对象,运行的结果又是什么?你能对此作出解释吗?如果在遍历时非要删除集合中的元素,应如何实现?
import java.util.*;
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Collection<String> books = new ArrayList<String>();
books.add("One book");
books.add("Two book");
books.add("Three book");
System.out.println("原始元素之后:"+books);
Iterator<String> it = books.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
String book = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(book);
if (book.equals("One book"))
{
books.remove(book);
}
}
System.out.println("移除元素之后:"+books);
}
}运行结果为:
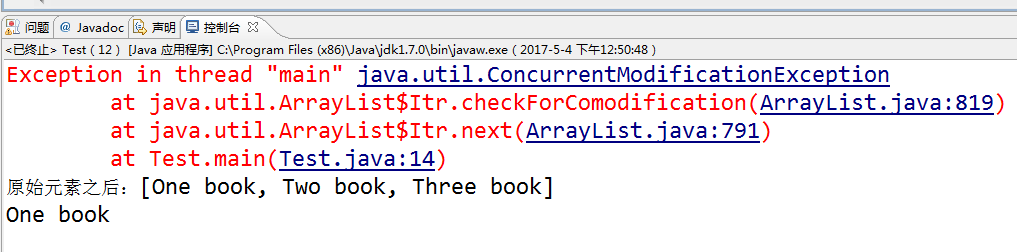
原因:在ArrayList遍历的时候删掉其中的元素,大小发生改变,产生了异常
删除最后一个对象的运行结果为:

原因:在使用Iterator输出时集合的大小没有发生变化,正常输出,但是删除时调用了集合的remove()方法,发生变化,输出发生异常。
修改后的代码为:
import java.util.*;
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Collection<String> books = new ArrayList<String>();
books.add("One book");
books.add("Two book");
books.add("Three book");
System.out.println("原始元素之后:"+books);
Iterator<String> it = books.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
String book = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(book);
if (book.equals("one book"))
{
it.remove();
}
}
System.out.println("移除元素之后:"+books);
}
}4.HashSet存储的元素是不可重复的。运行下面的程序,分析为什么存入了相同的学生信息?如果要去掉重复元素,应该如何修改程序。
import java.util.*;
class Student {
String id;
String name;
public Student(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student id=" + id + ", name=" + name ;
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet<Student> set = new HashSet<Student>();
set.add(new Student("1","Jack"));
set.add(new Student("2","Rose"));
set.add(new Student("2","Rose"));
System.out.println(set);
}
}原因:实例化对象的时候发生了问题
解决方法:重写写equals()方法和hashcode()方法
import java.util.*;
class Student {
String id;
String name;
public Student(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (id == null) {
if (other.id != null)
return false;
} else if (!id.equals(other.id))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
public String toString() {
return "Student id=" + id + ", name=" + name ;
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet<Student> set = new HashSet<Student>();
set.add(new Student("1","Jack"));
set.add(new Student("2","Rose"));
set.add(new Student("2","Rose"));
System.out.println(set);
}
}(二)实验总结
实验内容:
1.模拟KTV点歌系统
分别用LinkedList和ArrayList集合,实现一个模拟KTV点歌系统的程序。实现以下功能:
(1)显示歌曲列表
(2)添加歌曲到列表
(3)删除歌曲
(4)将歌曲置顶
(5)将歌曲前移一位
(6)退出
题目扩展:歌曲包括曲名、演唱者。增加排序显示歌曲列表功能。
设计思路:
创建Mu类,类中包含歌曲名和歌手名,分别定义方法显示歌曲列表,添加歌曲。删除歌曲,指定歌曲,将歌曲前移一位。
问题:
如何将歌曲置顶,和前移一位。
解决方法:
case 4:
System.out.println("请输入置顶的歌曲名称和歌手");
Scanner in3 = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = in.next();
for (int i = 0; i < Gequs.size(); i++) {
if (name.equals(Gequs.get(i).getName())) {
Mu temp = Gequs.get(i);
Gequs.remove(i);
Gequs.add(0, temp);
}
}
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("请输入前移的歌曲");
Scanner in4 = new Scanner(System.in);
String name1 = in.next();
for (int i = 0; i <Gequs.size(); i++) {
if (name1.equals(Gequs.get(i).getName())) {
Mu temp = Gequs.get(i - 1);
Gequs.set(i - 1, Gequs.get(i));
Gequs.set(i, temp);
}
}
break;(三)代码托管(https://git.oschina.net/hebau_cs15/shiyanliu.git)






















 16
16











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








