YOLOV7正负样本策略及ComputeLossOTA学习笔记
class ComputeLossOTA:
# Compute losses
def __init__(self, model, autobalance=False):
super(ComputeLossOTA, self).__init__()
device = next(model.parameters()).device # get model device
h = model.hyp # hyperparameters
# Define criteria
BCEcls = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.tensor([h['cls_pw']], device=device))
BCEobj = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.tensor([h['obj_pw']], device=device))
# Class label smoothing https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.04103.pdf eqn 3
self.cp, self.cn = smooth_BCE(eps=h.get('label_smoothing', 0.0)) # positive, negative BCE targets, 1.0, 0.0
# Focal loss
g = h['fl_gamma'] # focal loss gamma, 0.0
if g > 0:
BCEcls, BCEobj = FocalLoss(BCEcls, g), FocalLoss(BCEobj, g)
det = model.module.model[-1] if is_parallel(model) else model.model[-1] # Detect() module
self.balance = {3: [4.0, 1.0, 0.4]}.get(det.nl, [4.0, 1.0, 0.25, 0.06, .02]) # P3-P7, [4.0, 1.0, 0.4]
self.ssi = list(det.stride).index(16) if autobalance else 0 # stride 16 index, 0
self.BCEcls, self.BCEobj, self.gr, self.hyp, self.autobalance = BCEcls, BCEobj, model.gr, h, autobalance
for k in 'na', 'nc', 'nl', 'anchors', 'stride':
setattr(self, k, getattr(det, k))
def __call__(self, p, targets, imgs): # predictions, targets, model
import sys
device = targets.device
lcls, lbox, lobj = torch.zeros(1, device=device), torch.zeros(1, device=device), torch.zeros(1, device=device)
bs, as_, gjs, gis, targets, anchors = self.build_targets(p, targets, imgs) # 返回匹配到的image索引, anchor索引, gj, gi, GT, anchor
# pre_gen_gains=[tensor([80, 80, 80, 80], device='cuda:0'), tensor([40, 40, 40, 40], device='cuda:0'), tensor([20, 20, 20, 20], device='cuda:0')]
pre_gen_gains = [torch.tensor(pp.shape, device=device)[[3, 2, 3, 2]] for pp in p]
# Losses
for i, pi in enumerate(p): # layer index, layer predictions
b, a, gj, gi = bs[i], as_[i], gjs[i], gis[i] # image, anchor, gridy, gridx
tobj = torch.zeros_like(pi[..., 0], device=device) # target obj, tobj.shape=torch.Size([bs, 3, 80, 80]) or torch.Size([bs, 3, 40, 40]) or torch.Size([bs, 3, 20, 20])
n = b.shape[0] # number of targets
if n:
ps = pi[b, a, gj, gi] # prediction subset corresponding to targets, 设匹配到GT的正样本数为p, ps.shape=torch.Size([p, 85])
# Regression
grid = torch.stack([gi, gj], dim=1) # grid.shape=torch.Size([p, 2])
pxy = ps[:, :2].sigmoid() * 2. - 0.5 # pxy.shape=torch.Size([p, 2])
pwh = (ps[:, 2:4].sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * anchors[i] # pwh.shape=torch.Size([p, 2])
pbox = torch.cat((pxy, pwh), 1) # predicted box, pbox.shape=torch.Size([p, 4])
selected_tbox = targets[i][:, 2:6] * pre_gen_gains[i] # selected_tbox.shape=torch.Size([p, 4])
selected_tbox[:, :2] -= grid # 将选中的tbox减去网格坐标,得到偏移量
iou = bbox_iou(pbox.T, selected_tbox, x1y1x2y2=False, CIoU=True) # iou(prediction, target)
lbox += (1.0 - iou).mean() # iou loss
# Objectness
tobj[b, a, gj, gi] = (1.0 - self.gr) + self.gr * iou.detach().clamp(0).type(tobj.dtype) # iou ratio, tobj[b, a, gj, gi]=iou.detach().clamp(0).type(tobj.dtype)
# Classification
selected_tcls = targets[i][:, 1].long()
if self.nc > 1: # cls loss (only if multiple classes)
t = torch.full_like(ps[:, 5:], self.cn, device=device) # targets
t[range(n), selected_tcls] = self.cp # t相当于one-hot编码, 里面的元素仅在所属类别那一列为1, 其余为0
lcls += self.BCEcls(ps[:, 5:], t) # BCE
obji = self.BCEobj(pi[..., 4], tobj)
lobj += obji * self.balance[i] # obj loss, self.balance=[4.0, 1.0, 0.4]
if self.autobalance:
self.balance[i] = self.balance[i] * 0.9999 + 0.0001 / obji.detach().item()
if self.autobalance:
self.balance = [x / self.balance[self.ssi] for x in self.balance]
lbox *= self.hyp['box'] # self.hyp['box']=0.05
lobj *= self.hyp['obj'] # self.hyp['obj']=0.7
lcls *= self.hyp['cls'] # self.hyp['cls']=0.3
bs = tobj.shape[0] # batch size
loss = lbox + lobj + lcls
return loss * bs, torch.cat((lbox, lobj, lcls, loss)).detach()
def build_targets(self, p, targets, imgs):
#indices, anch = self.find_positive(p, targets)
indices, anch = self.find_3_positive(p, targets) # 正样本
#indices, anch = self.find_4_positive(p, targets)
#indices, anch = self.find_5_positive(p, targets)
#indices, anch = self.find_9_positive(p, targets)
device = torch.device(targets.device)
matching_bs = [[] for pp in p]
matching_as = [[] for pp in p]
matching_gjs = [[] for pp in p]
matching_gis = [[] for pp in p]
matching_targets = [[] for pp in p]
matching_anchs = [[] for pp in p]
nl = len(p)
for batch_idx in range(p[0].shape[0]): # 遍历batch size中的每一张图片
b_idx = targets[:, 0]==batch_idx # 找出targets中与batch_idx相等的索引
this_target = targets[b_idx] # 根据索引找出对应的GT
if this_target.shape[0] == 0: # 如果GT数量为0,则处理下一张图片
continue
txywh = this_target[:, 2:6] * imgs[batch_idx].shape[1] # 将GT的坐标由0~1映射到与输入图片大小匹配的数值
txyxy = xywh2xyxy(txywh) # 将坐标由[cx,cy,w,h]转换为[x1,y1,x2,y2](左上角及右下角坐标)
pxyxys = []
p_cls = []
p_obj = []
from_which_layer = []
all_b = []
all_a = []
all_gj = []
all_gi = []
all_anch = []
for i, pi in enumerate(p):
b, a, gj, gi = indices[i] # image, anchor, grid indices, 对gj、gi进行截断,不能超出特征图的范围
idx = (b == batch_idx) # 从b中找出与batch_idx相等的目标
b, a, gj, gi = b[idx], a[idx], gj[idx], gi[idx]
all_b.append(b)
all_a.append(a)
all_gj.append(gj)
all_gi.append(gi)
all_anch.append(anch[i][idx])
from_which_layer.append((torch.ones(size=(len(b),)) * i).to(device))
fg_pred = pi[b, a, gj, gi] # 选出相应的预测值,假设数量为n
p_obj.append(fg_pred[:, 4:5]) # obj预测值
p_cls.append(fg_pred[:, 5:]) # cls预测值
grid = torch.stack([gi, gj], dim=1)
pxy = (fg_pred[:, :2].sigmoid() * 2. - 0.5 + grid) * self.stride[i] # 预测的cx、cy
pwh = (fg_pred[:, 2:4].sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * anch[i][idx] * self.stride[i] # 预测的w、h
pxywh = torch.cat([pxy, pwh], dim=-1) # 预测的cx、cy、w、h
pxyxy = xywh2xyxy(pxywh) # 将cx、cy、w、h转换为x1、y1、x2、y2
pxyxys.append(pxyxy)
pxyxys = torch.cat(pxyxys, dim=0) # pxyxys.shape=torch.Size([n, 4])
if pxyxys.shape[0] == 0:
continue
p_obj = torch.cat(p_obj, dim=0) # p_obj.shape=torch.Size([n, 1])
p_cls = torch.cat(p_cls, dim=0) # p_cls.shape=torch.Size([n, 80])
from_which_layer = torch.cat(from_which_layer, dim=0)
all_b = torch.cat(all_b, dim=0) # torch.Size([n])
all_a = torch.cat(all_a, dim=0) # torch.Size([n])
all_gj = torch.cat(all_gj, dim=0) # torch.Size([n])
all_gi = torch.cat(all_gi, dim=0) # torch.Size([n])
all_anch = torch.cat(all_anch, dim=0) # torch.Size([n, 2])
pair_wise_iou = box_iou(txyxy, pxyxys) # 计算GT与预测边界框之间的iou
pair_wise_iou_loss = -torch.log(pair_wise_iou + 1e-8) # iou loss
top_k, _ = torch.topk(pair_wise_iou, min(10, pair_wise_iou.shape[1]), dim=1) # 从大到小对iou进行排序,取前10个iou
dynamic_ks = torch.clamp(top_k.sum(1).int(), min=1) # 对topk进行求和、取整,将该数值作为一个GT需要匹配到的正样本数,匹配的正样本数不能小于1
gt_cls_per_image = (
F.one_hot(this_target[:, 1].to(torch.int64), self.nc)
.float()
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, pxyxys.shape[0], 1)
) # 将GT类别转换成one-hot编码
num_gt = this_target.shape[0] # GT数量, 假设为t
cls_preds_ = (
p_cls.float().unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_()
* p_obj.unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_()
) # 各类别的预测分数
y = cls_preds_.sqrt_()
pair_wise_cls_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
torch.log(y/(1-y)) , gt_cls_per_image, reduction="none"
).sum(-1) # cls loss
del cls_preds_
cost = (
pair_wise_cls_loss
+ 3.0 * pair_wise_iou_loss
)
matching_matrix = torch.zeros_like(cost, device=device) # torch.Size([t, n])
for gt_idx in range(num_gt):
_, pos_idx = torch.topk(
cost[gt_idx], k=dynamic_ks[gt_idx].item(), largest=False
) # 对每个GT的loss由小到大排序,取排在前dynamic_ks个数值的索引
matching_matrix[gt_idx][pos_idx] = 1.0 # 按照索引,给matching_matrix的相应元素置1
del top_k, dynamic_ks
anchor_matching_gt = matching_matrix.sum(0) # torch.Size([n]), 对所有正样本匹配的GT数进行求和
if (anchor_matching_gt > 1).sum() > 0: # 如果大于0, 则认为一个正样本匹配多个GT
_, cost_argmin = torch.min(cost[:, anchor_matching_gt > 1], dim=0) # 如果同一个正样本匹配到的GT数量大于1,则比较多个GT,取cost小作为正样本,其他的舍去
matching_matrix[:, anchor_matching_gt > 1] *= 0.0 # 首先将大于1的列的元素置0
matching_matrix[cost_argmin, anchor_matching_gt > 1] = 1.0 # 再根据cost_argmin,将对应位置的元素置1
fg_mask_inboxes = (matching_matrix.sum(0) > 0.0).to(device) # 找出与GT成功匹配的正样本
matched_gt_inds = matching_matrix[:, fg_mask_inboxes].argmax(0) # 根据fg_mask_inboxes找出符合条件的列,再求每列的argmax。这步操作目的在于找出与GT匹配的正样本的索引值
from_which_layer = from_which_layer[fg_mask_inboxes]
all_b = all_b[fg_mask_inboxes] # 为匹配到正样本对应的图像索引
all_a = all_a[fg_mask_inboxes] # 为匹配到正样本对应的anchor索引
all_gj = all_gj[fg_mask_inboxes] # 为匹配到正样本对应的gj
all_gi = all_gi[fg_mask_inboxes] # 为匹配到正样本对应的gi
all_anch = all_anch[fg_mask_inboxes] # 为匹配到正样本对应的anchor
this_target = this_target[matched_gt_inds]
for i in range(nl):
layer_idx = from_which_layer == i
matching_bs[i].append(all_b[layer_idx])
matching_as[i].append(all_a[layer_idx])
matching_gjs[i].append(all_gj[layer_idx])
matching_gis[i].append(all_gi[layer_idx])
matching_targets[i].append(this_target[layer_idx])
matching_anchs[i].append(all_anch[layer_idx])
for i in range(nl):
if matching_targets[i] != []:
matching_bs[i] = torch.cat(matching_bs[i], dim=0)
matching_as[i] = torch.cat(matching_as[i], dim=0)
matching_gjs[i] = torch.cat(matching_gjs[i], dim=0)
matching_gis[i] = torch.cat(matching_gis[i], dim=0)
matching_targets[i] = torch.cat(matching_targets[i], dim=0)
matching_anchs[i] = torch.cat(matching_anchs[i], dim=0)
else:
matching_bs[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_as[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_gjs[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_gis[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_targets[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_anchs[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
return matching_bs, matching_as, matching_gjs, matching_gis, matching_targets, matching_anchs
def find_3_positive(self, p, targets):
# p为预测值(p[0].shape=torch.Size([8, 3, 80, 80, 85]), p[1].shape=torch.Size([8, 3, 40, 40, 85]), p[2].shape=torch.Size([8, 3, 20, 20, 85])), targets=(image,class,x,y,w,h)
na, nt = self.na, targets.shape[0] # anchors的数量, GT的数量; na=3, nt=n
indices, anch = [], []
gain = torch.ones(7, device=targets.device).long() # normalized to gridspace gain, gain=tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
ai = torch.arange(na, device=targets.device).float().view(na, 1).repeat(1, nt) # same as .repeat_interleave(nt), ai.shape=torch.Size([3, n])
targets = torch.cat((targets.repeat(na, 1, 1), ai[:, :, None]), 2) # append anchor indices, targets.shape=torch.Size([3, n, 7])
g = 0.5 # bias
off = torch.tensor([[0, 0],
[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1], # j,k,l,m
], device=targets.device).float() * g # offsets, [0,0]为中间网格,[1, 0]、[0, 1]、[-1, 0]、[0, -1]为相邻右、下、左、上的网格
for i in range(self.nl): # self.nl=3
anchors = self.anchors[i]
'''
anchors=tensor([[1.50000, 2.00000],
[2.37500, 4.50000],
[5.00000, 3.50000]], device='cuda:0')
'''
gain[2:6] = torch.tensor(p[i].shape)[[3, 2, 3, 2]] # xyxy gain, gain[2:6]=tensor([80, 80, 80, 80]) or tensor([40, 40, 40, 40]) or tensor([20, 20, 20, 20])
# gain = tensor([1, 1, 80, 80, 80, 80, 1]) or tensor([1, 1, 40, 40, 40, 40, 1]) or tensor([1, 1, 20, 20, 20, 20, 1])
# Match targets to anchors
t = targets * gain # 将targets里的坐标从0~1映射到与特征图大小匹配的坐标
if nt:
# Matches
r = t[:, :, 4:6] / anchors[:, None] # wh ratio
j = torch.max(r, 1. / r).max(2)[0] < self.hyp['anchor_t'] # compare
t = t[j] # filter, 去掉大于self.hyp['anchor_t']的GT, 设余下数量为m
# Offsets
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy, GT中心点坐标(以左上角为参考点)
gxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy # inverse, GT中心点坐标(以右下角为参考点)
j, k = ((gxy % 1. < g) & (gxy > 1.)).T # 对gxy取余,也就是把坐标的小数提出来与0.5做对比,对坐标做近似值处理
l, m = ((gxi % 1. < g) & (gxi > 1.)).T # 原理与上面的一致,l为横坐标,m为纵坐标
j = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m)) # j.shape=torch.Size([5, m])
'''
复制5个t, 选其中的3个, 第一个torch.ones_like(j)必选, 在剩下的4个相邻网格中选2个(j、l互斥, 点只能落在左右两边的其中一边; k、m互斥; 点只能落在上下两边的其中一边),
因此总共选择了3个网格作为正样本的中心点。每个layer分配了3个anchor, 理论上一个GT最多可以匹配9个正样本。YOLOV7的输出有3个layer, 则一个GT最多可以匹配27个正样本。
'''
t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j]
offsets = (torch.zeros_like(gxy)[None] + off[:, None])[j]
else:
t = targets[0]
offsets = 0
# Define
b, c = t[:, :2].long().T # image, class
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy
gwh = t[:, 4:6] # grid wh
gij = (gxy - offsets).long() # 坐标减去偏移量
gi, gj = gij.T # grid xy indices
# Append
a = t[:, 6].long() # anchor indices
indices.append((b, a, gj.clamp_(0, gain[3] - 1), gi.clamp_(0, gain[2] - 1))) # image, anchor, grid indices, 对gj、gi进行截断,不能超出特征图的范围
anch.append(anchors[a]) # anchors
return indices, anch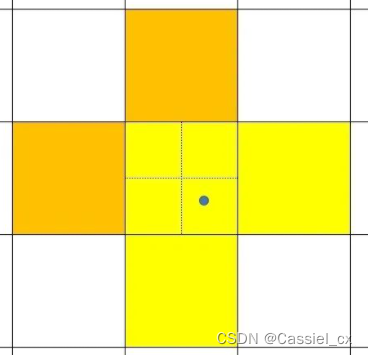
假设图中蓝色的点为GT的中心点,则YOLOV7中的ComputeLossOTA会把3个黄色的框视为正样本(对应着ComputeLossOTA类中的find_3_positive函数),而ComputeLossAuxOTA会把黄色框以及橙色框,总共5个框视为正样本(对应着ComputeLossAuxOTA类中的find_5_positive函数)。
参考:

























 6936
6936











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










