一 简介
CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)不是锁,而属于线程控制工具的范围。CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)与CyclicBarrier(循环栅栏)很相似,作用都是拦截线程并在满足条件后放行,但两者的实现思想与作用场景都有些差异。在实现思想上,CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)采用的是与CyclicBarrier(循环栅栏)相反的减法计数。而在作用场景上,虽然两者都能达到相同的作用效果,但如果说CyclicBarrier(循环栅栏)适合让线程批量的从指定起点“同时”开始,那CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)就更适合让线程批量的从指定终点“同时”结束。最后还要提及的一点是,CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)是一次性的,无法像CyclicBarrier(循环栅栏)那般循环使用,因此每次使用都需要实例化一个新的CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)对象。
二 实现
CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)底层采用AQS共享模式实现。线程在被拦截前会执行递减操作,该操作有两个作用,一是将预定拦截计数减一;二是当计数归零时触发放行,令前期被拦截及后至的线程一并向下执行。而当线程正式拦截时,则会先判断当前计数是否为零,是则直接通过,否则便封装一个共享模式的节点加入AQS的同步队列中并挂起,直至计数归零时被唤醒。
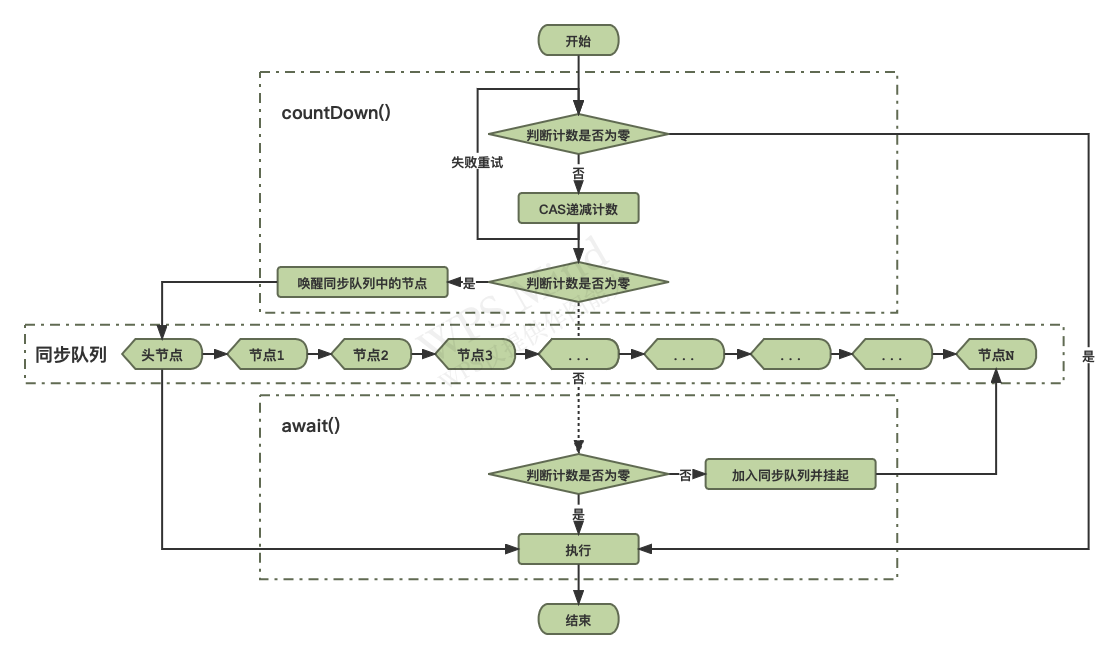
三 同步
CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)实现了一个AQS的子类作为CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)的同步机制。
/**
* Synchronization control For CountDownLatch.
* Uses AQS state to represent count.
*
* @Description: 同步机制类
*/
private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
/**
* @Description: 设置计数
*/
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
/**
* @Description: 获取计数
*/
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
/**
* @Description: 定义上是尝试获取共享许可,但从实现上看是判断当前的计数是否为0。
*/
@Override
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
// 判断可用许可是否为0。
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
/**
* @Description: 定义上是尝试释放共享许可,但从实现上是对计数进行递减。
*/
@Override
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
// 死循环,
for (; ; ) {
// 获取可用许可(快照),如果等于0,则直接返回失败。
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
return false;
}
// 释放一个共享许可,即通过CAS减少一个计数。如果失败,说明有其它线程一同参与了竞争,自旋重试,直至成功为止。
int nextc = c - 1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) {
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
}
四 初始
CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)只有一个构造函数,可在创建实例的同时设置预定计数。预定计数只能通过构造函数指定,且无法后期修改。预定计数的值被保存在AQS的state(状态)字段中。
/**
* Constructs a {@code CountDownLatch} initialized with the given count.
*
* @param count the number of times {@link #countDown} must be invoked
* before threads can pass through {@link #await}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code count} is negative
* @Description: 构造函数:设置总数
*/
public CountDownLatch(int count) {
// 如果总数的值小于0,则直接抛出异常。
if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
// 声明一个同步机制实例。
this.sync = new Sync(count);
}
五 递减
递减方法countDown()是CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)的两大核心方法之一。其有两个功能,一是递减计数;而是当计数为零时,唤醒同步队列中的节点使之继续执行,以达到放行的目的。
/**
* Decrements the count of the latch, releasing all waiting threads if
* the count reaches zero.
*
* <p>If the current count is greater than zero then it is decremented.
* If the new count is zero then all waiting threads are re-enabled for
* thread scheduling purposes.
*
* <p>If the current count equals zero then nothing happens.
*
* @Description: 递减计数
*/
public void countDown() {
// 该操作的本质是对计数进行递减,当计数为0时会触发对同步队列中节点的唤醒,以达到对拦截的线程放行的目的。
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
/**
* Releases in shared mode. Implemented by unblocking one or more
* threads if {@link #tryReleaseShared} returns true.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryReleaseShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryReleaseShared}
* <p>
* @Description: 释放共享许可
*/
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
// 尝试释放共享许可。
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// 唤醒同步队列中共享模式的节点。
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* @Description: 定义上是尝试释放共享许可,但从实现上是对计数进行递减。
*/
@Override
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
// 死循环,
for (; ; ) {
// 获取可用许可(快照),如果等于0,则直接返回失败。
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
return false;
}
// 释放一个共享许可,即通过CAS减少一个计数。如果失败,说明有其它线程一同参与了竞争,自旋重试,直至成功为止。
int nextc = c - 1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) {
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
六 等待
等待方法awiat()是CountDownLatch(闭锁/计数器)的两大核心方法之一。其作用是在计数不为零的情况下将线程加入AQS的同步队列挂起,以达到拦截的目的。当计数为零时这些节点会因为共享许可的传播性被一并唤醒从而继续执行。除了awiat()方法外还存在一个可限时等待的方法await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit),其运行逻辑与await()相同,但是多了时间限制,当线程因为等待时间超时而被唤醒时,会最后一次尝试获取许可,虽然无论是否成功都会令线程退出等待继续执行,但通过其返回的布尔值,可以知道其是因为获取了许可而退出还是因为获取许可失败而退出。
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until the latch has counted down to
* zero, unless the thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}.
*
* <p>If the current count is zero then this method returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the current count is greater than zero then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies
* dormant until one of two things happen:
* <ul>
* <li>The count reaches zero due to invocations of the
* {@link #countDown} method; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread.
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the current thread:
* <ul>
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting,
* </ul>
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* while waiting
* @Description: 等待(会抛出中断异常)
*/
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 该方法的作用是令线程挂起,即在计数不为0的情况下将线程等待。其会先尝试获取共享许可,但本质是判断计数的数量是否为0,
// 是则返回1,否则返回-1。返回1意味着计数已经归零,无需对线程进行拦截,因此不做任何操作直接放任线程执行。但是如果返回了-1,
// 这就说明当前计数还没有归零,这表示到达计数器的线程数量还不足计数,因此计数器需要将该线程拦截,具体的做法是将线程纳入
// 同步队列中挂起,直至计数归零时被唤醒。
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
/**
* Acquires in shared mode, aborting if interrupted. Implemented
* by first checking interrupt status, then invoking at least once
* {@link #tryAcquireShared}, returning on success. Otherwise the
* thread is queued, possibly repeatedly blocking and unblocking,
* invoking {@link #tryAcquireShared} until success or the thread
* is interrupted.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument.
* This value is conveyed to {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is
* otherwise uninterpreted and can represent anything
* you like.
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* @Description: 获取共享许可
*/
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
// 如果线程被中断,则直接抛出中断异常。
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 尝试获取共享许可,如果获取失败了,则将线程封装为节点置入同步队列中(可中断)
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) {
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
}
/**
* Acquires in shared interruptible mode.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @Description: 获取共享许可
*/
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
// 向同步队列中新增一个共享模式的线程节点。
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
// 如果前驱节点为头节点,则尝试获取许可。
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
// 如果可用许可大于0,唤醒后继节点,该方法是共享许可传播性的直接实现。
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) {
// 如果显示方法被中断过,则直接抛出中断异常,因此可知lockInterruptibly允许被中断的。
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
} finally {
if (failed) {
// 取消节点,把失败的节点进行取消,并唤醒后继节点进行清理及许可的获取。
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
}
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until the latch has counted down to
* zero, unless the thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted},
* or the specified waiting time elapses.
*
* <p>If the current count is zero then this method returns immediately
* with the value {@code true}.
*
* <p>If the current count is greater than zero then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies
* dormant until one of three things happen:
* <ul>
* <li>The count reaches zero due to invocations of the
* {@link #countDown} method; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread; or
* <li>The specified waiting time elapses.
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the count reaches zero then the method returns with the
* value {@code true}.
*
* <p>If the current thread:
* <ul>
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting,
* </ul>
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>If the specified waiting time elapses then the value {@code false}
* is returned. If the time is less than or equal to zero, the method
* will not wait at all.
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the {@code timeout} argument
* @return {@code true} if the count reached zero and {@code false}
* if the waiting time elapsed before the count reached zero
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* while waiting
* @Description: 限时等待(会抛出中断异常)
*/
public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
// 该方法逻辑与无参await()类似,但节点在同步队列中的挂起的时间不是无限的。一旦达到了指定时间就会自我唤醒,并最后一次尝试获取
// 共享许可,如果最后一次都失败了就会直接返回false,意味着其并没有成功的获取许可,但线程依然可以正常的继续执行。
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/**
* Attempts to acquire in shared mode, aborting if interrupted, and
* failing if the given timeout elapses. Implemented by first
* checking interrupt status, then invoking at least once {@link
* #tryAcquireShared}, returning on success. Otherwise, the
* thread is queued, possibly repeatedly blocking and unblocking,
* invoking {@link #tryAcquireShared} until success or the thread
* is interrupted or the timeout elapses.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
* @param nanosTimeout the maximum number of nanoseconds to wait
* @return {@code true} if acquired; {@code false} if timed out
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* @Description: 限时获取共享许可。
*/
public final boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 尝试获取共享许可,成功直接返回,失败则加入同步队列,在一定的时间范围内继续尝试获取。
return tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0 || doAcquireSharedNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
/**
* Acquires in shared timed mode.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @param nanosTimeout max wait time
* @return {@code true} if acquired
* @Description: 限时获取共享许可。
*/
private boolean doAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
// 如果时间范围不合法,则直接返回失败。
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L) {
return false;
}
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
// 向同步队列中新增一个共享模式的线程节点。
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
// 如果前驱节点为头节点,则尝试获取许可。
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
// 如果可用许可大于0,唤醒后继节点,该方法是共享许可传播性的直接实现。
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
// 如果时间范围不足,则直接返回失败,该节点将被取消。
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L) {
return false;
}
// 如果成功把前驱节点设置为信号状态,并且剩余时间大于1毫秒,则进行限时挂起。
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold) {
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
}
// 线程被唤醒后,判断线程是否中断,中断则直接抛出中断异常。
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
} finally {
// 取消节点,将因为中断/超时等原因获取许可失败的节点进行取消,并唤醒后继节点进行清理及许可的获取。
if (failed) {
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
}























 572
572











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










