附带详细的理论+代码详解视频,见某站lvqaq的数学建模
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import copy
import random
def drawGantt(timeList):
T = timeList.copy()
# 创建一个新的图形
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
# 颜色映射字典,为每个工件分配一个唯一的颜色
color_map = {}
for schedule in T[0]:
color_map[schedule[1]] = (random.random(), random.random(), random.random())
# 遍历机器
for machine_idx, machine_schedule in enumerate(T):
for task_data in machine_schedule:
start_time, job_idx, operation_idx, end_time = task_data
color = color_map[job_idx] # 获取工件的颜色
# 绘制甘特图条形,使用工件的颜色
ax.barh(machine_idx, end_time - start_time, left=start_time, height=0.4, color=color)
# 在色块内部标注工件-工序
label = f'{job_idx}-{operation_idx}'
ax.text((start_time + end_time) / 2, machine_idx, label, ha='center', va='center', color='white',
fontsize=10)
# 设置Y轴标签为机器名称
ax.set_yticks(range(len(T)))
ax.set_yticklabels([f'Machine {i}' for i in range(len(T))])
# 设置X轴标签
plt.xlabel("时间")
# 添加标题
plt.title("FSP问题甘特图")
# 创建图例,显示工件颜色
legend_handles = []
for job_idx, color in color_map.items():
legend_handles.append(plt.Rectangle((0, 0), 1, 1, color=color, label=f'Job {job_idx}'))
plt.legend(handles=legend_handles, title='工件')
def decode(Ind, pTime, nAll=None):
"""
function:
解码函数,用于计算C_max和生成甘特图。
parameter:
- Ind: 工件序列。
- pTime: 加工时间矩阵,大小为n*m。
- nAll: 总工件数,如果未提供,则使用Ind的长度。
return:
- T: 用于绘制甘特图的矩阵,格式为[起始时间, 工件号, 工序号, 完工时间]。
- C: 工件在每台机器上的完工时间矩阵。
"""
if len(Ind) <= 1:
raise ValueError(f"列表的长度应大于等于2,但实际长度为 {len(Ind)}")
nAll = nAll or len(Ind)
n, m = len(Ind), pTime.shape[1] # 初始化工件数和机器数
T, C = [], np.zeros((nAll, m)) # 初始化甘特图矩阵T和完工时间C
# 初始化甘特图并处理第一个工件
for machine in range(m):
T.append([]) # 初始化每个机器的调度方案
first_job_id = Ind[0] # 记录第一个工件id
last_time = C[first_job_id, machine - 1] if machine > 0 else 0 # 记录上一个机器的完工时间。如果是第一个机器,即0
C[first_job_id, machine] = last_time + pTime[first_job_id, machine] # 记录第一个工件的完工时间
T[machine].append([last_time, first_job_id, machine, C[first_job_id, machine]]) # 记录第一个工件对应各机器的甘特图矩阵
# 处理剩余的工件
for job_index in range(1, n): # 循环剩下的工件
current_job_id = Ind[job_index] # 记录当前工件号
for machine in range(m): # 循环机器
last_time_by_machine = C[Ind[job_index - 1], machine] if job_index > 0 else 0 # 记录同一个机器上一个工件的完工时间
last_time_by_job = C[current_job_id, machine - 1] if machine > 0 else 0 # 记录同一个工序上一个工序(机器)的完工时间
last_time = max(last_time_by_machine, last_time_by_job) # 求max,计算最大值
C[current_job_id, machine] = last_time + pTime[current_job_id, machine] # 记录当前工件的完工时间
T[machine].append([last_time, current_job_id, machine, C[current_job_id, machine]]) # 记录甘特图矩阵
return T, C
def createInd(n):
ind = list(range(n))
np.random.shuffle(ind)
return ind
def createNEHInd(n, pTime):
'''
利用NEH生成解:
1. 计算所有工件的总加工时间TP,按照TP递减顺序排列工件,得到初始排列\pi
2. 取前两个排序交换后的两个调度,评价后选择Cmax较小的
3. 取第k个,插入之前可能的所有位置,评价后选择Cmax较小的
'''
TP = pTime.sum(axis=1) # 总加工时间
pi = TP.argsort()[::-1].tolist() # 降序后的初始排列
# Cmax = pTime.sum() # 初始化Cmax
for i in range(1, n):
pi_ = pi[:i].copy() # 待插入的序列
k = pi[i] # 待插入的元素
l = 0
Cmaxpi = [] # 记录每次插入的Cmax
while l <= len(pi_): # 循环插入每个位置
newPi = [k] + pi_[l:] if l == 0 else pi_[:l] + [k] + pi_[l:]
Cmaxpi.append(decode(newPi, pTime, n)[1].max())
l += 1
minId = Cmaxpi.index(min(Cmaxpi)) # Cmax最小的下标就是该插入的位置
pi[:i+1] = pi_[:minId] + [k] +pi_[minId:]
return pi
def createPop(n, popSize, neh=False, pTime=[], split=0.5):
'''
创建种群,如果指定使用neh,需要提供加工时间(必须)
'''
ind = list(range(n))
pop = [ind.copy() for _ in range(popSize)]
for row in pop:
np.random.seed(None)
np.random.shuffle(row)
if neh:
nehId = createNEHInd(n, pTime)
for i in range(int(popSize*split)):
pop[i] = nehId
return pop
def cross(A, B):
'''
function: cross
content: cross two individual and return their result.
'''
n = len(A)
r1 = np.random.randint(n)
r2 = np.random.randint(n)
rl, rr = min(r1, r2), max(r1, r2)
if rl == rr:
return A, B
# for A
bt = copy.deepcopy(B)
afinal = copy.deepcopy(A)
for i in range(rl, rr+1):
bt.remove(A[i])
k = 0
for i in range(n):
if i < rl or i > rr:
afinal[i] = bt[k]
k += 1
# for B
at = copy.deepcopy(A)
bfinal = copy.deepcopy(B)
for i in range(rl, rr+1):
at.remove(B[i])
k = 0
for i in range(n):
if i < rl or i > rr:
bfinal[i] = at[k]
k += 1
return afinal, bfinal
def mutation(Ind):
'''
function: mutation
content: mutationg a individual with INV approach, then return the mutated individual.
revers a random sequence of gens in an individual
'''
A = Ind.copy()
n = len(A) # 工件数
index1, index2 = random.sample(range(n), 2) # 随即两个数
rl, rr = max(index1, index2)+1, min(index1, index2) # 为了避免[x:x]的索引为空,max需要+1
A[rr: rl] = A[rr: rl][::-1]
return A
def revers(Ind):
'''
function: revers
content: revers a individual and return the answer
'''
return Ind.copy()[::-1]
def load_data(path):
"""
function: load_data
content: load data from path, and return the process matrix
"""
with open(path, 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
# 解析工件数和机器数
workpiece, machines = map(int, lines[0].split())
# 初始化 J 和 P 数组
P = np.zeros((workpiece, len(lines[1].split()) // 2), dtype=int)
# 解析加工时间
for i in range(1, len(lines)):
data = list(map(int, lines[i].split()))
for j in range(0, len(data), 2):
P[i - 1][j // 2] = data[j+1]
return P
if __name__ == '__main__':
# process_time = np.array([[2, 1, 1], [3, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]) # 一个demo
process_time = load_data('car01.txt') # 读取数据
jobNumber = process_time.shape[0]
mechineNumber = process_time.shape[1]
popSize = 40 # 种群大小
# pop = createPop(jobNumber, popSize, neh=True, pTime=process_time, split=0.1)
pop = createPop(jobNumber, popSize)
# gen = jobNumber*mechineNumber # 迭代次数
gen = min(max(100, jobNumber * mechineNumber), 120)
# 初始化
Tmax, C = decode(pop[0], process_time)
Cmax = C.max()
fitness = [Cmax]
bestInd = pop[0].copy()
for i in range(1, popSize):
T_, C_ = decode(pop[i], process_time)
C_max = C_.max()
fitness.append(C_max)
if C_max < Cmax:
Tmax = T_
Cmax = C_max
bestInd = pop[i].copy()
# 迭代
chistory = []
g = 0
while g < gen:
g += 1
# 交叉
l = 0
newInd = []
newFitness = []
while l < popSize / 2:
tm = np.random.randint(popSize) # 随机一个与最优个体交叉
I1, I2 = cross(pop[tm], bestInd)
T1, C1 = decode(I1, process_time) # 对交叉后的解码
newInd.append(I1) # 交叉后的个体添加入newInd
newFitness.append(C1.max()) # 交叉后的适应度添加入newFitness
if C1.max() < Cmax: # 如果适应度比已知最优个体还好
Cmax = C1.max() # 更新最佳适应度
Tmax = T1 # 更新最优调度
bestInd = copy.deepcopy(I1) # 更新最优个体
T2, C2 = decode(I2, process_time)
newInd.append(I2)
newFitness.append(C2.max())
if C2.max() < Cmax:
Cmax = C2.max()
Tmax = T2
bestInd = copy.deepcopy(I2)
l += 1
newpop = pop + newInd # 交叉后的种群与原来种群合并
newFit = fitness + newFitness # 适应度也合并
newId = np.array(newFit).argsort()[:popSize] # 取最好的40个的ID
pop = copy.deepcopy([newpop[i] for i in newId])
fitness = [newFit[i] for i in newId]
# 逆序操作
for j in range(popSize):
newInd = revers(pop[j])
newT, newC = decode(newInd, process_time)
newCmax = newC.max()
if newCmax < fitness[j]:
fitness[j] = newCmax
pop[j] = newInd
if newCmax < Cmax:
Cmax = newCmax
Tmax = newT
bestInd = copy.deepcopy(newInd)
# 变异
for j in range(popSize):
Ind = copy.deepcopy(mutation(pop[j]))
Tt, Ct = decode(Ind, process_time)
fitness[i] = Ct.max()
if Ct.max() < Cmax:
Cmax = Ct.max()
Tmax = Tt
bestInd = Ind
print('第{}代,Cmax={}'.format(g, Cmax))
wait_time = 0
print('第{}代,平均机器等待时间={}'.format(g, (Cmax * mechineNumber - process_time.sum()) / mechineNumber))
chistory.append(Cmax)
index = chistory.index(Cmax)
print(f"{Cmax}首次出现的索引是:{index}")
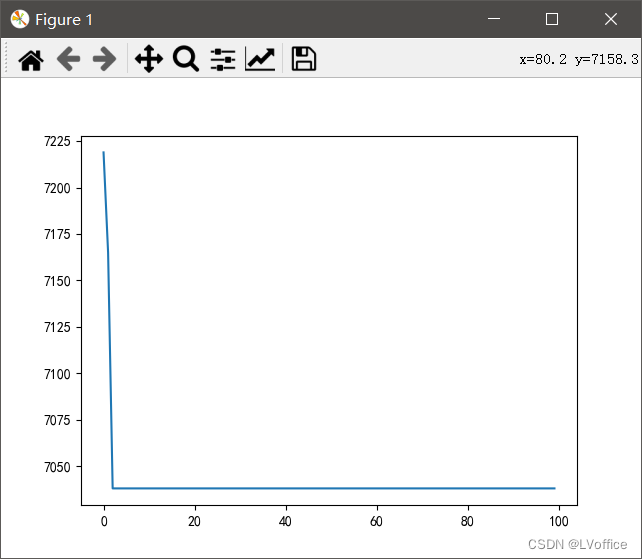
plt.plot(chistory)
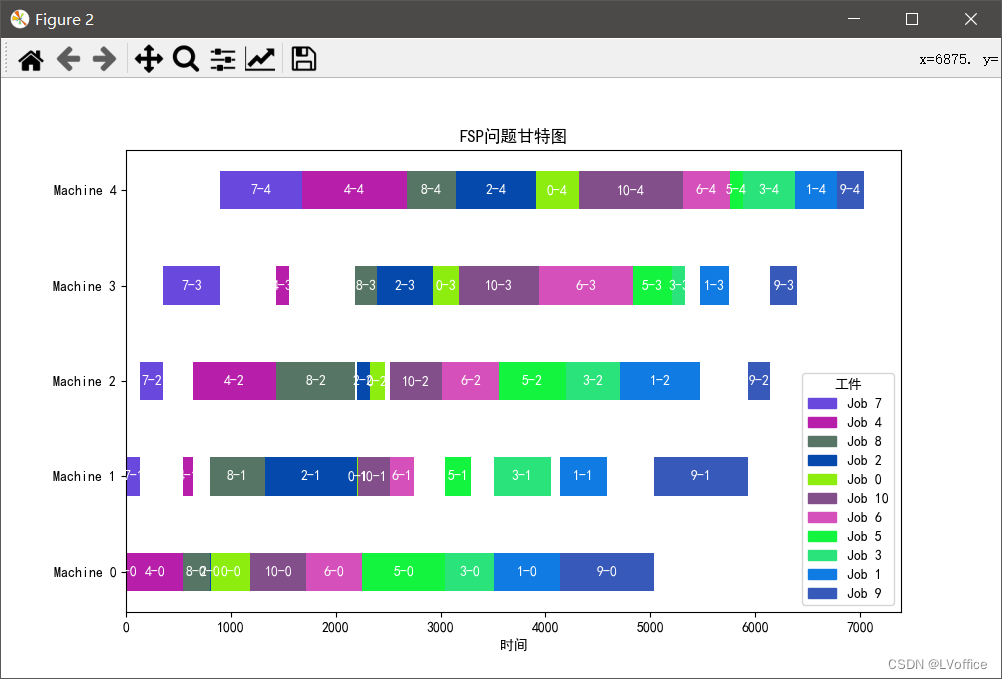
drawGantt(Tmax)
print(Tmax)
plt.show()
遗传算法收敛曲线:
car01数据集甘特图






















 1670
1670

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








