1. 两数之和 – 剑指offer57-I
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素不能使用两遍。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
-
方法一:两个for循环
class Solution { public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { if(nums==null || nums.length<=1){ return new int[0]; } for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){ for(int j=i+1;j<nums.length;j++){ if(nums[i]+nums[j]==target){ return new int[]{i,j}; } } } return new int[0]; } } -
方法二:hash法
class Solution_2 { public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { int[] indexs = new int[2]; // 建立k-v ,一一对应的哈希表 HashMap<Integer,Integer> hash = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){ if(hash.containsKey(nums[i])){ indexs[0] = i; //当前元素的下标 //差值,即:和当前元素值相等的(target-nums[i])的下标value值 indexs[1] = hash.get(nums[i]); return indexs; } // 将数据存入 key为补数 ,value为下标 // 每一次将 key值作为:target-nums[i] 差, value 作为 下标值 // 上面的 if 语句 就是往下判断是否 hash里面是否有 该差值(target-nums[i]) hash.put(target-nums[i],i); } return indexs; } }
20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
注意:空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
示例 1:
输入: "()"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: "()[]{}"
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: "(]"
输出: false
示例 4:
输入: "([)]"
输出: false
示例 5:
输入: "{[]}"
输出: true
-
代码实现一:
class Solution { public boolean isValid(String s) { LinkedList<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>(); for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { if (c == '[') stack.push(']'); else if (c == '(') stack.push(')'); else if (c == '{') stack.push('}'); //主要在这里,如果 s串是: ]],栈里面是空,返回false // 0 1 2 3 // [ ] [ ] 0位置入栈的是 ] , 到1位置 [,来到这里c != stack.pop() // stack.pop()会将 [ 出栈,和 1位置的 [] 比较,相等,继续for循环。 else if (stack.isEmpty() || c != stack.pop()) return false; } return stack.isEmpty(); } } -
代码实现二:
class Solution { private static final Map<Character,Character> map = new HashMap<Character,Character>(){ { put('{','}'); put('[',']'); put('(',')'); put('?','?'); } }; public boolean isValid(String s) { if(s.length() > 0 && !map.containsKey(s.charAt(0))) return false; LinkedList<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>() {{ add('?'); }}; for(Character c : s.toCharArray()){ //如果 map中的key:{,[,( 包含c,就进栈 if(map.containsKey(c)) stack.addLast(c); //如果 不包含,那c 就是 ),},] //如果是这三种情况的话,如1: // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 // { [ ] } ) [ ] // 刚开始 0 , 1 位置的入栈,到3位置时, 让刚刚入栈的1位置 [ 出栈,去map // 中到对应的value和当前的 3位置的比较,如果是相等就继续for循环。end // 如2:(相等的情况) // 即,来到位置4的地方,栈中的元素只剩一个 ?, ? 与位置4的 ) 不匹配。end else if(map.get(stack.removeLast()) != c) return false; } return stack.size() == 1; } }
21. 合并两个有序链表 --剑指offer25
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
-
代码实现一:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { if(l1==null && l2==null){ return null; } if(l1==null){ return l2; } if(l2==null){ return l1; } ListNode mergeList = new ListNode(-1); ListNode movePoint = mergeList; while(l1!=null && l2!=null){ if(l1.val<l2.val){ movePoint.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; }else{ movePoint.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } movePoint = movePoint.next; } movePoint.next = l1==null ? l2 : l1; return mergeList.next; } } -
代码实现二:(递归)
class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { if (l1 == null) { return l2; } else if (l2 == null) { return l1; } else if (l1.val < l2.val) { //牛批! 递归 //l1.next = (下次 l1.next串,与 l2串比较的结果) l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2); return l1; } else { //l2.next = (下次 l1与 l2.next串比较的结果) l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next); return l2; } } }
53. 最大子序和 --剑指offer42
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
示例:
输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
输出: 6
解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
进阶:
如果你已经实现复杂度为 O(n) 的解法,尝试使用更为精妙的分治法求解。
代码实现:
/**
动态规划: 可是话又说过来了, 动态规划为啥可行?
*/
/**
这题动态规划要确定两个问题:
1. 负数会产生负相关
2. dp方程的dp[i]的意义是:当前数组最大的子序列和
*/
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==1){
return nums[0];
}
//这个maxSum就是dp[i]
int maxSum = nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
//这里才是关键,如果要是 <0的那么一定是越加越小,所以直接去第一个元素就行了。
if(nums[i-1]>0){
nums[i] = nums[i-1]+nums[i];
}
//注意这里也是关键 maxSum是和nums[i]比较的
maxSum = (maxSum>nums[i])?maxSum:nums[i];
}
return maxSum;
}
}
70. 爬楼梯 --剑指offer 12
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
**注意:**给定 n 是一个正整数。
示例 1:
输入: 2
输出: 2
解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 2 阶
示例 2:
输入: 3
输出: 3
解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
方法一:递归
/**
其实是可行的。
*/
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==1){
return 1;
}
if(n==2){
return 2;
}
return climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);
}
}
方法二:空间换时间,用循环,倒着找n
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==1){
return 1;
}
if(n==2){
return 2;
}
int[] methodCount = new int[n+1];
methodCount[0] = 0;
methodCount[1] = 1;
methodCount[2] = 2;
for(int i = 3;i<=n;i++){
methodCount[i] = methodCount[i-1]+methodCount[i-2];
}
return methodCount[n];
}
}
//这种舒服
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int a=0,b=1,sum;
for(int i = 0;i<=n;i++){
sum = a + b;
a = b;
b = sum;
}
return a;
}
}
101. 对称二叉树 --剑指offer 28
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
进阶:
你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
代码实现一:
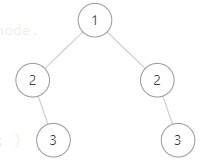
//这种思路应该是比较能想到的,但是不好使
class Solution {
ArrayList<TreeNode> listLeft = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> listRight = new ArrayList<>();
public void preLeftOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
//这里是对于 空结点处理,要不然对于上面图中的做不了处理
// 会导致两个 list 链表中存放的序列是一样的,但是却不是对称的。
listLeft.add(new TreeNode(-1));
return ;
}
listLeft.add(root);
preLeftOrder(root.left);
preLeftOrder(root.right);
}
public void preRightOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
//这里是对于 空结点处理,要不然对于上面图中的做不了处理
// 会导致两个 list 链表中存放的序列是一样的,但是却不是对称的。
listRight.add(new TreeNode(-1));
return ;
}
listRight.add(root);
preRightOrder(root.right);
preRightOrder(root.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
preLeftOrder(root);
preRightOrder(root);
for(int i=0;i<listLeft.size();i++){
if(listLeft.get(i).val!=listRight.get(i).val){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
代码实现二:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
/**
分析:对称的二叉树
画图可以分析出来,正常前序遍历该二叉树, 如果二叉树对称,那么可以利用“对称方式前序遍历二叉树”
的方式:
前序遍历是:根左右;
对称方式前序遍历是:根右左;
如(1):
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
前序遍历:1234234
对称方式:1234234 所以对称
如(2):
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
前序遍历: 1,2,null,3, 2, null, 3
对称方式: 1,2,3 null,2, 3 , null
所以不对称。
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
return doublePreOrder(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean doublePreOrder(TreeNode rootL ,TreeNode rootR){
//左右同时为空,也是对称的!
if(rootL==null && rootR==null){
return true;
}
//rootL==null || rootR==null可以当做一组
// 二者同时不为空,就看看二者值相不相等。相等跳过if,不相等,返回false;
// 二者一个为空/一个不为空,直接返回false
if(rootL==null || rootR==null || rootL.val!=rootR.val){
return false;
}
//rootL前序遍历,rootR对称方式的前序遍历
//★这里需要注意的填入的参数结点是怎么填入的。
return doublePreOrder(rootL.left,rootR.right) &&
doublePreOrder(rootL.right,rootR.left);
}
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历–剑指offer32-II
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例:
二叉树:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
代码实现:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return new ArrayList<>();
}
//1、先构建了一个双层列表,用于存储结果
LinkedList<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<>();
//2、再创建一个队列,用于存储每一层的节点,然后再pop
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null){
queue.add(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//4、创建一个单层列表,用来存储每一层的结果
List<Integer> middle = new LinkedList<>();
int num = queue.size();
//5、开始遍历队列输出
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
middle.add(node.val);
//6、判断节点的左右子节点
if(node.left!=null){
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null){
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
result.add(middle);
}
return result;
}
}
输入
[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出
[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
预期结果
[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
104. 二叉树的最大深度 --剑指offer55-I
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
代码实现:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
/**
1.递归实现
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth1(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
/**
2.BFS实现
*/
/**
* BFS迭代实现二叉树最大深度
* 时间复杂度O(n)
* 空间复杂度:线性表最差O(n)、二叉树完全平衡最好O(logn)
* @param root 根节点
* @return 最大深度
*/
private static int maxDepth2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
//BFS的层次遍历思想,记录二叉树的层数,
//遍历完,层数即为最大深度
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int maxDepth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
maxDepth++;
for (int i = 0; i < queue.size(); i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
/**
3.DFS实现
*/
private static int maxDepth4(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
/**
* Pair<key,value>
* key : 记录结点
* value : 记录深度
*/
LinkedList<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(new Pair<>(root, 1));
int maxDepth = 0;
//DFS实现前序遍历,每个节点记录其所在深度
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Pair<TreeNode, Integer> pair = stack.pop();
TreeNode node = pair.getKey();
//DFS过程不断比较更新最大深度
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, pair.getValue());
//记录当前节点所在深度
int curDepth = pair.getValue();
//当前节点的子节点入栈,同时深度+1
/*
* ★很巧妙,是DFS!
* 这里是先将right结点入到list里面
*/
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(new Pair<>(node.right, curDepth + 1));
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(new Pair<>(node.left, curDepth + 1));
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机–剑指offer63
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
如果你最多只允许完成一笔交易(即买入和卖出一支股票一次),设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
注意:你不能在买入股票前卖出股票。
示例 1:
输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出: 5
解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
示例 2:
输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
输出: 0
解释: 在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
动态规划:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length<=1){
return 0;
}
int max = 0;
for(int i=1;i<prices.length;i++){
max = (prices[i]-prices[i-1] > max) ? prices[i]-prices[i-1] : max;
if(prices[i]>prices[i-1]){
prices[i] = prices[i-1]; //这里就很灵性
}
}
return max;
}
}
136. 只出现一次的数字
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,1]
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,1,2,1,2]
输出: 4
代码实现一:(求异或即可)
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null){
return -1;
}
int oneResult = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
oneResult = oneResult^nums[i];
}
return oneResult;
}
}
代码实现二:(哈希表)
key值为 nums数组中出现的没有数组, value为出现的次数
141. 环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
示例 1:
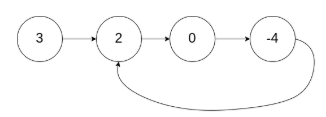
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
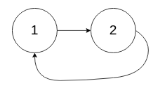
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
代码实现:(双指针,一个慢指针,一个快指针,当快的指针赶上慢的指针就说明有环)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return false;
}
ListNode slowPoint = head;
ListNode quickPoint = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while(quickPoint!=null){
if(slowPoint==quickPoint){
flag=true;break;
}
//这里可能走得快的指针先走到头了,即,没有环
if(quickPoint.next==null){
flag=false;break;
}
quickPoint = quickPoint.next.next;
slowPoint = slowPoint.next;
}
return flag;
}
}
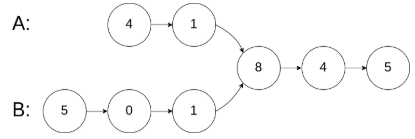
160. 相交链表 --剑指offer52
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
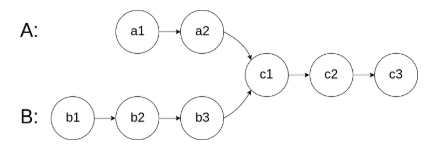
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
示例 2:
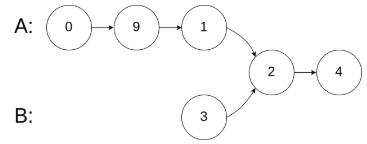
示例 3:
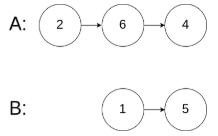
代码实现:
//大佬代码!
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode ha = headA, hb = headB;
while (ha != hb) {
ha = ha != null ? ha.next : headB;
hb = hb != null ? hb.next : headA;
}
return ha;
}
}
//★★★下面的while条件是出不来的。
//因为 helpA=helpA.next)==null,如果是空,就会立马helpA = headB;
//导致A,B如果没有交点,两个链表一直在连接,一直出不来。
//所以if要先判断是否为null, 如果为空了,在拼接
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
while(helpA!=helpB){
if((helpA=helpA.next)==null){
helpA = headB;
}
if((helpB=helpB.next)==null){
helpB = headA;
}
}
return helpA;
}
}
//两个if要这样写才ok, 因为 helpA=null和 helpA=helpA.next; 每一次循环只能执行一个;
//而上面的 if是 如果null了,是 helpA=helpA.next执行了, helpA = headB也执行了;
if(helpA==null){
helpA = headB;
}else{
helpA=helpA.next;
}
if(helpB==null){
helpB = headA;
}else{
helpB=helpB.next;
}
169. 多数元素
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3]
输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
输出: 2
代码实现一:哈希方式
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0){
return -1;
}
HashMap<Integer,Integer> hash = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int i = 0 ;i<nums.length ;i++){
if(hash.containsKey(nums[i])){
hash.put(nums[i],hash.get(nums[i])+1);
}else{
hash.put(nums[i],1);
}
}
int maxCount = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int result = 0;
for (Integer key : hash.keySet()) {
if(hash.get(key)>maxCount){
maxCount = hash.get(key);
result = key;
}
}
return result;
}
}
代码实现二:排序,取中位数即可
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0){
return -1;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length/2];
}
198. 打家劫舍
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 不触动警报装置的情况下 ,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入:[1,2,3,1]
输出:4
解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 1) ,然后偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 3)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 1 + 3 = 4 。
示例 2:
输入:[2,7,9,3,1]
输出:12
解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 2), 偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 9),接着偷窃 5 号房屋 (金额 = 1)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 。
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 400
代码实现: 动态规划
//自己能写出来来时牛逼了! 其实方程还不算写出来,只是说推出来了。
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null || nums.length==0){
return 0;
}
if(nums.length==1){
return nums[0];
}
if(nums.length==2){
return nums[0] > nums[1] ? nums[0] : nums[1];
}
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = nums[0]> nums[1]? nums[0]:nums[1];
dp[2] = dp[0]+nums[2] > dp[1] ? dp[0]+nums[2] : dp[1];
for(int i=3;i<nums.length;i++){
//这里是计算出了每一个dp[i]的值
int temp = (dp[i-2]+nums[i]) > (dp[i-3]+nums[i]) ?
(dp[i-2]+nums[i]) : (dp[i-3]+nums[i]);
dp[i] = temp>dp[i-1] ? temp : dp[i-1];
}
return dp[dp.length-1];
}
}
分析:
如果房屋数量大于两间,应该如何计算能够偷窃到的最高总金额呢?对于第 k (k>2) 间房屋,有两个选项:
- 偷窃第 k 间房屋,那么就不能偷窃第k−1 间房屋,偷窃总金额为前 k−2 间房屋的最高总金额与第 k间房屋的金额之和。
- 不偷窃第 k 间房屋,偷窃总金额为前 k−1 间房屋的最高总金额。
在两个选项中选择偷窃总金额较大的选项,该选项对应的偷窃总金额即为前 k 间房屋能偷窃到的最高总金额:
用 dp[i] 表示前 i 间房屋能偷窃到的最高总金额,那么就有如下的状态转移方程:
dp[i]=max(dp[i−2]+nums[i],dp[i−1])

class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null || nums.length==0){
return 0;
}
if(nums.length==1){
return nums[0];
}
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = nums[0]> nums[1]? nums[0]:nums[1];
for(int i=2;i<nums.length;i++){
dp[i] = (dp[i-2]+nums[i]) > dp[i-1] ? (dp[i-2]+nums[i]) : dp[i-1];
}
return dp[dp.length-1];
}
}
//上面的也可以将dp数组的个数变为两个,使用滑动窗口的方式解决
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null || nums.length==0){
return 0;
}
if(nums.length==1){
return nums[0];
}
int first = nums[0];
int second = nums[0]> nums[1]? nums[0]:nums[1];
for(int i=2;i<nums.length;i++){
int temp = second;
second = (first+nums[i]) > second ? (first+nums[i]) : second;
first = temp;
}
return second;
}
}
206. 反转链表 --剑指offer24
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
**代码实现:**头插法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//尾插法建立链表即可
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode resultList = new ListNode(-1);
while(head!=null){
//头插法 3步曲
//1.建立新节点
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(head.val);
//2. 其实可以说这个头结点(resultList),是一个移动指针。
// 让 newNode的next 指向 resultList的next域,就于与链表连接起来了
newNode.next = resultList.next;
//3. 这里让头结点的 next指向新的结点
resultList.next = newNode;
// 这个就是移动原始链表了, 和头插法没有关系了。
head = head.next;
}
return resultList.next;
}
}
代码实现二:(递归法)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode node = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return node;
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:
输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
代码实现:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return null;
}
TreeNode temp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = temp;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}
234. 回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
进阶:你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
代码实现一: 将值复制到数组中后用双指针法
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(head==null){
return true;
}
//这里将其复制到数组中去判断
while(head!=null){
list.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int i=0,j=list.size()-1;
while(i<j){
if(!list.get(i).equals(list.get(j))){
return false;
}
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
}
代码实现二:递归
/**
currentNode 指针是先到尾节点,由于递归的特性再从后往前进行比较。
frontPointer 是递归函数外的指针。
若currentNode.val!=frontPointer.val 则返回false。反之,frontPointer向前移动并返回 true。
算法的正确性在于递归处理节点的顺序是相反的(回顾上面打印的算法),而我们在函数外又记录了一个变量,因此从本质上,我们同时在『正向和逆向』迭代匹配。
*/
class Solution {
//这个目的是为了保留头结点
private ListNode frontPointer;
private boolean recursivelyCheck(ListNode currentNode) {
if (currentNode != null) {
//★这里会递归走到尾结点,走到尾结点之后,就是跳出这个if,
// 逆向往前迭代与frontPointer进行比较
if (!recursivelyCheck(currentNode.next)) {
return false;
}
//不相等,直接返回 false
if (currentNode.val != frontPointer.val) {
return false;
}
//相等,则让 frontPointer指针后移
frontPointer = frontPointer.next;
}
return true;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
frontPointer = head;
return recursivelyCheck(head);
}
}
代码实现三:快慢指针
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
// 找到前半部分链表的尾节点并反转后半部分链表
ListNode firstHalfEnd = endOfFirstHalf(head);
ListNode secondHalfStart = reverseList(firstHalfEnd.next);
// 判断是否回文
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = secondHalfStart;
boolean result = true;
//result 写在这里的目的是为了跳出 while循环,然后去恢复链表
while (result && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val != p2.val) {
result = false;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
// 还原链表并返回结果
firstHalfEnd.next = reverseList(secondHalfStart);
return result;
}
//反转后面的链表,即采用头插法建表
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
/**利用快慢指针来找到中间结点*/
private ListNode endOfFirstHalf(ListNode head) {
//一定要注意这里是:新建立两个指针一定,而不是使用 head来移动
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
283. 移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
说明:
- 必须在原数组上操作,不能拷贝额外的数组。
- 尽量减少操作次数。
代码实现一: 双指针法,遍历两次
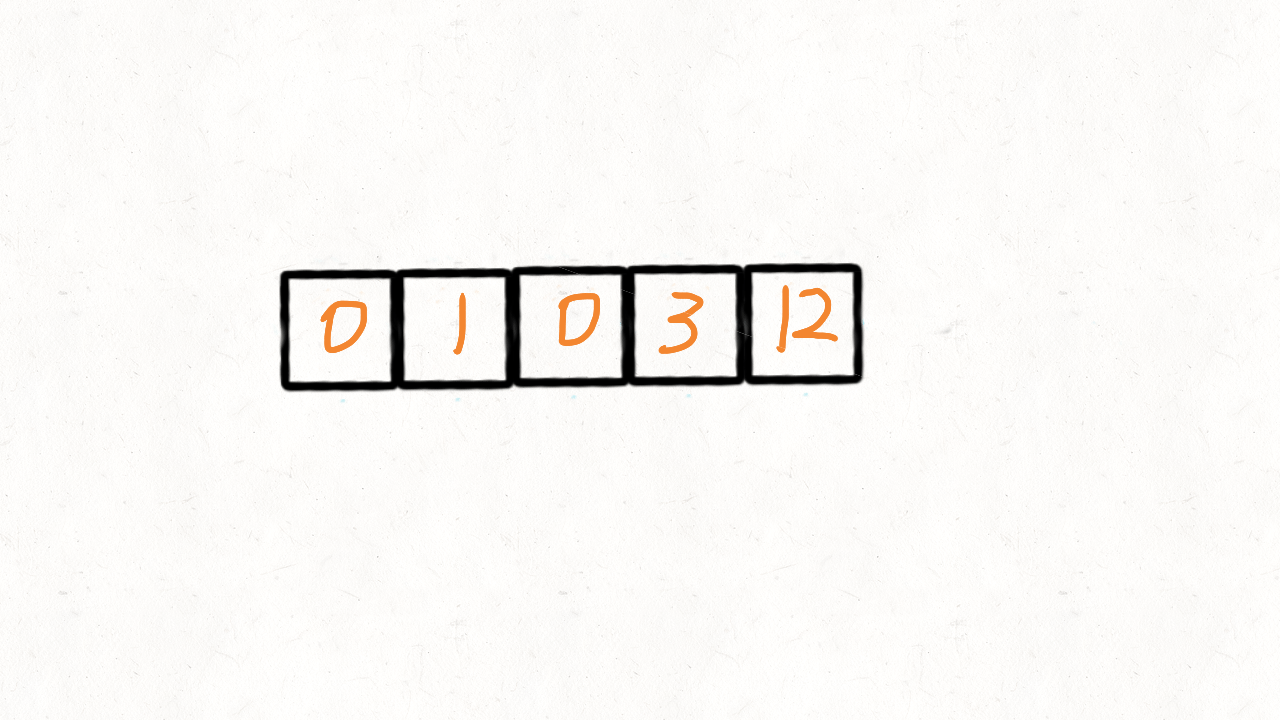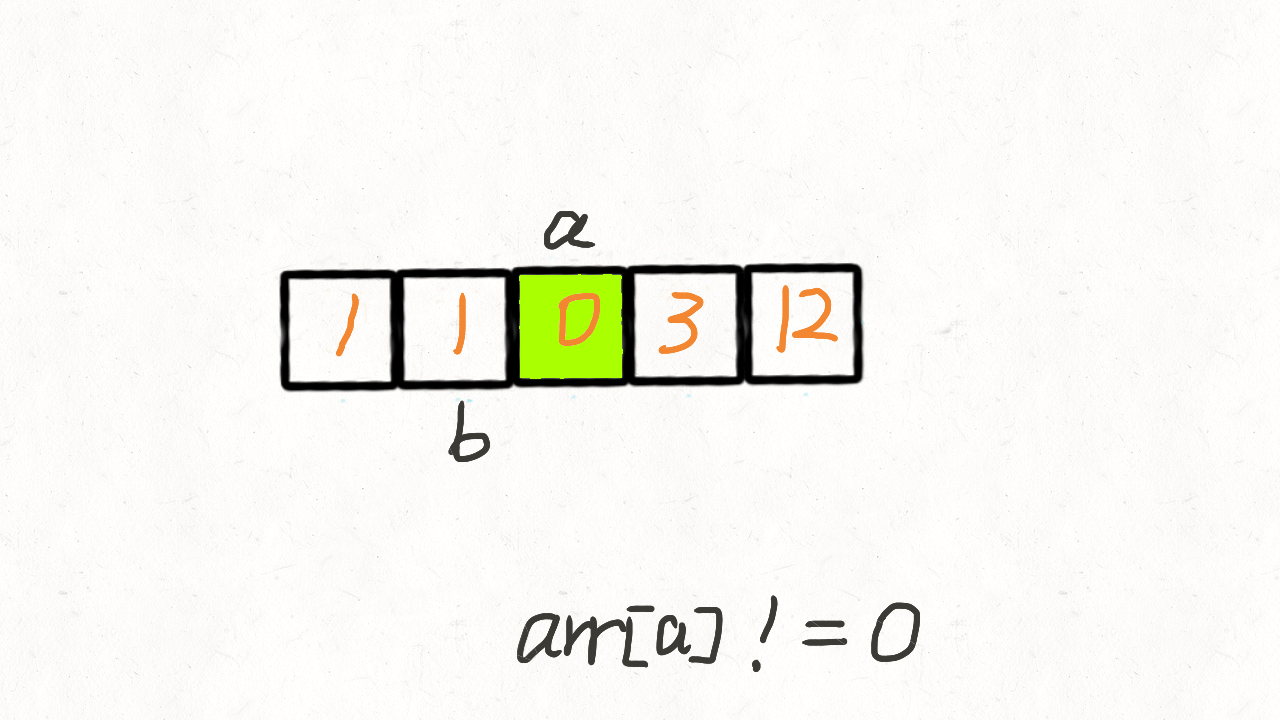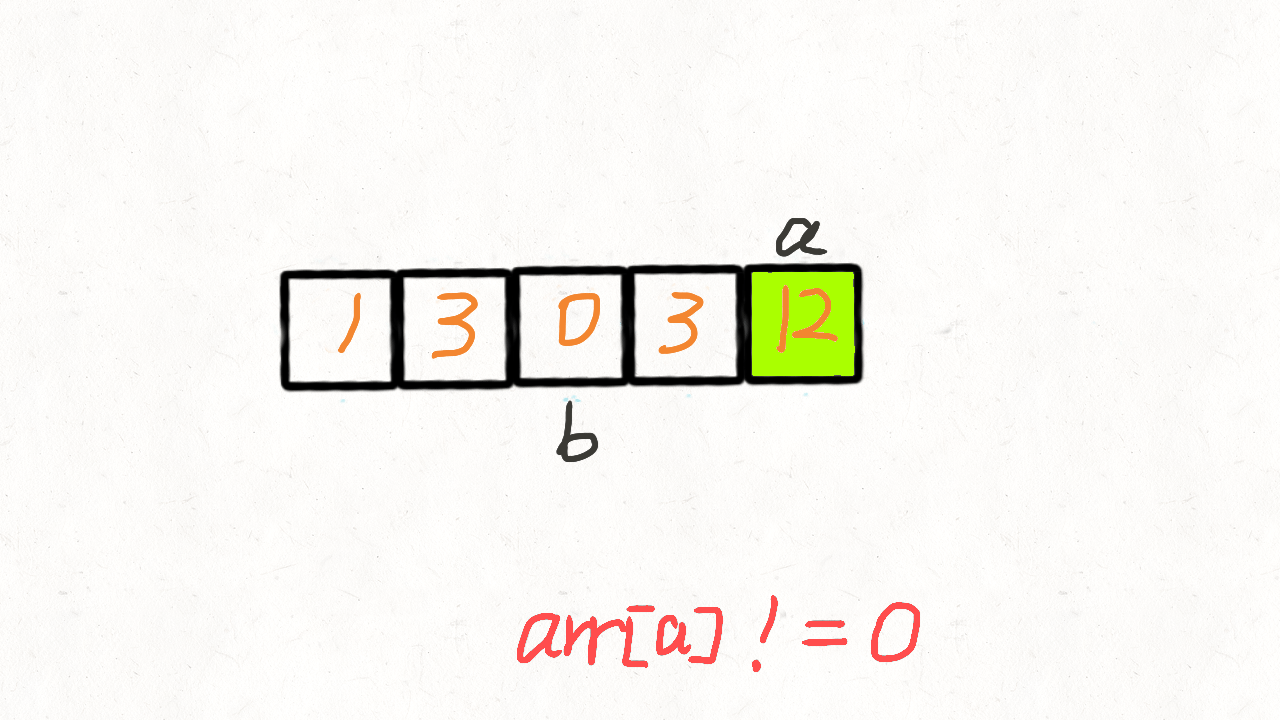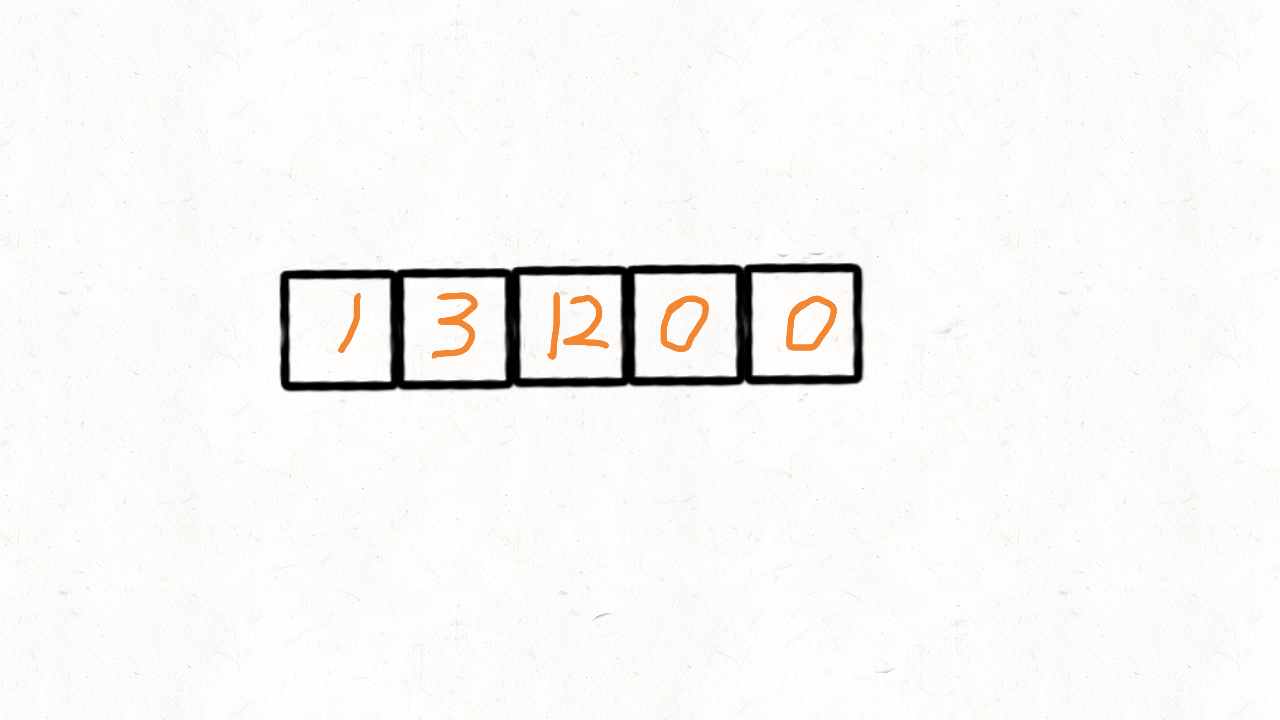
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null) {
return;
}
//第一次遍历的时候,j指针记录非0的个数,只要是非0的统统都赋给nums[j]
int j = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;++i) {
if(nums[i]!=0) {
nums[j++] = nums[i];
}
}
//非0元素统计完了,剩下的都是0了
//所以第二次遍历把末尾的元素都赋为0即可
for(int i=j;i<nums.length;++i) {
nums[i] = 0;
}
}
}
代码实现二:遍历一次 牛批啊

class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null) {
return;
}
//两个指针i和j
int j = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {
//当前元素!=0,就把其交换到左边,等于0的交换到右边
if(nums[i]!=0) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j++] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
0 1 0 3 12
第一次: 0 1 0 3 12 j=0 i=1 [i,j指的是下标]
第二次: 1 0 0 3 12 j=1 i=2 ★
第三次: 1 0 0 3 12 j=1 i=3
第四次: 1 3 0 0 12 j=2 i=4 ★
448. 找到所有数组中消失的数字
给定一个范围在 1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n ( n = 数组大小 ) 的 整型数组,数组中的元素一些出现了两次,另一些只出现一次。
找到所有在 [1, n] 范围之间没有出现在数组中的数字。
您能在不使用额外空间且时间复杂度为*O(n)*的情况下完成这个任务吗? 你可以假定返回的数组不算在额外空间内。
示例:
输入:
[4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
输出:
[5,6]
代码实现:妙啊
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int newIndex = Math.abs(nums[i]) - 1;
if (nums[newIndex] > 0) {
//这里就是将出现的元素,该元素值 = 下标位置标记为 负数。
//如果没有别标记的下标,就说明不在范围内
nums[newIndex] = -1 * nums[newIndex];
}
}
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 1; i <= nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i-1] > 0) {
result.add(i);
}
}
return result;
}
}
461. 汉明距离
两个整数之间的汉明距离指的是这两个数字对应二进制位不同的位置的数目。
给出两个整数 x 和 y,计算它们之间的汉明距离。
示例:
输入: x = 1, y = 4
输出: 2
解释:
1 (0 0 0 1)
4 (0 1 0 0)
↑ ↑
上面的箭头指出了对应二进制位不同的位置。
代码实现:
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
x = x^y;
int count = 0;
while(x!=0){
if((x&1)==1){
count++;
}
x = x>>>1;
}
return count;
}
}
543. 二叉树的直径
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
示例:给定二叉树
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
注意:两结点之间的路径长度是以它们之间边的数目表示。
代码实现:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return res;
}
public int dfs(TreeNode treeNode){
if(treeNode == null){
return 0;
}
//自底向上递归,计算每个节点的左右子树深度,相加来更新ans
int left = dfs(treeNode.left);
int right = dfs(treeNode.right);
if(left+right>res){
res = left + right;
}
//这个是递归往上返回时候,看这个结点到叶子结点的路径,哪个大(左右),这个结点的就返回哪个值。
return Math.max(left,right)+1;
}
}
617. 合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。
你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
示例 1:
输入:
Tree 1 Tree 2
1 2
/ \ / \
3 2 1 3
/ \ \
5 4 7
输出:
合并后的树:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
5 4 7
注意: 合并必须从两个树的根节点开始。
代码实现一:递归方式
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if(t1==null || t2==null){
return t1==null?t2:t1;
}
t1.val = t1.val + t2.val;
t1.left = mergeTrees(t1.left,t2.left);
t1.right = mergeTrees(t1.right,t2.right);
return t1;
}
}
代码实现二:迭代方式
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
//如果 t1和t2中,只要有一个是null,函数就直接返回
if(t1==null || t2==null) {
return t1==null? t2 : t1;
}
java.util.LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new java.util.LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(t1);
queue.add(t2);
while(queue.size()>0) {
TreeNode r1 = queue.remove();
TreeNode r2 = queue.remove();
r1.val += r2.val;
//如果r1和r2的左子树都不为空,就放到队列中
//如果r1的左子树为空,就把r2的左子树挂到r1的左子树上
if(r1.left!=null && r2.left!=null){
queue.add(r1.left);
queue.add(r2.left);
}else if(r1.left==null) {
r1.left = r2.left;
}
//对于右子树也是一样的
if(r1.right!=null && r2.right!=null) {
queue.add(r1.right);
queue.add(r2.right);
}else if(r1.right==null) {
r1.right = r2.right;
}
}
return t1;
}
}






















 1110
1110











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








