1. Motivation
- patch-based methods:不能提取到图像的高级特征,难以生成语义上很合理的结果;
- deep learning based method:从图像密集的潜在特征中生成视觉上很合理的结果仍具有挑战性。
2. Approach
2.1 Network structure
生成器采用了编码和解码的结构,编码器采用的金字塔式的编码器,一个关键的地方是作者设计了Attention Transfer Network(ATN),可以让已知区域的特征迁移到缺失区域,实现更好的填充效果,反正这边的ATN我只看论文是不太懂,还是得看源代码,所以我将ATN的代码附在了下面。
解码器的生成图片包含不同尺度的图片,为了实现金字塔损失(这里点在之后的loss部分介绍)。
class AtnConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels=128, output_channels=64, groups=4, ksize=3, stride=1, rate=2, softmax_scale=10., fuse=True, rates=[1,2,4,8]):
super(AtnConv, self).__init__()
self.ksize = ksize
self.stride = stride
self.rate = rate
self.softmax_scale = softmax_scale
self.groups = groups
self.fuse = fuse
if self.fuse:
for i in range(groups):
self.__setattr__('conv{}'.format(str(i).zfill(2)), nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels//groups, kernel_size=3, dilation=rates[i], padding=rates[i]),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
)
def forward(self, x1, x2, mask=None):
""" Attention Transfer Network (ATN) is first proposed in
Learning Pyramid Context-Encoder Networks for High-Quality Image Inpainting. Yanhong Zeng et al. In CVPR 2019.
inspired by
Generative Image Inpainting with Contextual Attention, Yu et al. In CVPR 2018.
Args:
x1: low-level feature maps with larger resolution.
x2: high-level feature maps with smaller resolution.
mask: Input mask, 1 indicates holes.
ksize: Kernel size for contextual attention.
stride: Stride for extracting patches from b.
rate: Dilation for matching.
softmax_scale: Scaled softmax for attention.
training: Indicating if current graph is training or inference.
Returns:
torch.Tensor, reconstructed feature map.
"""
# get shapes
x1s = list(x1.size())
x2s = list(x2.size())
# extract patches from low-level feature maps x1 with stride and rate
kernel = 2*self.rate
raw_w = extract_patches(x1, kernel=kernel, stride=self.rate*self.stride)
raw_w = raw_w.contiguous().view(x1s[0], -1, x1s[1], kernel, kernel) # B*HW*C*K*K
# split tensors by batch dimension; tuple is returned
raw_w_groups = torch.split(raw_w, 1, dim=0)
# split high-level feature maps x2 for matching
f_groups = torch.split(x2, 1, dim=0)
# extract patches from x2 as weights of filter
w = extract_patches(x2, kernel=self.ksize, stride=self.stride)
w = w.contiguous().view(x2s[0], -1, x2s[1], self.ksize, self.ksize) # B*HW*C*K*K
w_groups = torch.split(w, 1, dim=0)
# process mask
if mask is not None:
mask = F.interpolate(mask, size=x2s[2:4], mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
else:
mask = torch.zeros([1, 1, x2s[2], x2s[3]])
if torch.cuda.is_available():
mask = mask.cuda()
# extract patches from masks to mask out hole-patches for matching
m = extract_patches(mask, kernel=self.ksize, stride=self.stride)
m = m.contiguous().view(x2s[0], -1, 1, self.ksize, self.ksize) # B*HW*1*K*K
m = m.mean([2,3,4]).unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
mm = m.eq(0.).float() # (B, HW, 1, 1)
mm_groups = torch.split(mm, 1, dim=0)
y = []
scale = self.softmax_scale
padding = 0 if self.ksize==1 else 1
for xi, wi, raw_wi, mi in zip(f_groups, w_groups, raw_w_groups, mm_groups):
'''
O => output channel as a conv filter
I => input channel as a conv filter
xi : separated tensor along batch dimension of front;
wi : separated patch tensor along batch dimension of back;
raw_wi : separated tensor along batch dimension of back;
'''
# matching based on cosine-similarity
wi = wi[0]
escape_NaN = torch.FloatTensor([1e-4])
if torch.cuda.is_available():
escape_NaN = escape_NaN.cuda()
# normalize
wi_normed = wi / torch.max(torch.sqrt((wi*wi).sum([1,2,3],keepdim=True)), escape_NaN)
yi = F.conv2d(xi, wi_normed, stride=1, padding=padding)
yi = yi.contiguous().view(1, x2s[2]//self.stride*x2s[3]//self.stride, x2s[2], x2s[3])
# apply softmax to obtain
yi = yi * mi
yi = F.softmax(yi*scale, dim=1)
yi = yi * mi
yi = yi.clamp(min=1e-8)
# attending
wi_center = raw_wi[0]
yi = F.conv_transpose2d(yi, wi_center, stride=self.rate, padding=1) / 4.
y.append(yi)
y = torch.cat(y, dim=0)
y.contiguous().view(x1s)
# adjust after filling
if self.fuse:
tmp = []
for i in range(self.groups):
tmp.append(self.__getattr__('conv{}'.format(str(i).zfill(2)))(y))
y = torch.cat(tmp, dim=1)
return y
# extract patches
def extract_patches(x, kernel=3, stride=1):
if kernel != 1:
x = nn.ZeroPad2d(1)(x)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
all_patches = x.unfold(1, kernel, stride).unfold(2, kernel, stride)
return all_patches2.2 Loss function
Pyramid L1 losses:
if feats is not None:
pyramid_loss = 0
for _, f in enumerate(feats):
pyramid_loss += self.l1_loss(f, F.interpolate(images, size=f.size()[2:4], mode='bilinear', align_corners=True))
gen_loss += pyramid_loss * self.config['losses']['pyramid_weight']
self.add_summary(self.gen_writer, 'loss/pyramid_loss', pyramid_loss.item())代码中的feats就是生成的不同尺度(分辨率)的图片,作者希望这些生成的不同尺度的图片和真实图片下采样的结果是很接近的,其实就是生成图片和真实图片在不同分辨率下损失的和。
Adversarial training loss:
Final loss:
3. Discussion
我认为本文的创新点主要有两个:ATN的设计和金字塔式损失,我觉得比较有意思的是金字塔式
损失,通过生成不同尺度的图片,建立更加严格的loss,使模型达到更好的效果。
4. References
【1】Zeng, Yanhong, et al. "Learning pyramid-context encoder network for high-quality image inpainting." Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2019.








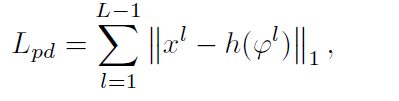
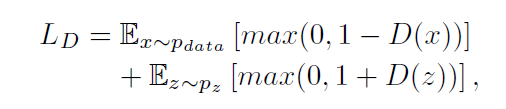
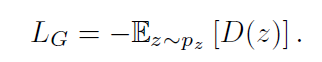















 3138
3138











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








