定义于头文件 <algorithm>
算法库提供大量用途的函数(例如查找、排序、计数、操作),它们在元素范围上操作。注意范围定义为 [first, last) ,其中 last 指代要查询或修改的最后元素的后一个元素。
判断范围是否已按给定的谓词划分
std::is_partitioned| template< class InputIt, class UnaryPredicate > | (1) | (C++11 起) (C++20 前) |
| template< class InputIt, class UnaryPredicate > | (C++20 起) | |
| template< class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt, class UnaryPredicate > | (2) | (C++17 起) |
1) 若范围 [first, last) 中的所有满足 p 的元素都出现在所有不满足的元素前则返回 true 。若 [first, last) 为空亦返回 true 。
2) 同 (1) ,但按照 policy 执行。此重载仅若 std::is_execution_policy_v<std::decay_t<ExecutionPolicy>> 为 true 才参与重载决议。
参数
| first, last | - | 要检查的元素范围 |
| policy | - | 所用的执行策略。细节见执行策略。 |
| p | - | 若期待在范围开始找到该元素则返回 true 的一元谓词。 对每个(可为 const 的) |
| 类型要求 | ||
- InputIt 必须满足遗留输入迭代器 (LegacyInputIterator) 的要求。 | ||
- ForwardIt 必须满足遗留向前迭代器 (LegacyForwardIterator) 的要求。而其值类型必须可转换为 UnaryPredicate 的参数类型 | ||
- UnaryPredicate 必须满足谓词 (Predicate) 的要求。 | ||
返回值
若范围 [first, last) 为空或以 p 划分则为 true 。否则为 false 。
复杂度
至多应用 std::distance(first, last) 次 p 。
异常
拥有名为 ExecutionPolicy 的模板形参的重载按下列方式报告错误:
- 若作为算法一部分调用的函数的执行抛出异常,且
ExecutionPolicy为标准策略之一,则调用 std::terminate 。对于任何其他ExecutionPolicy,行为是实现定义的。 - 若算法无法分配内存,则抛出 std::bad_alloc 。
可能的实现
template< class InputIt, class UnaryPredicate >
bool is_partitioned(InputIt first, InputIt last, UnaryPredicate p)
{
for (; first != last; ++first)
if (!p(*first))
break;
for (; first != last; ++first)
if (p(*first))
return false;
return true;
}调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
struct Cell
{
int x;
int y;
Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell)
{
x += cell.x;
y += cell.y;
return *this;
}
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{
os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";
return os;
}
int main()
{
std::cout.setf(std::ios_base::boolalpha);
auto func1 = [](Cell & cell, const Cell & t)
{
cell += t;
return cell;
};
Cell cell{99, 100};
Cell t{2, 3};
auto func2 = std::bind(func1, cell, t);
vector<Cell> cells(8);
std::generate(cells.begin(), cells.end(), func2);
std::cout << "cells : ";
std::copy(cells.begin(), cells.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
auto is_even = [](const Cell & cell)
{
return cell.x % 2 == 1 && cell.y % 2 == 1;
};
std::cout << "is_partitioned: " << std::is_partitioned(cells.begin(), cells.end(), is_even);
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
std::partition(cells.begin(), cells.end(), is_even);
std::cout << "cells : ";
std::copy(cells.begin(), cells.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "is_partitioned: " << std::is_partitioned(cells.begin(), cells.end(), is_even);
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
std::reverse(cells.begin(), cells.end());
std::cout << "cells : ";
std::copy(cells.begin(), cells.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "is_partitioned: " << std::is_partitioned(cells.begin(), cells.end(), is_even);
std::cout << std::endl ;
return 0;
}
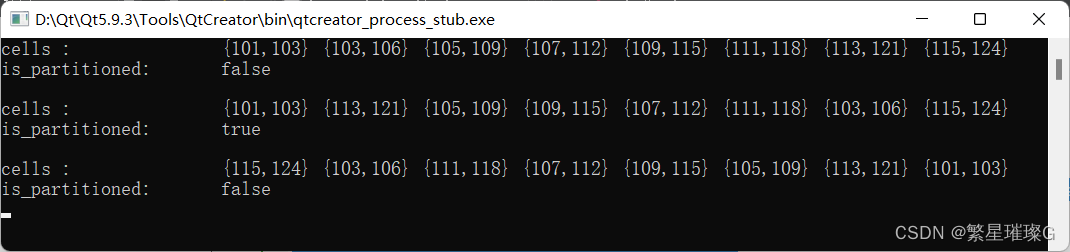
输出






















 1024
1024











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








