嵌入式中常使用pthread_kill(pthread_t pthread)函数来判断,即pthread_kill(pthread, 0),向pthread线程传递一个信号,返回值为0,表示存在;ESRCH(3)表示信号不存在;EINVAL(22)表示无效参数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <errno.h>
int exit_flag = 0;
void sighandler(int signum)
{
printf("capture signal number %d...\n", signum);
if(SIGKILL == signum)
exit(1);
}
void *threadfunc(void *parm)
{
int i = 0;
signal(SIGQUIT, sighandler);
while(1){
printf("threadfunc i=%d\n",i++);
sleep(1);
if(exit_flag)
break;
}
printf("exit from hreadfunc\n");
return NULL;
}
void main()
{
int rc = 0;
pthread_t threads;
rc = pthread_kill(threads, 0);
printf("ESRCH=%d EINVAL=%d\n",ESRCH,EINVAL);
printf("start rc=%d\n",rc);
pthread_create(&threads, NULL, threadfunc, NULL);
sleep(1);
rc = pthread_kill(threads, 0);
printf("pthread_kill(threads, 0) rc=%d\n",rc);
sleep(5);
rc = pthread_kill(threads, SIGQUIT);
sleep(1);
printf("after SIGQUIT rc=%d\n",rc);
exit_flag = 1;
sleep(3);
rc = pthread_kill(threads, 0);
printf("after set exit_flag 1 rc=%d\n",rc);
rc = pthread_kill(threads, SIGKILL);
sleep(1);
printf("after SIGKILL rc=%d\n",rc);
while(1);
return ;
}测试结果:
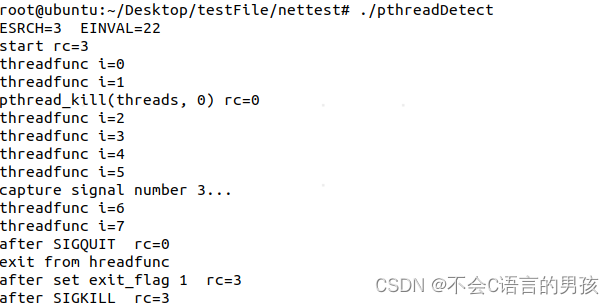







 本文详细介绍了如何在C语言嵌入式环境中使用pthread_kill函数发送信号给线程,展示了SIGKILL、SIGQUIT和无效参数错误的情况,并分析了相应的返回值。
本文详细介绍了如何在C语言嵌入式环境中使用pthread_kill函数发送信号给线程,展示了SIGKILL、SIGQUIT和无效参数错误的情况,并分析了相应的返回值。















 1067
1067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










