目录
15,Brian Kernighan算法(n&(n-1)算法)
1,1021. 删除最外层的括号:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-outermost-parentheses/
2,347. 前 K 个高频元素:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/
3,丑数https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ugly-number/
4,179. 最大数https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-number/
5,121. 买卖股票的最佳时机https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
6,1130. 叶值的最小代价生成树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-cost-tree-from-leaf-values/
7,122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/
8, 递增顺序搜索树 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/increasing-order-search-tree/
1,最大子序和 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/
2,746. 使用最小花费爬楼梯 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/min-cost-climbing-stairs/
3,面试题 16.17. 连续数列 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contiguous-sequence-lcci/
5,1217. 玩筹码 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-cost-to-move-chips-to-the-same-position/
6, 91. 解码方法 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/decode-ways/
7,45. 跳跃游戏 II https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/
8,5. 最长回文子串 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
1,220. 存在重复元素 III https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate-iii/
2,710. 黑名单中的随机数 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/random-pick-with-blacklist/
3,969. 煎饼排序 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pancake-sorting/
1,338. 比特位计数 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/counting-bits/
2, 78. Subsets https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/
1,刷题小技巧
1,c++中的for(auto a:b)用法
for(auto a:b)中b为一个容器,效果是利用a遍历并获得b容器中的每一个值,但是a无法影响到b容器中的元素。
for(auto &a:b)中加了引用符号,可以对容器中的内容进行赋值,即可通过对a赋值来做到容器b的内容填充。
2,c++中map的元素进行按照值排序(默认按照键排序)
为什么不能对map进行按值排序呢?因为sort排序只能对线性结构进行排序,而map是采用红黑树的数据结构。
一是通过将map转换到序列容器,再用STL提供的sort方法得以实现的。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef pair<string, int> Pair; //第3参数为函数名 bool my_compare(const Pair &p1, const Pair &p2){ return p1.second < p2.second; } //第3参数为重载了operator()操作符的类对象 struct MyCompare{ public: bool operator()(const Pair &p1, const Pair &p2) const{ return p1.second < p2.second; } }; int main(){ map<string, int> test; test["Alice"] = 3; test["Cindy"] = 5; test["Bob"] = 7; cout << "> sort by key" << endl; for(auto itr = test.begin(); itr != test.end(); ++itr){ cout << itr->first << ": " << itr->second << endl; } cout << endl; vector<Pair> vec; for(auto itr = test.begin(); itr != test.end(); ++itr){ vec.push_back(make_pair(itr->first, itr->second)); } sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), MyCompare()); //my_compare或者MyCompare()都可以 cout << "> sort by value" << endl; for(auto itr = vec.begin(); itr != vec.end(); ++itr){ cout << itr->first << ": " << itr->second << endl; } return 0; }二是通过将map的key和value位置替换
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef pair<string, int> Pair; int main(){ map<string, int> test; test["Alice"] = 3; test["Cindy"] = 5; test["Bob"] = 7; cout << "> sort by key" << endl; for(auto itr = test.begin(); itr != test.end(); ++itr){ cout << itr->first << ": " << itr->second << endl; } cout << endl; map<int, string> result; transform(test.begin(), test.end(), inserter(result, result.begin()), [](pair<string, int> a) { return pair<int, string>(a.second, a.first); }); cout << "> sort by value" << endl; for(auto itr = result.begin(); itr != result.end(); ++itr){ cout << itr->first << ": " << itr->second << endl; } return 0; }
3,pair的认识
1,pair是将2个数据组合成一个数据,当需要这样的需求时就可以使用pair,如stl中的map就是将key和value放在一起来保存。另一个应用是,当一个函数需要返回2个数据的时候,可以选择pair。 pair的实现是一个结构体,主要的两个成员变量是first second 因为是使用struct不是class,所以可以直接使用pair的成员变量。
2,
template pair make_pair(T1 a, T2 b) { return pair(a, b); }很明显,我们可以使用pair的构造函数也可以使用make_pair来生成我们需要的pair。 一般make_pair都使用在需要pair做参数的位置,可以直接调用make_pair生成pair对象很方便,代码也很清晰。 另一个使用的方面就是pair可以接受隐式的类型转换,这样可以获得更高的灵活度。
3,对于pair类,由于它只有两个元素,分别名为first和second,因此直接使用普通的点操作符即可访问其成员。
4,质数判断的方法
1,常见方法,直接通过遍历到n的开平法进行整除判断,效率不高。
2,通过标志方法,设置一个bool数组,先进行初始化,奇数设置为true,偶数设置为false,只需将前面为true表示为质数的倍数设置为flase即可,效率较上面高。
3,质数分布的规律:大于等于5的质数一定和6的倍数相邻。例如5和7,11和13,17和19等等;
bool isPrime( int num ) { //两个较小数另外处理 if(num == 2||num == 3 ) return 1; //不在6的倍数两侧的一定不是质数 if(num % 6 != 1&&num % 6 != 5) return 0; int tmp = sqrt(num); //在6的倍数两侧的也可能不是质数 for(int i = 5;i <= tmp;i += 6) if(num %i == 0||num % (i+ 2) == 0) return 0; //排除所有,剩余的是质数 return 1; }
5,自定义数据结构的根堆(Priority_queue)
1,方法一
必须自己重载 operator< 或者自己写仿函数(有些编译器重载运算符会很坑,还是两个都掌握的比较稳妥)。 重载运算符,推荐采用下面这种方法: struct cow { int s, e; cow(int a = 0, int b = 0) { s = a, e = b; } }c[MAX]; bool operator<(const cow & c1, const cow & c2) { return c1.s < c2.s; } priority_queue<cow>q;2,方法二
自己写仿函数,也就是刚才出现的greater<int>这种函数,怎么写呢? struct cow { int s, e; cow(int a = 0, int b = 0) { s = a, e = b; } }c[MAX]; struct cmp { bool operator()(cow c1, cow c2) { return c1.s < c2.s; } }; priority_queue<cow, vector<cow>, cmp>p;
6,用栈实现二叉树的中序遍历和后序遍历
1,中序遍历
class Solution { public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) { vector<int> res; stack<TreeNode*> s; TreeNode *p = root; while (p || !s.empty()) { while (p) { s.push(p); p = p->left; } p = s.top(); s.pop(); res.push_back(p->val); p = p->right; } return res; } };2,后序遍历
class Solution { public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { stack<TreeNode*> s1; stack<TreeNode*> s2; vector<int> res; if(!root){ return res; } s1.push(root); while(!s1.empty()){ TreeNode* cur = s1.top(); s1.pop(); s2.push(cur); //先将left压到栈里,再将right压到栈里,然后取出将右子树压到s2 //中,最后再压左子树 //待右子树全部压完,然后将左子树全部压到栈s2中 //此时栈s2从上到下依次是左子树、右子树、根 if(cur->left){ s1.push(cur->left); } //后压右子树,然后全部将有子树压到栈s2中 if(cur->right){ s1.push(cur->right); } } while(!s2.empty()){ //弹出s2栈顶元素,依次尾插到vector中,最终得到二叉树的后序 //遍历 res.push_back(s2.top()->val); s2.pop(); } return res; } };
7,怎样判断一个整数是否能由另一个整数平方得到
int t1;// 目标整数
int t2=sqrt(t1);
if(t2*t2==t1)return "t1能够开平方且开平方后的数为整数";
8,用vector定义固定长度的二维数组
vector>dp(col,vector(row,0));//定义行col列row的二维数组dp[col][row];
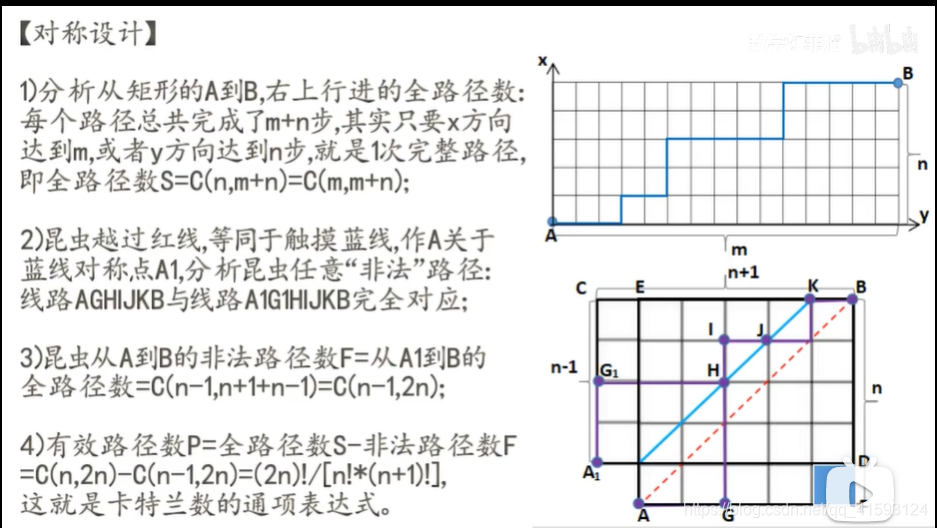
9,明安图数-卡特兰数的计算以及常见的应用
百度百科的定义:
明安图数,又称卡塔兰数,英文名Catalan number,是组合数学中一个常出现于各种计数问题中的数列。以中国蒙古族数学家明安图 (1692-1763)和比利时的数学家欧仁·查理·卡塔兰 (1814–1894)的名字来命名,其前几项为(从第零项开始) : 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, 208012, 742900, 2674440, 9694845, 35357670, 129644790, 477638700, 1767263190, 6564120420, 24466267020, 91482563640, 343059613650, 1289904147324, 4861946401452, ...
int catalan(int n){ if (n == 0)return 1; if (n == 1)return 1; int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i <=n-1;i++){ res += catalan(i)*catalan(n-1-i); } return res; }明安图数的应用:
(1)括号化
矩阵连乘: P=a1×a2×a3×……×an,依据乘法结合律,不改变其顺序,只用括号表示成对的乘积,试问有几种括号化的方案。( h(n) 种)
(2)出栈次序
一个栈(无穷大)的进栈序列为1,2,3,…,n,有多少个不同的出栈序列? [5-6]
(3)凸多边形三角划分
在一个凸多边形中,通过若干条互不相交的对角线,把这个多边形划分成了若干个三角形。任务是键盘上输入凸多边形的边数n,求不同划分的方案数f(n)。比如当n=6时,f(6)=14。
(4)给定节点组成二叉搜索树
(能构成 h(N) 个)
(这个公式的下标是从h(0)=1开始的)
(5)n对括号正确匹配数目
给定n对括号,求括号正确配对的字符串数,例如:
0对括号:[空序列] 1种可能
1对括号:() 1种可能
2对括号:()() (()) 2种可能
3对括号:((())) ()(()) ()()() (())() (()()) 5种可能
10,用深度遍历实现元素互不相同数组全排列思想
深度遍历+备忘录visited[]可以解决很多实际问题,例如迷宫、数组下标选择问题等。
11,树状数组思想
树状数组或二叉索引树(英语:Binary Indexed Tree),又以其发明者命名为Fenwick树,最早由Peter M. Fenwick于1994年以A New Data Structure for Cumulative Frequency Tables为题发表在SOFTWARE PRACTICE AND EXPERIENCE。其初衷是解决数据压缩里的累积频率(Cumulative Frequency)的计算问题,现多用于高效计算数列的前缀和, 区间和。
class BIT { private: vector<int> tree; int n; public: BIT(int _n): n(_n), tree(_n + 1) {} static constexpr int lowbit(int x) { return x & (-x); } void update(int x, int d) { while (x <= n) { tree[x] += d; x += lowbit(x); } } int query(int x) const { int ans = 0; while (x) { ans += tree[x]; x -= lowbit(x); } return ans; } };















 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 1365
1365

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










