一、max()、min() 和 abs()
max(x,y) 和 min(x,y) 分别返回 x 和 y 中的最大值和最小值,且参数必须是两个(可以是浮点数)。如果想要返回三个数 x,y,z 的最大值,可以使用 max(x,max(y,z))的写法。
abs(x) 返回 x 的绝对值。
注意:x 必须是整数,浮点型的绝对值请用 math 头文件下的 fabs。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
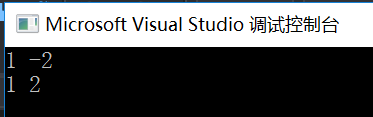
int x = 1, y = -2;
printf("%d %d \n", max(x,y), min(x,y));
printf("%d %d \n", abs(x), abs(y));
return 0;
}
二、swap()
swap(x,y) 用来交换 x 和 y 的值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 1, y = 2;
swap(x, y);
printf("%d %d \n", x, y);
return 0;
}
三、reverse()
reverse(it,it2) 可以将数组指针在 [it,it2) 之间的元素或容器的迭代器在 [it,it2) 范围内的元素进行反转。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10] = { 10,11,12,13,14,15 };
reverse(a, a + 4);//将 a[0]~a[3] 反转
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("%d \n",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
如果是对容器中的元素(例如 string 字符串)进行反转,结果也一样。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "abcdefghi";
reverse(str.begin()+2, str.begin()+6);//对 str[2]~str[5] 反转
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
{
printf("%c \n",str[i]);
}
return 0;
}
四、next_permutation()
next_permutation() 给出一个序列在全排列中的下一个序列。
例如:当 n=3 时的全排列为:123;132;213;231;312;321.
这样 231 的下一个序列就是 312.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10] = { 1,2,3 };
// a[0]~a[2] 之间的序列需要求解 next_permutation
do
{
printf("%d%d%d\n", a[0], a[1], a[2]);
} while (next_permutation(a,a+3));
return 0;
}
五、fill()
fill() 可以把数组或容器中的某一段区间赋为某个相同的值。和 memset 不同,这里的赋值可以是数组类型对应范围中的任意值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[8] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
fill(a, a + 4, 233); //将a[0]~a[3]均赋值为233.
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
六、sort()
sort 是用来排序的函数,它根据具体情形使用不同的排序方法,效率较高。(一般来说,不推荐使用 C 语言中的 qsort 函数,原因是 qsort 用起来比较烦索,涉及到很多指针的操作。
sort 在实现中规避了经典快速排序中可能出现的会导致实际复杂度退化到 O(n2)的极端情况。
sort(首元素地址(必填),尾元素地址的下一个地址(必填),比较函数(非必填));
如果不写比较函数,则默认对前面给出的区间进行递增排序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[6] = { 9,4,2,5,6,-1};
sort(a, a + 4); //将a[0]~a[3]从小到大排序.
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", a[i]);
}
printf("..........\n");
double b[] = { 2.1,-1.3,0.3 };
sort(b, b + 3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("%.1f\n", b[i]);
}
printf("..........\n");
char c[5] = { 'M','L','A','F','G' };
sort(c, c + 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%c\n", c[i]);
}
return 0;
}

(1)基本数据类型数组的排序(比较函数cmp的写法)

七、lower_bound() 和 upper_bound()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10] = { 1,2,2,3,3,3,5,5,5,5 };
int* lowerPos = lower_bound(a, a + 10, -1);
int* upperPos = upper_bound(a, a + 10, -1);
printf("%d , %d\n", lowerPos - a, upperPos - a);
//寻找1
lowerPos = lower_bound(a, a + 10, 1);
upperPos = upper_bound(a, a + 10, 1);
printf("%d , %d\n", lowerPos - a, upperPos - a);
//寻找3
lowerPos = lower_bound(a, a + 10, 3);
upperPos = upper_bound(a, a + 10, 3);
printf("%d , %d\n", lowerPos - a, upperPos - a);
//寻找4
lowerPos = lower_bound(a, a + 10, 4);
upperPos = upper_bound(a, a + 10, 4);
printf("%d , %d\n", lowerPos - a, upperPos - a);
//寻找6
lowerPos = lower_bound(a, a + 10, 6);
upperPos = upper_bound(a, a + 10, 6);
printf("%d , %d\n", lowerPos - a, upperPos - a);
return 0;
}























 301
301











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








