文章目录
前言
1、自动装配原理
2、多种方式给属性赋值
3、多环境配置
4、自动配置
一、配置文件及自动配置原理
1、配置文件
springboot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名称是固定的
- application.properties 语法结构: key = value
- application.yml 语法结构: key :空格 value
配置文件的作用:修改springboot自动配置的默认值,因为Spring Boot在底层都给我们自动配置好了
2、yaml
标记语言:
以前的配置文件,大多数使用xml来配置;比如一个简单的端口配置

properties和yaml配置的区别:
yaml:
# 普通的key - value
name: bwy
# 对象
student:
name: bwy
age: 24
# 行内写法
student: {name: bwy,age: 24}
# 数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
# 行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
properties:
# properties只能保存键值对
# 普通的key - value
name=bwy
student.name = bwy
student.age = 24
1、注解注入方式给属性赋值
实体类:
@Component
public class Dog {
@Value("旺财")
private String name;
@Value("3")
private Integer age;
public Dog(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Dog() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类:
@SpringBootTest
class HelloworldApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(dog);
}
}
测试结果:

2、yaml给实体类赋值
实体类:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", happy=" + happy +
", birth=" + birth +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boolean getHappy() {
return happy;
}
public void setHappy(Boolean happy) {
this.happy = happy;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Boolean happy, Date birth, Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists, Dog dog) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.happy = happy;
this.birth = birth;
this.maps = maps;
this.lists = lists;
this.dog = dog;
}
public Person() {
}
}
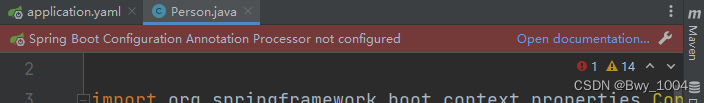
可以通过这个配置产生提示,如果不配置使用了@ConfigurationProperties这个注解就会爆红
添加依赖即可,不添加也不会运行出错
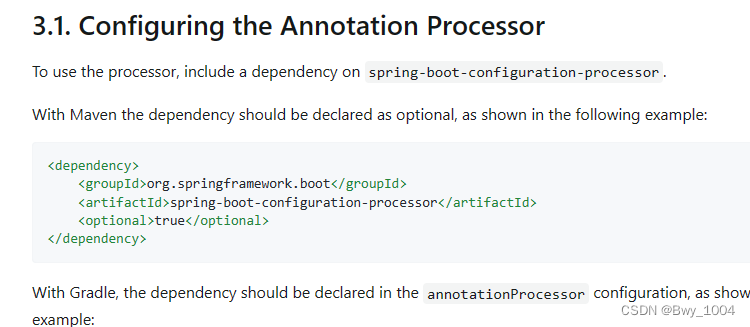
@ConfigurationProperties的作用:
将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中;
告诉springboot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
参数:prefix = “person” :将配置文件中的person下面的所有属性一一对应
只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能使用容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能,因此实体类上还需要添加注解:@Component
yaml配置文件:
注意 yaml文件中不能有大写
person:
name: bwy
age: 24
happy: true
birth: 2023/3/6
maps: {k1: 60, k2: 80}
lists:
- code
- music
- picture
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 3
测试类:
@SpringBootTest
class HelloworldApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
测试结果:

3、Properties给属性赋值
加载指定配置文件:
@PropertySource(value = “classpath:bwy.properties”)
实体类:
只测试name属性
@Component
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//加载指定配置文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:bwy.properties")
public class Person {
@Value("${name")
private String name;
……
}
properties配置文件
name = bwy
测试类同上
运行结果:


- 松散绑定:比如yml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是一样的,-后面跟着的字母默认是大写的,这就是松散绑定
- JSR303数据校验:判断输入的格式是否合法,这个就是我们可以在字段上增加一层过滤器验证,可以保证数据的合法性,@Validated
二、springboot的多环境配置
spring.profiles.active:可以选择激活哪一个配置文件
#spring.profiles.active=dev
spring.profiles.active=test
ymal配置:
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: test
四、自动配置
在配置文件中能配置的东西,都存在一个固有的规律 ,xxxAutoConfiguration:默认值 xxxProperties 和配置文件绑定,我们就可以使用自定义的配置了!
- springboot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
- 看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中
- 看自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要手动配置了)
- 给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性,我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可
- XXXAutoConfiguration:自动配置类;给容器中添加组件
- XXXProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性
总结
- 配置yml和配置properties都可以获取到值,强烈推荐yml
- 如果在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用@value
- 如果,我们编写了一个JavaBean来和配置文件进行映射,就直接使用@configurationProperties





















 3435
3435











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








