1、定义一个接口Component
public interface Component {
void operation();
}
2、创建一个实现了Component接口的简单类SimpleComponent
public class SimpleComponent implements Component {
@Override
public void operation() {
System.out.println("SimpleComponent operation.");
}
}
3、创建一个装饰器基类Decorator,它也实现了Component接口,并持有一个对Component对象的引用
public abstract class Decorator implements Component {
protected Component component;
public Decorator(Component component) {
this.component = component;
}
@Override
public void operation() {
if (component != null) {
component.operation();
}
}
}
4、创建一个具体的装饰器类,例如ConcreteDecoratorA,它添加了一些额外的功能
public class ConcreteDecoratorA extends Decorator {
public ConcreteDecoratorA(Component component) {
super(component);
}
@Override
public void operation() {
super.operation();
addedFunctionA();
}
private void addedFunctionA() {
System.out.println("ConcreteDecoratorA added function.");
}
}
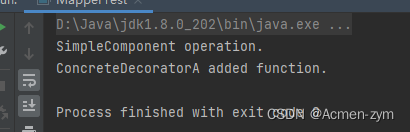
5、编写一个测试类来展示如何使用装饰器
public class DecoratorPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component simpleComponent = new SimpleComponent();
Component decoratedComponent = new ConcreteDecoratorA(simpleComponent);
decoratedComponent.operation();
}
}
























 169万+
169万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










