6-1 虚继承(理论)
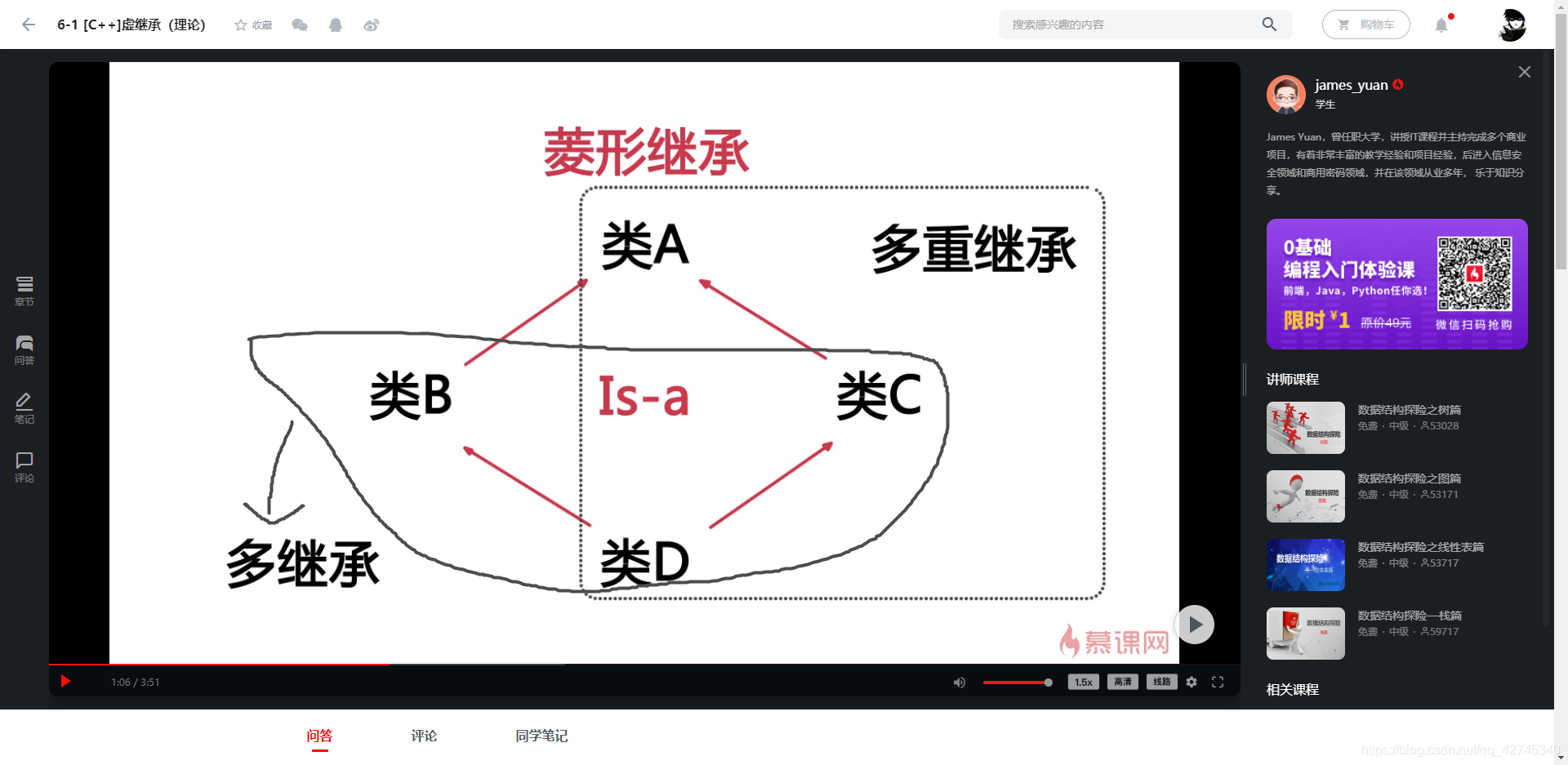
上图,当初始化一个D类对象时,D从B从A继承,D又从C从A继承,继承了两个A,这种情况是不能容忍的(在一份对象中有两次完全相同的数据,属于冗余数据,我们没办法承担他的系统开销);
例子:
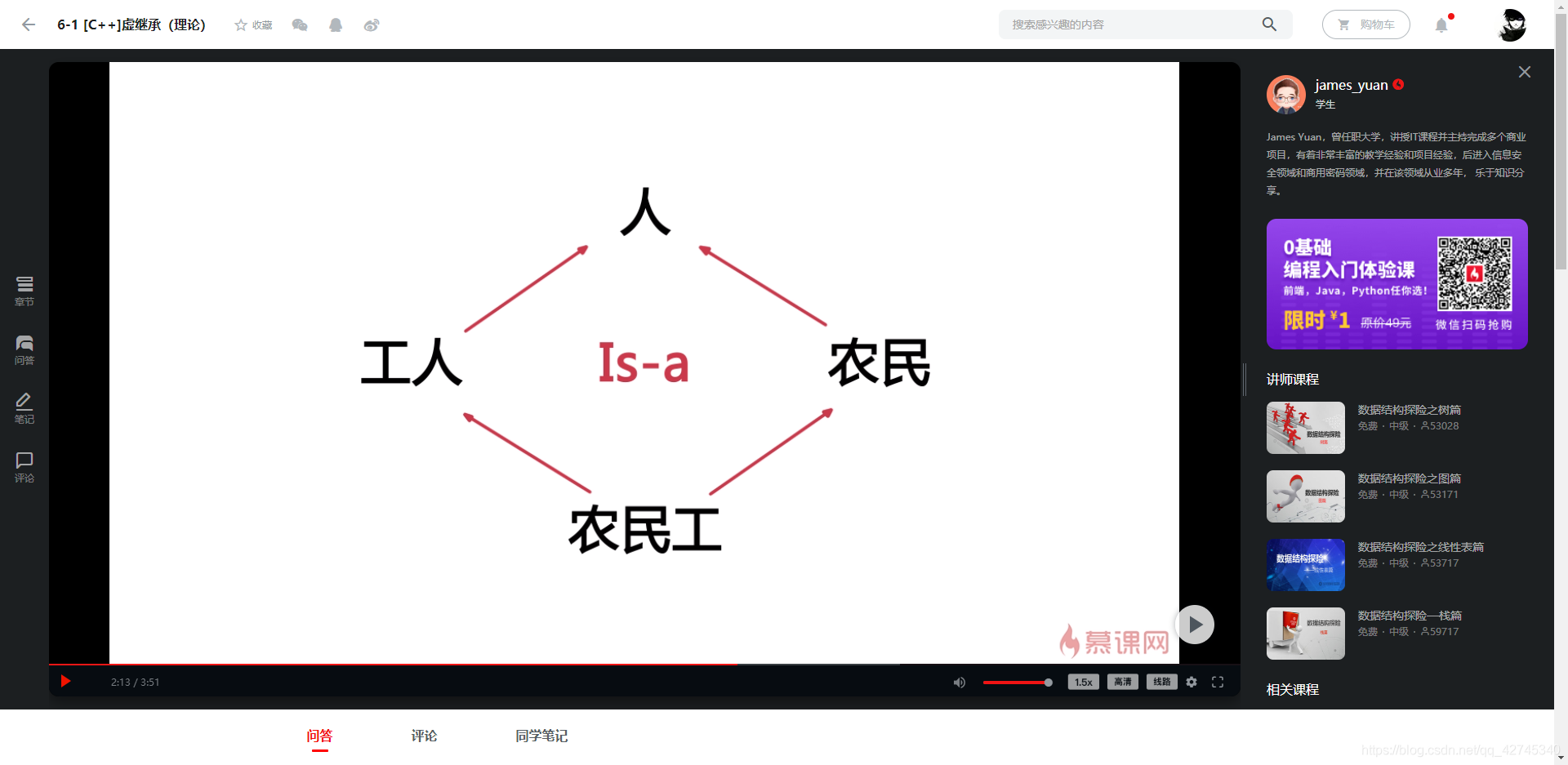
解决办法:虚继承
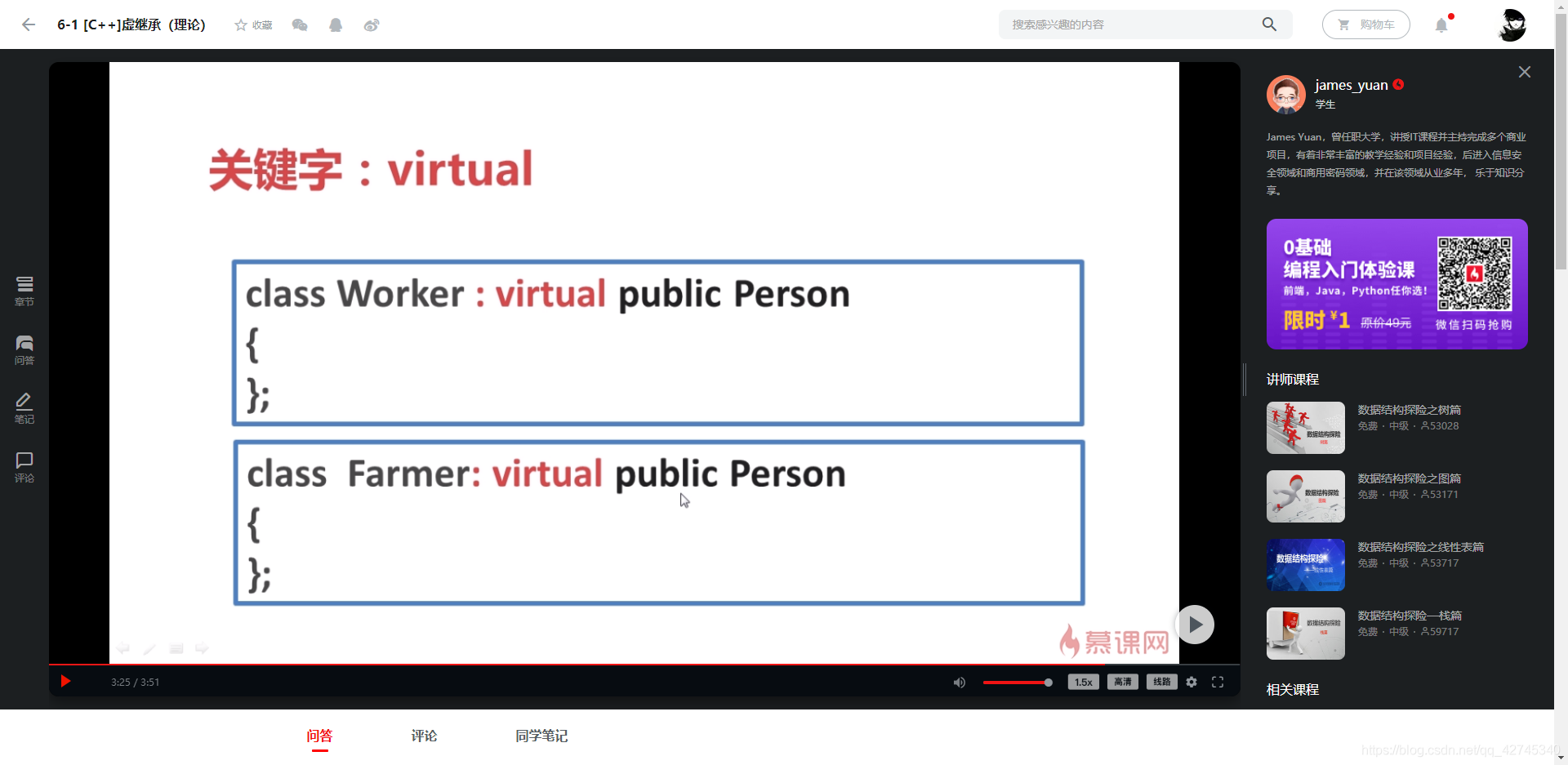
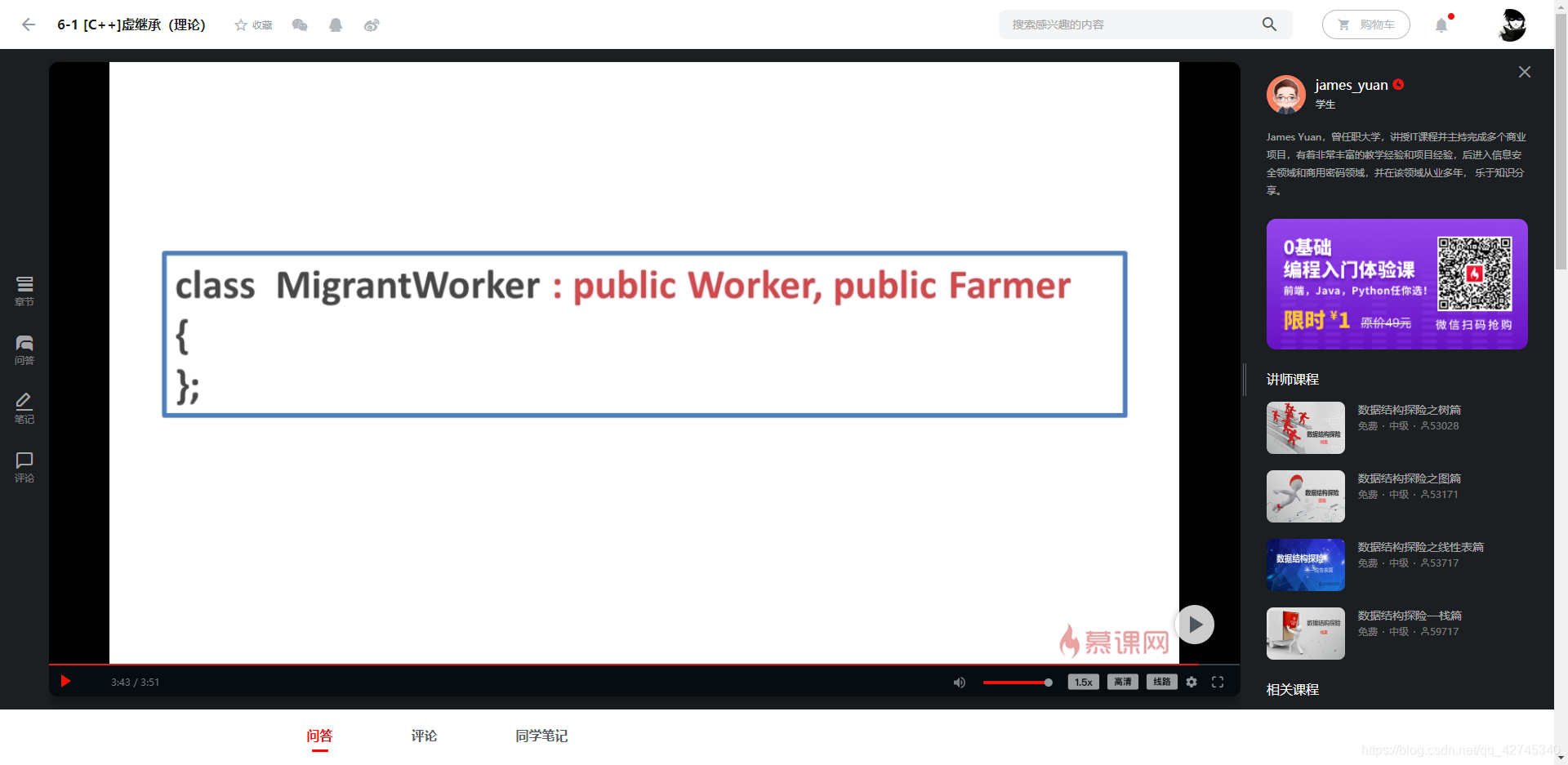
上图中的MigrantWorker只含有一份Person的数据;
6-2 虚继承(编码)

Person.h
#ifndef PERSON_H //解决重定义的方法,尤其适合于菱形继承中
#define PERSON_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string color = "blue");
virtual~Person();//虚的析构函数
void printColor();
protected:
string m_strColor;
};
#endif
Person. cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Person.h"
using namespace std;
Person::Person(string color)
{
m_strColor = color;
cout<<"Person()"<<endl;
}
Person::~Person()
{
cout<<"~Person()"<<endl;
}
void Person::printColor()
{
cout<<m_strColor<<endl;
cout<<"Person--printColor()"<<endl;
}
Farmer.h
#include <string>
#include "Person.h"
using namespace std;
class Farmer:virtual public Person
{
public:
Farmer(string name = "Jack",string color = "blue");
virtual~Farmer();
void sow();
protected:
string m_strName;
};
Farmer.cpp
#include "Farmer.h"
#include<iostream>
Farmer::Farmer(string name,string color):Person("Farmer"+color)
{
m_strName = name;
cout<<"Farmer()"<<endl;
}
Farmer::~Farmer()
{
cout<<"~Farmer()"<<endl;
}
void Farmer::sow()
{
cout<<m_strName<<endl;
cout<<"Farmer - sow()"<<endl;
}
Worker.h
#include <string>
#include "Person.h"
using namespace std;
class Worker:virtual public Person
{
public:
Worker(string code = "001",string color = "blue");
virtual~Worker();
void carry();
protected:
string m_strCode;
};
Worker.cpp
#include"Worker.h"
#include<iostream>
Worker::Worker(string code,string color):Person("Worker"+color)
{
m_strCode = code;
cout<<"Worker()"<<endl;
}
Worker::~Worker()
{
cout<<"~Worker()"<<endl;
}
void Worker::carry()
{
cout<<m_strCode<<endl;
cout<<"Worker - carry()"<<endl;
}
MigrantWorker.h
#include "Farmer.h"
#include "Worker.h"
class MigrantWorker:public Farmer,public Worker
{
public:
MigrantWorker(string name,string code,string color);
~MigrantWorker();
};
MigrantWorker.cpp
#include "MigrantWorker.h"
#include <iostream>
MigrantWorker::MigrantWorker(string name,string code,string color):Farmer(name,color),Worker(code,color)//先构造的Farmer再构造的Worker/最终把color传递到person的color;
{
cout<<"MigrantWorker()"<<endl;
}
MigrantWorker::~MigrantWorker()
{
cout<<"~MigrantWorker()"<<endl;
}
demo.cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "MigrantWorker.h"
int main()
{
MigrantWorker *p = new MigrantWorker("Merry","200","yellow");
cout<<endl;
p->Farmer::printColor();
p->Worker::printColor();
cout<<endl;
delete p;
p = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果
Person()
Farmer()
Worker()
MigrantWorker()
blue
Person--printColor()
blue
Person--printColor()
~MigrantWorker()
~Worker()
~Farmer()
~Person()
请按任意键继续. . .
运行结果中:在虚继承的情况下,作为菱形继承最顶层的父类,并没有进行参数的传递,也就是说参数只使用了顶层父类的默认参数,而无法从子类中获得传入的参数;
6-4 单元巩固
定义Person人类,worker工人类及children儿童类,
worker类中定义数据成员m_strName姓名,
children类中定义成员m_iAge年龄,
worker类及children类均虚公有继承Person类,
定义ChildLabourer童工类,公有继承工人类和儿童类,从而形成菱形继承关系
在main函数中通过new实例化ChildLabourer类的对象,并通过该对象调用Person,Worker及Children类中的成员函数,最后销毁该对象,掌握多重继承,多继承,虚继承的定义方法。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/**
* 定义人类: Person
*/
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person" << endl;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "~Person" << endl;
}
void eat()
{
cout << "eat" << endl;
}
};
/**
* 定义工人类: Worker
* 虚继承人类
*/
class Worker : virtual public Person
{
public:
Worker(string name)
{
m_strName = name;
cout << "Worker" << endl;
}
~Worker()
{
cout << "~Worker" << endl;
}
void work()
{
cout << m_strName << endl;
cout << "work" << endl;
}
protected:
string m_strName;
};
/**
* 定义儿童类:Children
* 虚继承人类
*/
class Children : virtual public Person
{
public:
Children(int age)
{
m_iAge = age;
cout << "Children" << endl;
}
~Children()
{
cout << "~Children" << endl;
}
void play()
{
cout << m_iAge << endl;
cout << "play" << endl;
}
protected:
int m_iAge;
};
/**
* 定义童工类:ChildLabourer
* 公有继承工人类和儿童类
*/
class ChildLabourer:public Worker,public Children
{
public:
ChildLabourer(string name, int age):Worker(name),Children(age)
{
cout << "ChildLabourer" << endl;
}
~ChildLabourer()
{
cout << "~ChildLabourer" << endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
// 用new关键字实例化童工类对象
ChildLabourer *p = new ChildLabourer("tom",14);
// 调用童工类对象各方法。
p->eat();
p->work();
p->play();
delete p;
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
运行成功
Person
Worker
Children
ChildLabourer
eat
tom
work
14
play
~ChildLabourer
~Children
~Worker
~Person





















 746
746

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








