Description
Once there was a rooted tree. The tree contained n nodes, which were numbered 1,…,n. The node numbered 1 was the root of the tree. Besides, every node i was assigned a number ai. Your were surprised to find that there were several pairs of nodes (i,j) satisfying
where ⊕ denotes the bitwise XOR operation, and lca(i,j) is the lowest common ancestor of i and j, or formally, the lowest (i.e. deepest) node that has both i and j as descendants.
Unfortunately, you cannot remember all such pairs, and only remember the sum of i⊕j for all different pairs of nodes (i,j) satisfying the above property. Note that (i,j) and (j,i) are considered the same here. In other words, you will only be able to recall
You are assumed to calculate it now in order to memorize it better in the future.
Input
The first line contains a single integer nn (2≤n≤10^5).
The second line contains nn integers, a1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤10^6).
Each of the next n−1 lines contains 2 integers u and v (1≤u,v≤n,u≠v), indicating that there is an edge between u and v. It is guaranteed that these edges form a tree.
Output
Print what you will memorize in the future.
Example
Input
6
4 2 1 6 6 5
1 2
2 3
1 4
4 5
4 6
Output
18
题目大意:
给定一个含有n个节点的树,求下式的值。
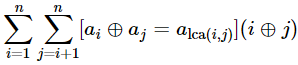
分析:
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45458915/article/details/109583484
具体解释见代码。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mst(a,num) memset(a,num,sizeof a)
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define repd(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PLL;
typedef vector<int> VI;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 100000 + 5;
int a[maxn];
VI edge[maxn];
int sz[maxn],son[maxn];
int cnt[1050000][22][2];
ll ans=0;
void dfs_son(int x,int fa){ //预处理出重儿子
sz[x]=1;
son[x]=0;
for(auto &nod:edge[x]){
if(nod==fa) continue;
dfs_son(nod,x);
sz[x]+=sz[nod];
if(!son[x]||sz[nod]>sz[son[x]]){
son[x]=nod;
}
}
}
void add_one(int x,int val){
for(int i=0;i<=20;i++){
cnt[a[x]][i][(x>>i)&1]+=val;
}
}
void add(int x,int fa,int val){
add_one(x,val);
for(auto &nod:edge[x]){
if(nod==fa) continue;
add(nod,x,val);
}
}
void calc(int x,int fa,int lca){
int tval=a[x]^a[lca];
for(int i=0;i<=20;i++){
ans+=1ll*cnt[tval][i][!((x>>i)&1)]*(1ll<<i);
}
for(auto &nod:edge[x]){
if(nod==fa) continue;
calc(nod,x,lca);
}
}
void dfs(int x,int fa,int keep){ //树上启发式合并
for(auto &nod:edge[x]){
if(nod==fa||nod==son[x]) continue;
dfs(nod,x,0);
}
if(son[x]) dfs(son[x],x,1);
add_one(x,1);
for(auto &nod:edge[x]){
if(nod==fa||nod==son[x]) continue;
calc(nod,x,x);
add(nod,x,1);
}
if(!keep){
add(x,fa,-1);
}
}
int main() {
int n,u,v;
scanf("%d",&n);
rep(i,1,n){
scanf("%d",a+i);
}
rep(i,1,n-1){
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
edge[u].push_back(v);
edge[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs_son(1,0);
dfs(1,0,1);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}
























 325
325











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








