核心编程
累加器——分布式共享只写变量
- 实现原理
累加器用来把 Executor 端变量信息聚合到 Driver 端。在 Driver 程序中定义的变量,在Executor 端的每个 Task 都会得到这个变量的一份新的副本,每个 task 更新这些副本的值后,传回 Driver 端进行 merge。
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(1, 2, 3, 4))
var sum = 0
rdd.foreach(
num => {
sum += num
println(sum)
}
)
println("sum " + sum) //sum 0

在Executor中的sum并未传回到Driver中,所以打印出来的sum值仍然是0。
//获取系统累加器
val sumAcc = sc.longAccumulator("sum")
rdd.foreach(
num => {
//使用累加器
sumAcc.add(num)
}
)
println(sumAcc.value) //10
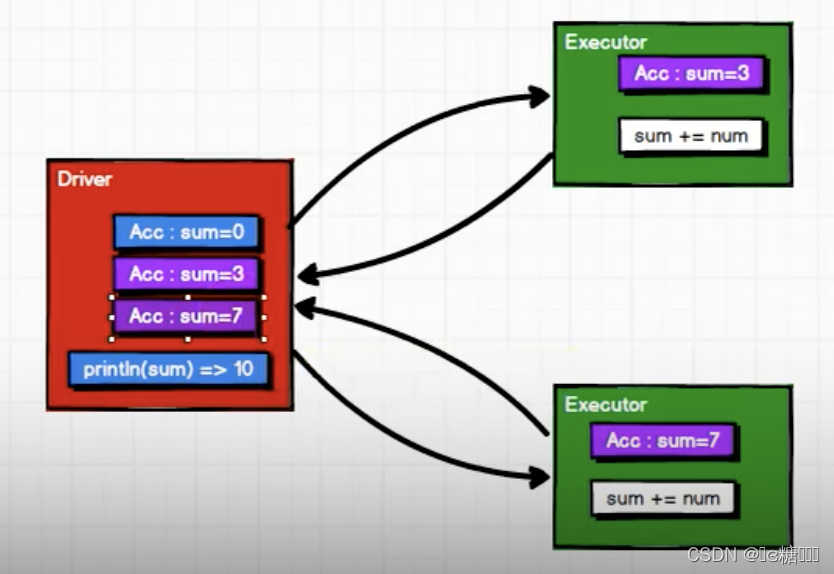
累加器将Executor端变量信息聚合到Driver端。
- 累加器的问题
(1)若累加器放在转换算子中执行,如map,如果没有行动算子,那么不会执行——少加
(2)如果累加器放在转换算子中,又多次调用了行动算子,那么就会多加
(3)所以一般情况下,累加器放置在行动算子中进行操作
- 自定义累加器(实现wordCount)
package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.acc
import org.apache.spark.util.AccumulatorV2
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import scala.collection.mutable
object Spark02_RDD_Acc_wordcount {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List("Hello", "Scala", "Hello", "Spark"))
//累加器:wordCount 不走reduceByKey,不进行shuffle操作
//创建累加器
val wcAcc = new MyAccumulator()
//向Spark进行注册
sc.register(wcAcc, "wordCountAcc")
rdd.foreach(
word => {
wcAcc.add(word)
}
)
println(wcAcc.value)
//Map(Hello -> 2, Spark -> 1, Scala -> 1)
sc.stop()
}
/*
自定义数据累加器:WordCount
1. 继承AccumulatorV2,定义泛型
IN:累加器输入的数据类型 String
OUT:累加器返回的数据类型 mutable.Map[String, Long]
*/
class MyAccumulator extends AccumulatorV2[String, mutable.Map[String, Long]] {
private var wcMap = mutable.Map[String, Long]()
//判断是否为初始状态
override def isZero: Boolean = {
wcMap.isEmpty
}
override def copy(): AccumulatorV2[String, mutable.Map[String, Long]] = {
new MyAccumulator()
}
//清空累加器
override def reset(): Unit = {
wcMap.clear()
}
override def add(word: String): Unit = {
val newCnt = wcMap.getOrElse(word, 0L) + 1
wcMap.update(word, newCnt)
}
//Driver 合并多个累加器
override def merge(other: AccumulatorV2[String, mutable.Map[String, Long]]): Unit = {
val map1 = this.wcMap
val map2 = other.value
//map的合并
map2.foreach{
case (word, count) => {
val newCount = map1.getOrElse(word, 0L) + count
map1.update(word, newCount)
}
}
}
//累加器结果
override def value: mutable.Map[String, Long] = {
wcMap
}
}
}
广播变量——分布式共享只读变量
广播变量用来高效分发较大的对象。向所有工作节点发送一个较大的只读值,以供一个或多个 Spark 操作使用。比如,如果你的应用需要向所有节点发送一个较大的只读查询表,广播变量用起来都很顺手。在多个并行操作中使用同一个变量,但是 Spark 会为每个任务分别发送。
package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.acc
import org.apache.spark.broadcast.Broadcast
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import scala.collection.mutable
object Spark03_RDD_BC {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(List(
("a", 1), ("a", 2), ("c", 3)
))
// val rdd2 = sc.makeRDD(List(
// ("a", 4), ("b", 5), ("c", 6)
// ))
//
// //笛卡尔积导致数据量增长较大,并且影响shuffle的性能 不推荐使用
// val joinRDD: RDD[(String, (Int, Int))] = rdd1.join(rdd2)
// joinRDD.collect().foreach(println)
val map = mutable.Map(("a", 4), ("b", 5), ("c", 6))
//封装广播变量
val bc: Broadcast[mutable.Map[String, Int]] = sc.broadcast(map)
rdd1.map {
case (w, c) => {
// 方法广播变量
val l: Int = bc.value.getOrElse(w, 0)
(w, (c, l))
}
}.collect().foreach(println)
//(a,(1,4))
//(b,(2,5))
//(c,(3,6))
sc.stop()
}
}
Spark案例实操
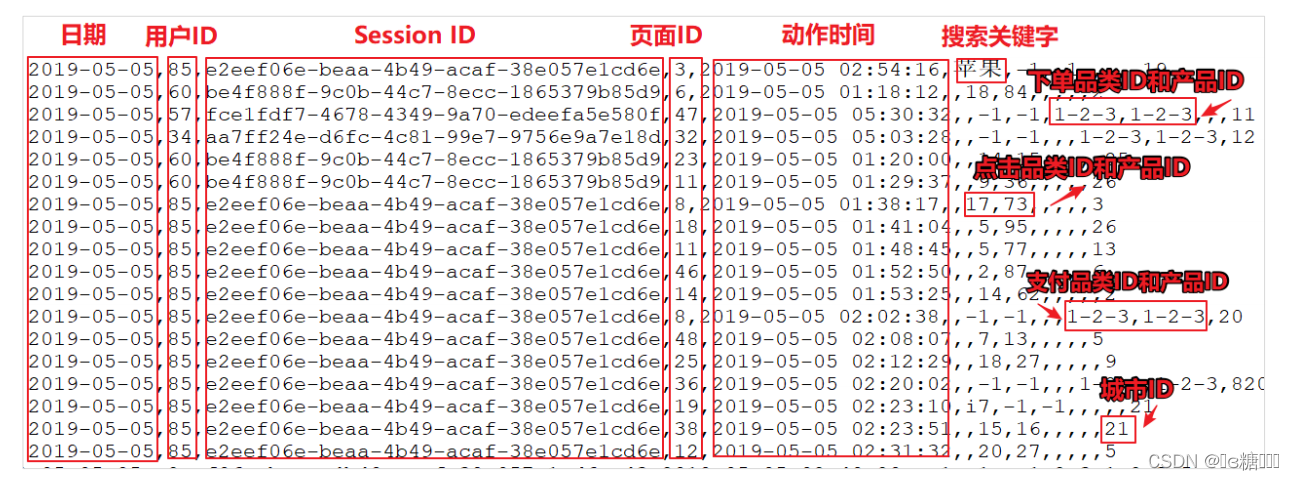
上面的数据图是从数据文件中截取的一部分内容,表示为电商网站的用户行为数据,主要包含用户的 4 种行为:搜索,点击,下单,支付。数据规则如下:
➢ 数据文件中每行数据采用下划线分隔数据
➢ 每一行数据表示用户的一次行为,这个行为只能是 4 种行为的一种
➢ 如果搜索关键字为 null,表示数据不是搜索数据
➢ 如果点击的品类 ID 和产品 ID 为-1,表示数据不是点击数据
➢ 针对于下单行为,一次可以下单多个商品,所以品类 ID 和产品 ID 可以是多个,id 之间采用逗号分隔,如果本次不是下单行为,则数据采用 null 表示
➢ 支付行为和下单行为类似
Top10热门品类
1. 按照每个品类的点击、下单、支付的量来统计热门品类,取前10。
方案一:
package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.Example
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object Spark01_Req1_HotCateTop10 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// Top10热门品类
//1. 读取数据
val actionRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/user_visit_action.txt")
//2. 统计品类的点击数量 (品类ID,点击数量)
val clickActionRDD: RDD[String] = actionRDD.filter(
action => {
val datas: Array[String] = action.split("_")
datas(6) != "-1"
}
)
val clickCountRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = clickActionRDD.map(
action => {
val datas = action.split(("_"))
(datas(6), 1)
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _)
//3. 统计品类的下单数量 (品类ID,下单数量)
val orderActionRDD: RDD[String] = actionRDD.filter(
action => {
val datas: Array[String] = action.split("_")
datas(8) != "null"
}
)
val orderCountRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = orderActionRDD.flatMap(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
val cid = datas(8) //取出订单品类集合
val cids = cid.split(",")
cids.map(id => (id, 1))
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _)
//4. 统计品类的支付数量 (品类ID,支付数量)
val payActionRDD: RDD[String] = actionRDD.filter(
action => {
val datas: Array[String] = action.split("_")
datas(10) != "null"
}
)
val payCountRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = payActionRDD.flatMap(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
val cid = datas(10)
val cids = cid.split(",")
cids.map(id => (id, 1))
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _)
//5. 品类排序,取前10 点击数量 下单数量 支付数量
// 元组排序:先比较第一个,再第二个,再第三个……
// (品类ID,(点击数量,下单数量,支付数量) )
//join就是把两个集合根据key,进行内容聚合, 在这里可能会出现点击A,并未下单A,下单了B的情况
// cogroup在聚合时会先对RDD中相同的key进行合并
val cogroupRDD: RDD[(String, (Iterable[Int], Iterable[Int], Iterable[Int]))] = {
clickCountRDD.cogroup(orderCountRDD, payCountRDD)}
val analysisRDD = cogroupRDD.mapValues{
case (clickIter, orderIter, payIter) =>
var clickCnt = 0
val iter1 = clickIter.iterator
if (iter1.hasNext) {
clickCnt = iter1.next()
}
var orderCnt = 0
val iter2 = orderIter.iterator
if (iter2.hasNext) {
orderCnt = iter2.next()
}
var payCnt = 0
val iter3 = payIter.iterator
if (iter3.hasNext) {
payCnt = iter3.next()
}
(clickCnt, orderCnt, payCnt)
}
val resultRdd = analysisRDD.sortBy(_._2, false).take(10)
//6. 采集结果,进行打印
resultRdd.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
存在的问题:
1.actionRdd重复使用 —>actionRdd.cache()
2.cogroup有可能存在shuffle,性能较低
方案二:不使用cogroup

package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.Example
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object Spark02_Req1_HotCateTop10 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// Top10热门品类
//1. 读取数据
val actionRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/user_visit_action.txt")
actionRDD.cache()
//2. 统计品类的点击数量 (品类ID,点击数量)
val clickActionRDD: RDD[String] = actionRDD.filter(
action => {
val datas: Array[String] = action.split("_")
datas(6) != "-1"
}
)
val clickCountRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = clickActionRDD.map(
action => {
val datas = action.split(("_"))
(datas(6), 1)
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _)
//3. 统计品类的下单数量 (品类ID,下单数量)
val orderActionRDD: RDD[String] = actionRDD.filter(
action => {
val datas: Array[String] = action.split("_")
datas(8) != "null"
}
)
val orderCountRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = orderActionRDD.flatMap(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
val cid = datas(8) //取出订单品类集合
val cids = cid.split(",")
cids.map(id => (id, 1))
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _)
//4. 统计品类的支付数量 (品类ID,支付数量)
val payActionRDD: RDD[String] = actionRDD.filter(
action => {
val datas: Array[String] = action.split("_")
datas(10) != "null"
}
)
val payCountRDD: RDD[(String, Int)] = payActionRDD.flatMap(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
val cid = datas(10)
val cids = cid.split(",")
cids.map(id => (id, 1))
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _)
//5. 品类排序,取前10 点击数量 下单数量 支付数量
// 元组排序:先比较第一个,再第二个,再第三个……
// (品类ID,(点击数量,下单数量,支付数量) )
val rdd1 = clickCountRDD.map {
case (cid, cnt) => {
(cid, (cnt, 0, 0))
}
}
val rdd2 = orderCountRDD.map {
case (cid, cnt) => {
(cid, (0, cnt, 0))
}
}
val rdd3 = payCountRDD.map {
case (cid, cnt) => {
(cid, (0, 0, cnt))
}
}
//将三个数据源合并在一起,然后统一进行聚合计算
val sourceRdd: RDD[(String, (Int, Int, Int))] = rdd1.union(rdd2).union(rdd3)
val analysisRDD = sourceRdd.reduceByKey(
(t1, t2) => {
(t1._1 + t2._1, t1._2 + t2._2, t1._3 + t2._3)
}
)
val resultRdd = analysisRDD.sortBy(_._2, false).take(10)
//6. 采集结果,进行打印
resultRdd.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
问题:
存在大量的shuffle操作(reduceByKey)
方案三: 减少reduceByKey操作
package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.Example
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object Spark03_Req1_HotCateTop10 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// Top10热门品类
//1. 读取数据
val actionRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/user_visit_action.txt")
//2. 将数据转换结构
val flatRDD: RDD[(String, (Int, Int, Int))] = actionRDD.flatMap(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
if (datas(6) != "-1") {
//点击的场合
List((datas(6), (1, 0, 0)))
} else if (datas(8) != "null") {
//下单的场合
val ids = datas(8).split(",")
ids.map(id => (id, (0, 1, 0)))
} else if (datas(10) != "null") {
//支付的场合
val ids = datas(10).split(",")
ids.map(id => (id, (0, 0, 1)))
} else {
Nil
}
}
)
//3. 将相同的品类ID的数据进行分组聚合
val analysisRDD: RDD[(String, (Int, Int, Int))] = flatRDD.reduceByKey(
(t1, t2) => {
(t1._1 + t2._1, t1._2 + t2._2, t1._3 + t2._3)
}
)
//4. 将统计结果进行排序
val resultRdd = analysisRDD.sortBy(_._2, false).take(10)
//5. 采集结果,进行打印
resultRdd.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
方案四:不使用shuffle,使用累加器
package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.Example
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.util.AccumulatorV2
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import scala.collection.mutable
object Spark04_Req1_HotCateTop10 {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// Top10热门品类
//1. 读取数据
val actionRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/user_visit_action.txt")
val acc = new HotCategoryAccumulator
sc.register(acc, "hotCategory")
//2. 将数据转换结构
actionRDD.foreach(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
if (datas(6) != "-1") {
//点击的场合
acc.add(datas(6), "click")
} else if (datas(8) != "null") {
//下单的场合
val ids = datas(8).split(",")
ids.foreach(
id => {
acc.add(id, "order")
}
)
} else if (datas(10) != "null") {
//支付的场合
val ids = datas(10).split(",")
ids.foreach(
id => {
acc.add(id, "pay")
}
)
}
}
)
val accVal: mutable.Map[String, HotCategory] = acc.value
val categories: mutable.Iterable[HotCategory] = accVal.map(_._2)
val sort = categories.toList.sortWith(
(left, right) =>
if (left.clickCnt > right.clickCnt) {
true
} else if (left.clickCnt == right.clickCnt) {
if (left.orderCnt > right.orderCnt) {
true
} else if (left.orderCnt == left.orderCnt) {
left.payCnt > right.payCnt
}
else {
false
}
} else {
false
}
)
//5. 采集结果,进行打印
sort.take(10).foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
case class HotCategory(cid: String, var clickCnt: Int, var orderCnt: Int, var payCnt: Int)
/**
* 自定义累加器
* 1. 继承AccumulatorV2,定义泛型
* IN:( 品类ID,行为类型)
* OUT:mutable.Map[String, HotCategory]
* 2. 重写方法
*/
class HotCategoryAccumulator extends AccumulatorV2[(String,String), mutable.Map[String, HotCategory]] {
private val hcMap: mutable.Map[String, HotCategory] = mutable.Map[String, HotCategory]()
override def isZero: Boolean = {
hcMap.isEmpty
}
override def copy(): AccumulatorV2[(String, String), mutable.Map[String, HotCategory]] = {
new HotCategoryAccumulator
}
override def reset(): Unit = {
hcMap.clear()
}
override def add(v: (String, String)): Unit = {
val cid = v._1
val actionType = v._2
val category = hcMap.getOrElse(cid, HotCategory(cid, 0, 0, 0))
if (actionType == "click") {
category.clickCnt += 1
}else if (actionType == "order") {
category.orderCnt += 1
}else if (actionType == "pay") {
category.payCnt += 1
}
hcMap.update(cid, category)
}
override def merge(other: AccumulatorV2[(String, String), mutable.Map[String, HotCategory]]): Unit = {
val map1 = this.hcMap
val map2 = other.value
map2.foreach {
case (cid, hc) => {
val category = map1.getOrElse(cid, HotCategory(cid, 0, 0, 0))
category.clickCnt += hc.clickCnt
category.orderCnt += hc.orderCnt
category.payCnt += hc.payCnt
map1.update(cid, category) //更新
}
}
}
override def value: mutable.Map[String, HotCategory] = hcMap
}
}
- Top10热门品类中每个品类的Top10活跃Session统计
package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.Example
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object Spark05_Req2_HotCateTop10Session {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// Top10热门品类
//1. 读取数据
val actionRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/user_visit_action.txt")
actionRDD.cache()
val top10ids: Array[String] = top10Category(actionRDD)
//1. 过滤原始数据,保留点击和前10品类ID ———— 过滤数据源
val filterActionRDD: RDD[String] = actionRDD.filter(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
if (datas(6) != "-1") {
top10ids.contains(datas(6))
} else {
false
}
}
)
//2. 根据品类ID和session进行点击量的统计 ((品类id,sessID),sum)
val reduceRDD: RDD[((String, String), Int)] = filterActionRDD.map(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
((datas(6), datas(2)), 1)
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _)
//3. 将统计的结果进行结构的转换 ((品类id,sessID),sum) =》 (品类ID,(sessID, sum))
val mapRDD: RDD[(String, (String, Int))] = reduceRDD.map {
case ((cid, sid), sum) =>
(cid, (sid, sum))
}
//4. 将相同的品类进行分组
val groupRDD: RDD[(String, Iterable[(String, Int)])] = mapRDD.groupByKey()
//5. 将分组后数据的点击量进行排序取前十
val resultRDD: RDD[(String, List[(String, Int)])] = groupRDD.mapValues(
iter => {
iter.toList.sortBy(_._2)(Ordering.Int.reverse).take(10)
}
)
resultRDD.cache().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
def top10Category(actionRDD: RDD[String]) = {
val flatRDD: RDD[(String, (Int, Int, Int))] = actionRDD.flatMap(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
if (datas(6) != "-1") {
//点击的场合
List((datas(6), (1, 0, 0)))
} else if (datas(8) != "null") {
//下单的场合
val ids = datas(8).split(",")
ids.map(id => (id, (0, 1, 0)))
} else if (datas(10) != "null") {
//支付的场合
val ids = datas(10).split(",")
ids.map(id => (id, (0, 0, 1)))
} else {
Nil
}
}
)
val analysisRDD: RDD[(String, (Int, Int, Int))] = flatRDD.reduceByKey(
(t1, t2) => {
(t1._1 + t2._1, t1._2 + t2._2, t1._3 + t2._3)
}
)
analysisRDD.sortBy(_._2, false).take(10).map(_._1)
}
}
- 页面单跳转换率统计
package com.yu.bigdata.spark.core.Example
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object Spark07_Req3_PageFlow {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
// Top10热门品类
val actionRDD: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("datas/user_visit_action.txt")
val actionDataRDD = actionRDD.map(
action => {
val datas = action.split("_")
UserVisitAction(
datas(0),
datas(1).toLong,
datas(2),
datas(3).toLong,
datas(4),
datas(5),
datas(6).toLong,
datas(7).toLong,
datas(8),
datas(9),
datas(10),
datas(11),
datas(12).toLong,
)
}
)
actionDataRDD.cache()
// TODO 对指定的页面连续跳转进行统计
val ids = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
val okflowIds: List[(Int, Int)] = ids.zip(ids.tail)
// TODO 计算分母
val pageidToCountMap: Map[Long, Long] = actionDataRDD.filter(
action => {
ids.init.contains(action.page_id)
}
).map(
action => {
(action.page_id, 1L)
}
).reduceByKey(_ + _).collect().toMap //采集形成结果 数组
// TODO 计算分子
// 根据session进行分组
val sessionRDD: RDD[(String, Iterable[UserVisitAction])] = actionDataRDD.groupBy(_.session_id)
// 分组后,根据访问时间进行排序(升序)
val mvRDD: RDD[(String, List[((Long, Long), Int)])] = sessionRDD.mapValues(
iter => {
val sortList: List[UserVisitAction] = iter.toList.sortBy(_.action_time)
// 取出id
val flowIds: List[Long] = sortList.map(_.page_id)
// 拉链形成 (首页id, 详情id)跳转页面
val pageflowIds: List[(Long, Long)] = flowIds.zip(flowIds.tail)
// 形成 (id, id, 1)
// 将不合法的页面跳转进行过滤
pageflowIds.filter(
t => {
okflowIds.contains(t)
}
).map(
t => (t, 1)
)
}
)
//(1, 2, 1)
val flatRDD: RDD[((Long, Long), Int)] = mvRDD.map(_._2).flatMap(list => list)
//val value: RDD[((Long, Long), Int)] = mvRDD.flatMap(_._2)
//(1, 2, sum)
val dataRDD: RDD[((Long, Long), Int)] = flatRDD.reduceByKey(_ + _)
// TODO 计算跳单转换率
// 分子除以分母
dataRDD.foreach{
case ((pageid1, pageid2), sum) => {
val long: Long = pageidToCountMap.getOrElse(pageid1, 0L)
println(s"页面${pageid1}跳转到${pageid2}单跳转换率为: " + sum.toDouble/long)
}
}
sc.stop()
}
//用户访问动作表
case class UserVisitAction(
date: String,//用户点击行为的日期
user_id: Long,//用户的 ID
session_id: String,//Session 的 ID
page_id: Long,//某个页面的 ID
action_time: String,//动作的时间点
search_keyword: String,//用户搜索的关键词
click_category_id: Long,//某一个商品品类的 ID
click_product_id: Long,//某一个商品的 ID
order_category_ids: String,//一次订单中所有品类的 ID 集合
order_product_ids: String,//一次订单中所有商品的 ID 集合
pay_category_ids: String,//一次支付中所有品类的 ID 集合
pay_product_ids: String,//一次支付中所有商品的 ID 集合
city_id: Long
)//城市 id
}
工程化代码——架构模式
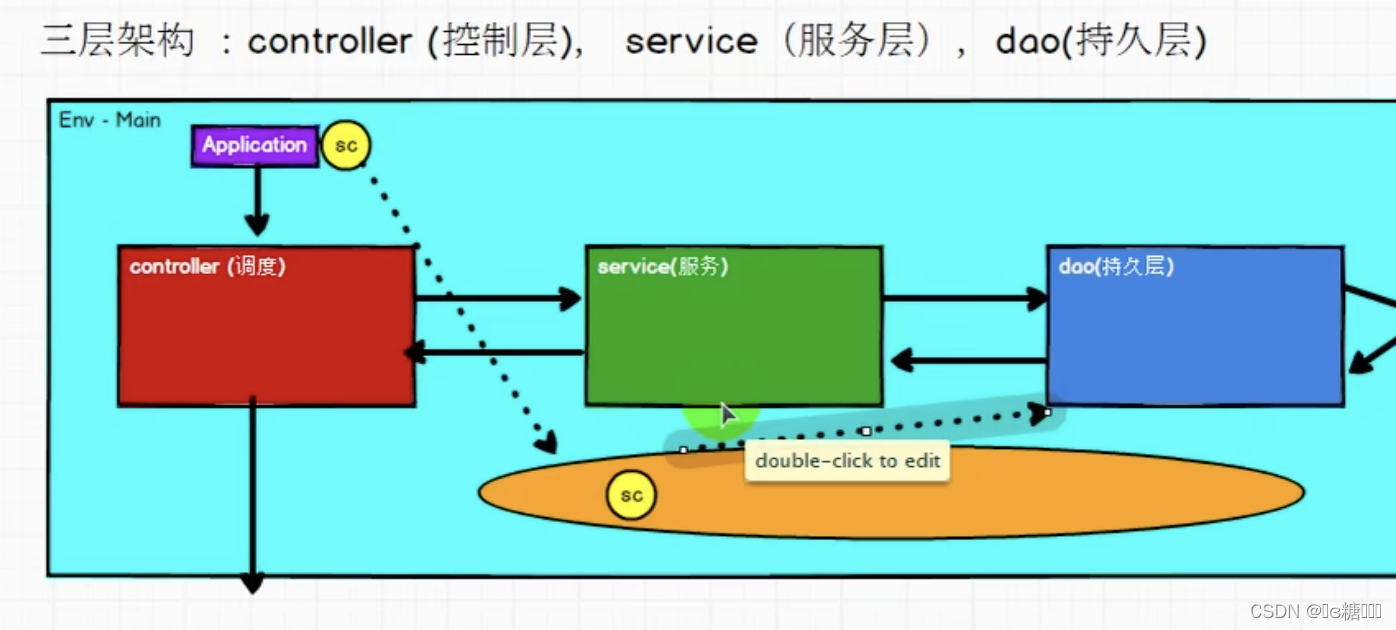
Dao读取数据给service,service中的逻辑执行完,结果返回到Controller,根据结果来做调度,再传到应用程序中。
数据–>Dao、逻辑–>Service、输出–>调度
ThreadLocal可以对线程的内存进行控制,存储数据,共享数据。





















 2829
2829











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








