典型的C++面向对象编程
元素
(1)头文件hpp中类的定义
(2)源文件cpp中类的实现(构造函数、析构函数、方法)
(3)主程序
案例
(1)用C++来编程“人一天的生活”
(2)“人”的属性:name、age、male
(3)“人”的方法:eat、work(coding/shopping)、sleep
(4)人的生活:eat1->work->eat2->work->sleep
实战中,一般一个cpp和一个hpp文件配对,描述一个class,class的名字和文件名相同的。
.h 文件
namespace MAN{
class testperson {
public:
//属性
string name;
int age;
bool male; //性别 男性 ture
//方法
void eat(void);
void work(void);
void sleep(void);
testperson(/* args */);
~testperson();
};
.c 文件
using namespace MAN;
testperson::testperson(/* args */) {}
testperson::~testperson() {}
void testperson::eat(void) { cout << this->name << "-eat" << endl; }
void testperson::work(void) {
if (this->male == 1) {
cout << name << "-coding" << endl;
} else {
cout << name << "-shopping" << endl;
}
}
void testperson::sleep(void) { cout << name << "-sleep" << endl; }
int test() {
testperson xioahong; //局部变量 分配在栈上
testperson *xiaoming =
new testperson(); // 动态内存 分配在自由内存空间,其实就是对堆上
// 自己管理内存
xiaoming->name = "jiajia";
xiaoming->age = 99;
xiaoming->male = true;
xiaoming->eat();
xiaoming->work();
xiaoming->eat();
xiaoming->work();
xiaoming->sleep();
return 0;
}
代码:
testperson xiaoming = new testperson();
报错:
error: conversion from ‘testperson*’ to non-scalar type ‘testperson’
requested 1071 | new testperson();version from ‘testperson*’ to
non-scalar type ‘testperson’ requested 1071 | new testperson();
修改:
testperson *xiaoming = new testperson();
-
C++面向对象式编程总结
(1)整个工作分为2大块:一个是建模和编写类库,一个是使用类库来编写主程序完成任务。
(2)有些人只负责建模和编写类库,譬如开发opencv的人。
(3)有些人直接调用现成类库来编写自己的主任务程序,譬如使用opencv分析一张图片中有没有电动车
(4)难度上不确定,2个都可能很难或者很简单。 -
C++学习的三重境界
(1)学习C++第一重境界就是语法层面,先学会如何利用C++来建模、来编程,学习语法时先别解决难度大问题。
(2)学习C++第二重境界是解决问题层面,学习如果理解并调用现成类库来编写主程序解决问题。
(3)学习C++第三重境界是编写类库和sample给别人用,需要基础好且有一定架构思维。
在构造和析构函数中使用动态内存
析构函数的使用
(1)析构函数在对象对销毁时自动调用,一般有2种情况
(2)用new分配的对象,用delete显式析构
(3)分配在栈上的对象,当栈释放时自动析构
(4)普通情况下析构函数都是空的,因为不必做什么特别的事情
class testperson {
public:
//属性
string name;
int age;
bool male; //性别 男性 ture
//方法
void eat(void);
void work(void);
void sleep(void);
testperson(/* args */);
~testperson();
};
testperson::testperson(/* args */) { cout << name << "1" << endl; }
testperson::~testperson() { cout << name << "2" << endl; }
void testperson::eat(void) { cout << this->name << "-eat" << endl; }
void testperson::work(void) {
if (this->male == 1) {
cout << name << "-coding" << endl;
} else {
cout << name << "-shopping" << endl;
}
}
void testperson::sleep(void) { cout << name << "-sleep" << endl; }
int test0625006() {
testperson *xiaohong1 =
new testperson(); // 动态内存 分配在自由内存空间,其实就是对堆上
// 自己管理内存
xiaohong1->name = "jiajia";
xiaohong1->age = 99;
xiaohong1->male = true;
xiaohong1->eat();
xiaohong1->work();
xiaohong1->eat();
xiaohong1->work();
xiaohong1->sleep();
delete xiaohong1; //添加才会执行析构函数
testperson xiaohong; //局部变量 分配在栈上
xiaohong.name = "meimei";
xiaohong.age = 99;
xiaohong.male = true;
xiaohong.eat();
xiaohong.work();
xiaohong.eat();
xiaohong.work();
xiaohong.sleep();
return 0;
}
- 在class中使用动态内存变量
(1)什么情况下用动态内存?需要大块内存,且需要按需灵活的申请和释放,用栈怕爆、用全局怕浪费和死板时
(2)在class person中增加一个int *指针,用于指向一个int类型元素的内存空间
(3)在构造函数中分配动态内存
(4)在析构函数中回收动态内存
(5)将动态内存从int变量升级到int数组变量
(6)实战中C++常用的动态内存往往是容器vector那些,课程第3部分会讲到
class testperson {
public:
//属性
string name;
int age;
bool male; //性别 男性 ture
int *pint;
//方法
void eat(void);
void work(void);
void sleep(void);
testperson(/* args */);
~testperson();
};
testperson::testperson(/* args */) {
this->pint = new int(99);//分配、初始化
cout << name << "1" << endl;
}
testperson::~testperson() {
cout << name << "2" << endl;
delete this->pint;//回收
}
void testperson::eat(void) { cout << this->name << "-eat" << endl; }
void testperson::work(void) {
if (this->male == 1) {
cout << name << "-coding" << endl;
} else {
cout << name << "-shopping" << endl;
}
cout << "this->pint:" << *(this->pint) << endl;//使用
}
void testperson::sleep(void) { cout << name << "-sleep" << endl; }
int test0625006() {
testperson *xiaohong1 =
new testperson(); // 动态内存 分配在自由内存空间,其实就是对堆上
// 自己管理内存
xiaohong1->name = "jiajia";
xiaohong1->age = 99;
xiaohong1->male = true;
xiaohong1->eat();
xiaohong1->work();
xiaohong1->eat();
xiaohong1->work();
xiaohong1->sleep();
delete xiaohong1; //添加才会执行析构函数
testperson xiaohong; //局部变量 分配在栈上
xiaohong.name = "meimei";
xiaohong.age = 99;
xiaohong.male = true;
xiaohong.eat();
xiaohong.work();
xiaohong.eat();
xiaohong.work();
xiaohong.sleep();
return 0;
}
申请更多的空间
class testperson {
public:
//属性
string name;
int age;
bool male; //性别 男性 ture
int *pint;
char *pchar;
//方法
void eat(void);
void work(void);
void sleep(void);
testperson(/* args */);
~testperson();
};
testperson::testperson(/* args */) {
this->pint = new int(99); //分配、初始化
this->pchar = new char[20]; //分配、初始化
cout << name << "1" << endl;
}
testperson::~testperson() {
cout << name << "2" << endl;
delete this->pint; //回收
delete[] this->pchar; //回收
}
void testperson::eat(void) { cout << this->name << "-eat" << endl; }
void testperson::work(void) {
if (this->male == 1) {
cout << name << "-coding" << endl;
} else {
cout << name << "-shopping" << endl;
}
cout << "this->pint:" << *(this->pint) << endl; //使用
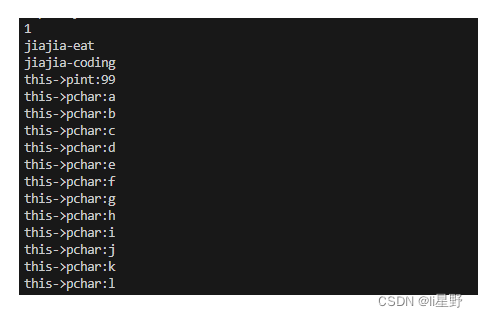
for (size_t i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
*(this->pchar) = 'a'+ i;
cout << "this->pchar:" << *(this->pchar) << endl; //使用
}
}
void testperson::sleep(void) { cout << name << "-sleep" << endl; }
int test0625006() {
testperson *xiaohong1 =
new testperson(); // 动态内存 分配在自由内存空间,其实就是对堆上
// 自己管理内存
xiaohong1->name = "jiajia";
xiaohong1->age = 99;
xiaohong1->male = true;
xiaohong1->eat();
xiaohong1->work();
xiaohong1->eat();
xiaohong1->work();
xiaohong1->sleep();
delete xiaohong1; //添加才会执行析构函数
testperson xiaohong; //局部变量 分配在栈上
xiaohong.name = "meimei";
xiaohong.age = 99;
xiaohong.male = true;
xiaohong.eat();
xiaohong.work();
xiaohong.eat();
xiaohong.work();
xiaohong.sleep();
return 0;
}
用valgrind工具查看内存泄漏
(1)valgrind工具介绍:参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u012662731/article/details/78652651
(2)安装:
sudo apt-get install valgrind
(ubuntu16.04 X64)sudo apt-get install valgrind
(3)编译程序:主要是添加-g参数便于调试时有行号 g++ person.cpp main.cpp -g -o apptest
(4)使用:valgrind --tool=memcheck --leak-check=full --show-reachable=yes --trace-children=yes ./app
- valgrind和Cmake工程结合
1、在CMakeLists.txt文件添加
SET(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug")
2、使用下面语句生成了日志3_g,将test换成你自己的工程名称
valgrind --leak-check=yes --log-file=3_g ./build/test
总结:
学会分文件创建一个类,并且使用起来
学会使用valgrind查看日志
学习记录,侵权联系删除。
来源:朱老师物联网大课堂

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










