增强现实(AR)是一种对摄像机拍摄的影像的基础上添加图像的技术。因为是初次的尝试,就先使用图像来实现添加图像的技术。
1.以平面和标记物进行姿态估计
先从简单的实现做起。平面和标记物姿态估计可以通过图像已标记的物体,和已经标定的照相机来计算得出相机拍摄时候的姿态(相机的位移和旋转变换)
这种方法的思路如下。我们有两张不同角度拍摄的图像。首先,通过sift特征提取,RANSAC算法得到估计的单应性矩阵(关于SIFT,RANSAC和单应性矩阵,在我之前的博文有介绍)。其次,因为这个单应性矩阵是估计出来,所以代码中会对其进行验证,通过画一个正方形来判断单应性矩阵是否正确。最后,在画出正方体来看出相机的物理位置的变换。
实现代码如下:
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
# If you have PCV installed, these imports should work
from PCV.geometry import homography, camera
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
"""
This is the augmented reality and pose estimation cube example from Section 4.3.
"""
def cube_points(c, wid):
""" Creates a list of points for plotting
a cube with plot. (the first 5 points are
the bottom square, some sides repeated). """
p = []
# bottom
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid]) # same as first to close plot
# top
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid]) # same as first to close plot
# vertical sides
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid])
return array(p).T
def my_calibration(sz):
"""
Calibration function for the camera (iPhone4) used in this example.
"""
row, col = sz
fx = 2555 * col / 2592
fy = 2586 * row / 1936
K = diag([fx, fy, 1])
K[0, 2] = 0.5 * col
K[1, 2] = 0.5 * row
return K
# compute features
sift.process_image('E:/Py_code/photo/Fourth/rs1.jpg', 'im0.sift')
l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')
sift.process_image('E:/Py_code/photo/Fourth/rs2.jpg', 'im1.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')
# match features and estimate homography
matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)
model = homography.RansacModel()
H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)
# camera calibration
K = my_calibration((1080, 1920))
# 3D points at plane z=0 with sides of length 0.2
box = cube_points([0, 0, 0.1], 0.1)
# project bottom square in first image
cam1 = camera.Camera(hstack((K, dot(K, array([[0], [0], [-1]])))))
# first points are the bottom square
box_cam1 = cam1.project(homography.make_homog(box[:, :5]))
# use H to transfer points to the second image
box_trans = homography.normalize(dot(H, box_cam1))
# compute second camera matrix from cam1 and H
cam2 = camera.Camera(dot(H, cam1.P))
A = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P[:, :3])
A = array([A[:, 0], A[:, 1], cross(A[:, 0], A[:, 1])]).T
cam2.P[:, :3] = dot(K, A)
# project with the second camera
box_cam2 = cam2.project(homography.make_homog(box))
# plotting
im0 = array(Image.open('E:/Py_code/photo/Fourth/rs1.jpg'))
im1 = array(Image.open('E:/Py_code/photo/Fourth/rs2.jpg'))
figure()
imshow(im0)
plot(box_cam1[0, :], box_cam1[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('2D projection of bottom square')
axis('off')
figure()
imshow(im1)
plot(box_trans[0, :], box_trans[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('2D projection transfered with H')
axis('off')
figure()
imshow(im1)
plot(box_cam2[0, :], box_cam2[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('3D points projected in second image')
axis('off')
show()
需要注意的是K = my_calibration((1080, 1920))表示图像的大小,需要根据自己的图像来调节。
实现结果如下:



2.在图像中放置虚拟物体
这个的实现,就类似AR的应用,在标记的物体中添加虚拟的物体,只是这个的实现是在图像上,而不是针对视频。这里需要使用两个工具包PyOpenGL和PyGame。安装这两个工具包只需要在cmd中分别输入
pip install PyOpenGL
pip install PyGame
等待安装成功就可以。
以下是代码的具体实现:
import math
import pickle
from pylab import *
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
import pygame, pygame.image
from pygame.locals import *
from PCV.geometry import homography, camera
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
def cube_points(c, wid):
""" Creates a list of points for plotting
a cube with plot. (the first 5 points are
the bottom square, some sides repeated). """
p = []
# bottom
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid]) # same as first to close plot
# top
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid]) # same as first to close plot
# vertical sides
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] - wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] - wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] + wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] + wid])
p.append([c[0] + wid, c[1] - wid, c[2] - wid])
return array(p).T
def my_calibration(sz):
row, col = sz
fx = 2555 * col / 2592
fy = 2586 * row / 1936
K = diag([fx, fy, 1])
K[0, 2] = 0.5 * col
K[1, 2] = 0.5 * row
return K
def set_projection_from_camera(K):
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)
glLoadIdentity()
fx = K[0, 0]
fy = K[1, 1]
fovy = 2 * math.atan(0.5 * height / fy) * 180 / math.pi
aspect = (width * fy) / (height * fx)
near = 0.1
far = 100.0
gluPerspective(fovy, aspect, near, far)
glViewport(0, 0, width, height)
def set_modelview_from_camera(Rt):
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
glLoadIdentity()
Rx = np.array([[1, 0, 0], [0, 0, -1], [0, 1, 0]])
R = Rt[:, :3]
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(R)
R = np.dot(U, V)
R[0, :] = -R[0, :]
t = Rt[:, 3]
M = np.eye(4)
M[:3, :3] = np.dot(R, Rx)
M[:3, 3] = t
M = M.T
m = M.flatten()
glLoadMatrixf(m)
def draw_background(imname):
bg_image = pygame.image.load(imname).convert()
bg_data = pygame.image.tostring(bg_image, "RGBX", 1)
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
glLoadIdentity()
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D)
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, glGenTextures(1))
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, bg_data)
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST)
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST)
glBegin(GL_QUADS)
glTexCoord2f(0.0, 0.0);
glVertex3f(-1.0, -1.0, -1.0)
glTexCoord2f(1.0, 0.0);
glVertex3f(1.0, -1.0, -1.0)
glTexCoord2f(1.0, 1.0);
glVertex3f(1.0, 1.0, -1.0)
glTexCoord2f(0.0, 1.0);
glVertex3f(-1.0, 1.0, -1.0)
glEnd()
glDeleteTextures(1)
def draw_teapot(size):
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING)
glEnable(GL_LIGHT0)
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST)
glClear(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_AMBIENT, [0, 0, 0, 0])
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_DIFFUSE, [0.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.0])
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_SPECULAR, [0.7, 0.6, 0.6, 0.0])
glMaterialf(GL_FRONT, GL_SHININESS, 0.25 * 128.0)
glutSolidTeapot(size)
width, height = 960,540
def setup():
pygame.init()
pygame.display.set_mode((width, height), OPENGL | DOUBLEBUF)
pygame.display.set_caption("OpenGL AR demo")
# compute features
sift.process_image('E:/Py_code/photo/Fourth/s_re1.jpg', 'im0.sift')
l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')
sift.process_image('E:/Py_code/photo/Fourth/s_re2.jpg', 'im1.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')
# match features and estimate homography
matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)
model = homography.RansacModel()
H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)
K = my_calibration((747, 1000))
cam1 = camera.Camera(hstack((K, dot(K, array([[0], [0], [-1]])))))
box = cube_points([0, 0, 0.1], 0.1)
box_cam1 = cam1.project(homography.make_homog(box[:, :5]))
box_trans = homography.normalize(dot(H, box_cam1))
cam2 = camera.Camera(dot(H, cam1.P))
A = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P[:, :3])
A = array([A[:, 0], A[:, 1], cross(A[:, 0], A[:, 1])]).T
cam2.P[:, :3] = dot(K, A)
Rt = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P)
setup()
draw_background("E:/Py_code/photo/Fourth/s_re2.jpg")
set_projection_from_camera(K)
set_modelview_from_camera(Rt)
draw_teapot(0.05)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
sys.exit()
其中有几个地方需要注意。draw_teapot 函数下面的 width, height表示图像的像素,需要根据自己图像大小来调整。draw_teapot中的glMaterialfv是插入物体的用于光照计算的材质属性的函数,具体的参数表示含义可以自行百度查看:glMaterialfv()百度百科词条。所以我们可以通过改变GL_DIFFUSE后面四个参数来改变颜色,这四个参数分别对应RGBA四个值。
实现的结果:

3.遇到的错误以及解决方法
在安装完了PyOpenGL之后,运行第二个代码出现以下错误:

请教同学之后,说是pip下载的是32位使用的包,所以这里推荐去网站中自己下载对应的版本,下载地址:PyOpenGL下载。可以通过ctrl+F来搜索对应的包。
下载之后进入你下载包的地址,打开cmd,输入pip install 文件名字.whl完成安装。
如果你在这之后又遇见这个错误:

可以通过删除对应文件夹下除glut64.vc9.dll之外的所有文件,我的路径是E:\Python\Anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\OpenGL\DLLS,如图:
删除前

删除后
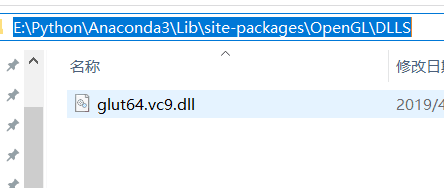
就可以解决问题。
这里着重感谢吴则彪同学在解决错误时候提供的方法。他的博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wuzebiao2016
























 1068
1068











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








