目录
一、要求:
模拟场景实现:有个名为“计算科学与应用”的专业,其专业编号为“J0001”,学制年限为“4年”。
3个学生报名该专业:
| 姓名 | 学号 | 性别 | 年龄 |
| 张三 | 01 | 男 | 18岁 |
| 李四 | 02 | 女 | 17岁 |
| 王五 | 03 | 男 | 18岁 |
使用面向对象思想去实现这个场景。
二、分析:
- 4个对象:
对象1:专业。
对象2:张三
对象3:李四
对象4:王五
- 2个类:
类1:专业
类2:学生
在类中添加专业对象作为属性,通过其属性获得相关信息。
三、编码:
注意:在方法中通过对象作为参数,传递的是它的引用,可通过引用获取该对象的所有信息。
Student类:
package com.model;
public class Student {
private String studentId;
private String studentName;
private String studentSex;
private int studentAge;
private Subject studentSubject; // 注意!
// 无参构造方法
public Student() {
}
public Student(String studentId, String studentName, String studentSex, int studentAge) {
super();
this.setStudentId(studentId);
this.setStudentName(studentName);
this.setStudentSex(studentSex);
this.setStudentAge(studentAge);
}
// 带参构造,实现对全部参数的赋值
public Student(String studentId, String studentName, String studentSex, int studentAge, Subject studentSubject) {
super();
this.setStudentId(studentId);
this.setStudentName(studentName);
this.setStudentSex(studentSex);
this.setStudentAge(studentAge);
this.setStudentSubject(studentSubject);
}
public String getStudentId() {
return studentId;
}
public void setStudentId(String studentId) {
this.studentId = studentId;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public String getStudentSex() {
return studentSex;
}
/**
* 给性别赋值,限制只能是“男”或“女”,否则强制赋值为“男”
*
* @param studentSex 传入的性别
*/
public void setStudentSex(String studentSex) {
if (!(studentSex == "男" || studentSex == "女")) {
this.studentSex = "男";
} else
this.studentSex = studentSex;
}
public int getStudentAge() {
return studentAge;
}
/**
* 给年龄赋值,限制在10——100之间,反之就设置为18
*
* @param studentAge传入的年龄
*/
public void setStudentAge(int studentAge) {
if (studentAge < 10 || studentAge > 100) {
this.studentAge = 18;
} else
this.studentAge = studentAge;
}
/**
* 获取专业对象,若没有实例化,则先实例化后再返回
*
* @return 专业对象信息
*/
public Subject getStudentSubject() {
if (studentSubject == null)
this.studentSubject = new Subject();
return studentSubject;
}
public void setStudentSubject(Subject studentSubject) {
this.studentSubject = studentSubject;
}
/**
* 法1 在方法中添加1个专业对象作为参数,通过其属性获得相关信息
* 更简单,获得参数方便
* @param sub1
*
* @return自我介绍的信息,包括姓名、学号、性别、年龄
*/
public String introduction(Subject mySubject) {
String str = "学生信息如下:\n姓名:" + this.getStudentName() + "\n学号:" + this.getStudentId() + "\n性别:"
+ this.getStudentSex() + "\n年龄:" + this.getStudentAge() + "\n所报专业名称:" + mySubject.getSubjectName()
+ "\n学制年限:" + mySubject.getSubjectYear() + "\n专业编号:" + mySubject.getSubjectId();
return str;
}
/**
* 法2 在类中添加专业作为属性,通过其属性获得相关信息
* 关联性更强
*/
public String introduction() {
String str = "学生信息如下:\n姓名:" + this.getStudentName() + "\n编号:" + this.getStudentId() + "\n性别:"
+ this.getStudentSex() + "\n年龄:" + getStudentAge() + "\n所报专业名称:"
+ this.getStudentSubject().getSubjectName() + "\n学制年限:" + this.getStudentSubject().getSubjectYear()
+ "年" + "\n专业编号:" + this.getStudentSubject().getSubjectId();
return str;
}
/**
* 法3 在方法中添加2个参数,分别表示专业名称和学制年限
* 易理解,但参数列表长
* @param subjectName
* @param subjectYear
* @return
*/
public String introduction(String subjectName, int subjectYear) {
String str = "学生信息如下:\n姓名:" + this.getStudentName() + "\n编号:" + this.getStudentId() + "\n性别:"
+ this.getStudentSex() + "\n年龄:" + getStudentAge() + "\n所报专业名称:" + subjectName + "\n学制年限:" + subjectYear
+ "年";
return str;
}
}
Subject类:
package com.model;
/**
* 专业类
* @author dell
*
*/
public class Subject {
//成员属性:学科名称,学科编号,学制年限,报名选修的学生信息,报名选修的学生个数
private String subjectName;
private String subjectId;
private int subjectYear;
private Student[] myStudents; //数组是引用类型,默认初始值是null
private int studentNum; //因为数组只能描述空间长度,无法准确描述其数据个数
// 无参构造方法
public Subject() {
}
//带参构造
public Subject(String subjectName, String subjectId, int subjectYear) {
this.subjectName = subjectName; // 赋值方法①
this.setSubjectId(subjectId); // 赋值方法②(推荐!)
this.setSubjectYear(subjectYear);
}
// 带参构造方法,实现对属性的全部赋值
public Subject(String subjectName, String subjectId, int subjectYear,Student[] myStudents) {
this.subjectName = subjectName; // 赋值方法①
this.setSubjectId(subjectId); // 赋值方法②(推荐!)
this.setSubjectYear(subjectYear);
this.setMyStudents(myStudents);
}
public String getSubjectName() {
return subjectName;
}
public void setSubjectName(String subjectName) {
this.subjectName = subjectName;
}
public String getSubjectId() {
return subjectId;
}
public void setSubjectId(String subjectId) {
this.subjectId = subjectId;
}
public int getSubjectYear() {
return subjectYear;
}
// 限制年限必须>0
public void setSubjectYear(int subjectYear) {
if (subjectYear <= 0)
return; // 结束
this.subjectYear = subjectYear;
}
/**
* 获取选修专业的学生信息
* 如果学生数组未被初始化,则给它开辟一块空间
* @return
*/
public Student[] getMyStudents() {
if (this.myStudents==null)
this.myStudents=new Student[200];
return myStudents;
}
public void setMyStudents(Student[] myStudents) {
this.myStudents = myStudents;
}
public int getStudentNum() {
return studentNum;
}
public void setStudentNum(int studentNum) {
this.studentNum = studentNum;
}
/**
* 专业介绍的方法
* @return专业介绍的相关信息,包括名称、编号和年限
*/
public String info() {
String str = "专业信息如下:\n专业名称:" + this.getSubjectName() + "\n专业编号:" + this.getSubjectId() + "\n学制年限:"
+ this.getSubjectYear()+"年";
return str;
}
public void addStudents(Student stu) {
//1.将学生保存在数组中
int i;
for (i = 0; i < this.getMyStudents().length; i++) {
if (this.getMyStudents()[i]==null) {
this.getMyStudents()[i]=stu;
//将学生个数保存在studentNum
this.studentNum=i+1;
return;
}
}
}
}
Test类:
package com.test;
import com.model.Student;
import com.model.Subject;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试Subject
Subject sub1=new Subject("计算机科学与应用","S100",4);
System.out.println(sub1.info());
System.out.println("**************************");
//测试Student
Student stu1=new Student("01","张三","你看",200,sub1);
System.out.println(stu1.introduction());
System.out.println("==========================");
Student stu2=new Student("02","李四","男",17);
System.out.println(stu2.introduction("计算机科学与应用",4));
System.out.println("==========================");
Student stu3=new Student("03","王五","女",18);
System.out.println(stu3.introduction(sub1));
System.out.println("==========================");
//测试指定专业中有多少学生报名
sub1.addStudents(stu1);
sub1.addStudents(stu2);
sub1.addStudents(stu3);
System.out.println(sub1.getSubjectName()+"专业已有"+sub1.getStudentNum()+"名学生报名");
}
}
结果:

![]()
通过上述代码可知:通过学生的实例化操作(Test类)建立了学生和专业之间的关联,然后通过专业中添加学生的方法(Subject 类)实现了专业和学生之间的关联:

通过2步才完成了双向联系。
简化:
修改Subject类:
package com.model;
/**
* 专业类
* @author dell
*
*/
public class Subject {
//成员属性:学科名称,学科编号,学制年限,报名选修的学生信息,报名选修的学生个数
private String subjectName;
private String subjectId;
private int subjectYear;
private Student[] myStudents; //数组是引用类型,默认初始值是null
private int studentNum; //因为数组只能描述空间长度,无法准确描述其数据个数
// 无参构造方法
public Subject() {
}
//带参构造
public Subject(String subjectName, String subjectId, int subjectYear) {
this.subjectName = subjectName; // 赋值方法①
this.setSubjectId(subjectId); // 赋值方法②(推荐!)
this.setSubjectYear(subjectYear);
}
// 带参构造方法,实现对属性的全部赋值
public Subject(String subjectName, String subjectId, int subjectYear,Student[] myStudents) {
this.subjectName = subjectName; // 赋值方法①
this.setSubjectId(subjectId); // 赋值方法②(推荐!)
this.setSubjectYear(subjectYear);
this.setMyStudents(myStudents);
}
public String getSubjectName() {
return subjectName;
}
public void setSubjectName(String subjectName) {
this.subjectName = subjectName;
}
public String getSubjectId() {
return subjectId;
}
public void setSubjectId(String subjectId) {
this.subjectId = subjectId;
}
public int getSubjectYear() {
return subjectYear;
}
// 限制年限必须>0
public void setSubjectYear(int subjectYear) {
if (subjectYear <= 0)
return; // 结束
this.subjectYear = subjectYear;
}
/**
* 获取选修专业的学生信息
* 如果学生数组未被初始化,则给它开辟一块空间
* @return
*/
public Student[] getMyStudents() {
if (this.myStudents==null)
this.myStudents=new Student[200];
return myStudents;
}
public void setMyStudents(Student[] myStudents) {
this.myStudents = myStudents;
}
public int getStudentNum() {
return studentNum;
}
public void setStudentNum(int studentNum) {
this.studentNum = studentNum;
}
/**
* 专业介绍的方法
* @return专业介绍的相关信息,包括名称、编号和年限
*/
public String info() {
String str = "专业信息如下:\n专业名称:" + this.getSubjectName() + "\n专业编号:" + this.getSubjectId() + "\n学制年限:"
+ this.getSubjectYear()+"年";
return str;
}
public void addStudents(Student stu) {
//1.将学生保存在数组中
int i;
for (i = 0; i < this.getMyStudents().length; i++) {
if (this.getMyStudents()[i]==null) {
stu.setStudentSubject(this); //将传入学生的专业对象设置为当前对象,谁调用谁是当前对象
this.getMyStudents()[i]=stu;
//将学生个数保存在studentNum
this.studentNum=i+1;
return;
}
}
}
}
修改Test类:
package com.test;
import com.model.Student;
import com.model.Subject;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试Subject
Subject sub1=new Subject("计算机科学与应用","S100",4);
/*
* System.out.println(sub1.info());
* System.out.println("**************************");
*/
//测试Student
Student stu1=new Student("01","张三","你看",200); //去掉与专业的关联
/*
* System.out.println(stu1.introduction());
* System.out.println("=========================="); Student stu2=new
* Student("02","李四","男",17);
* System.out.println(stu2.introduction("计算机科学与应用",4));
* System.out.println("=========================="); Student stu3=new
* Student("03","王五","女",18); System.out.println(stu3.introduction(sub1));
* System.out.println("==========================");
*/
//测试指定专业中有多少学生报名
sub1.addStudents(stu1);
/*
* sub1.addStudents(stu2); sub1.addStudents(stu3);
*/
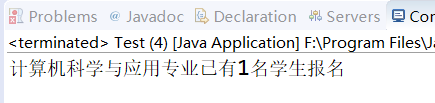
System.out.println(sub1.getSubjectName()+"专业已有"+sub1.getStudentNum()+"名学生报名");
}
}
结果:






















 1411
1411











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








