激活函数
ReLU函数
x = torch.arange(-10, 10, 0.1, requires_grad = True)
y = torch.relu(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(), y.detach(),'x', 'relu(x)',figsize=(7, 3.5))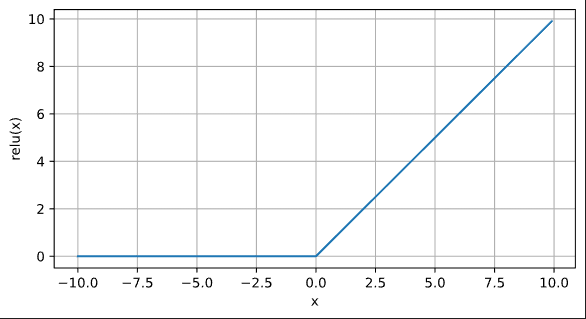
ReLU函数的导数
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x),retain_graph=True)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),x.grad,'x','grad of relu',figsize=(7,3.5))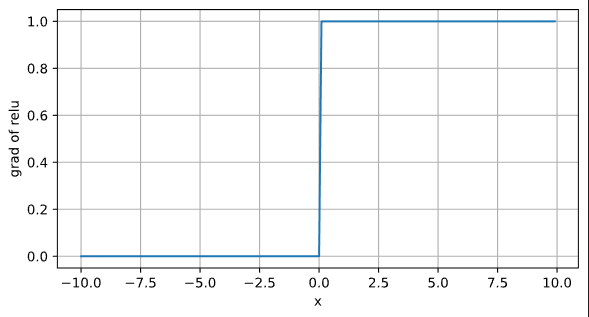
sigmoid函数
y = torch.sigmoid(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(), y.detach(),'x', 'sigmoid(x)',figsize=(7, 3.5))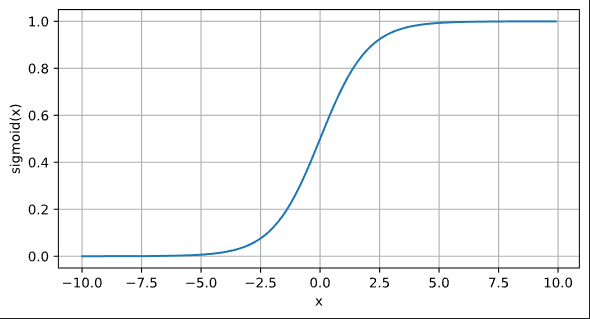
sigmoid函数的导数
x.grad.data.zero_()
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x),retain_graph=True)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),x.grad,'x','grad of sigmoid',figsize=(7,3.5))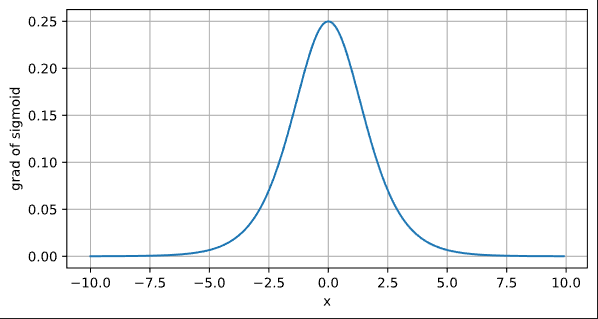
Tanh函数
y = torch.tanh(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(), y.detach(),'x', 'tanh(x)',figsize=(7, 3.5))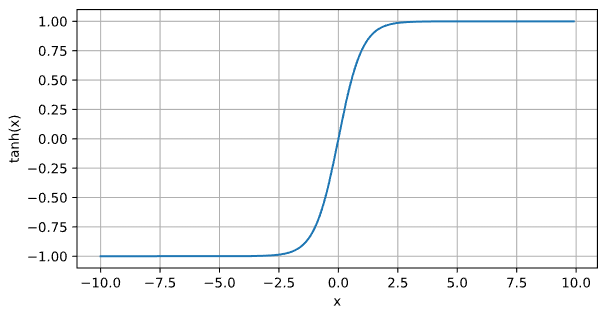
Tanh函数的导数
x.grad.data.zero_()
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x),retain_graph=True)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),x.grad,'x','grad of tanh',figsize=(7,3.5))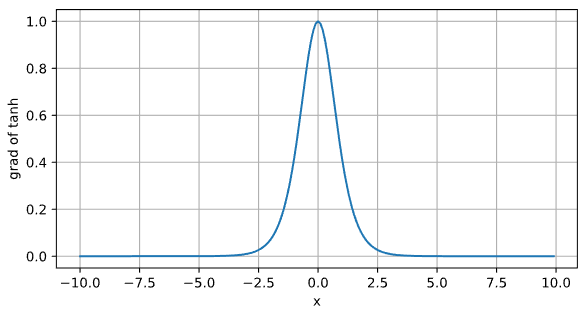
多层感知机的从零开始实现
from torch import nn
batch_size = 256
train_iter,test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)实现一个具有单隐藏层的多层感知机,其包含256个隐藏单元
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens = 784, 10, 256
W1 = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(num_inputs,num_hiddens,requires_grad = True) * 0.01)
b1 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_hiddens,requires_grad=True))
W2 = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(num_hiddens,num_outputs,requires_grad = True) * 0.01)
b2 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_outputs,requires_grad=True))
params = [W1, b1, W2, b2]定义relu激活函数
def relu(X):
a = torch.zeros_like(X)
return torch.max(X, a)定义模型
def net(X):
X = X.reshape(-1, num_inputs)
H = relu(X @ W1 + b1)
return relu(H @ W2 + b2)损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')训练
num_epochs, lr = 10, 0.1
updater = torch.optim.SGD(params,lr = lr)
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater)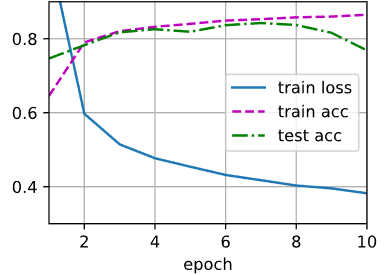
多层感知机的简易实现
隐藏层 包含256个隐藏单元,并使用了ReLU激活函数
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
from torch import nn
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(784,256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256,10)
)
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight,std = 0.01)
net.apply(init_weights)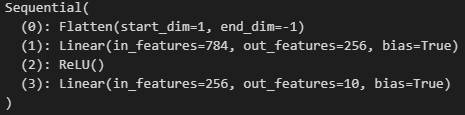
训练
batch_size, lr, num_epochs = 256, 0.1, 10
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr = lr)
train_iter,test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
d2l.train_ch3(net,train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)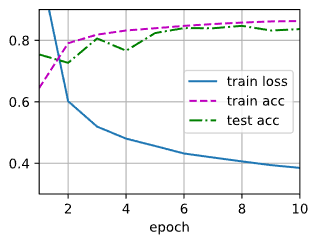
模型选择、过拟合、欠拟合
通过一个多项式拟合来探索上述概念
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l使用下述三阶多项式来生成训练和测试数据的标签
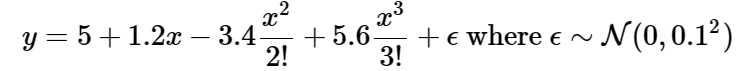
max_degree = 20
n_train, n_test = 100, 100
true_w = np.zeros(max_degree)
true_w[0:4] = np.array([5, 1.2, -3.4, 5.6])
features = np.random.normal(size=(n_train + n_test, 1))
np.random.shuffle(features)
poly_features = np.power(features, np.arange(max_degree).reshape(1, -1))
for i in range(max_degree):
poly_features[:, i] /= math.gamma(i + 1)
labels = np.dot(poly_features, true_w)
labels += np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=labels.shape)前两个样本
true_w, features, poly_features, labels = [
torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.float32)
for x in [true_w, features, poly_features, labels]]
features[:2], poly_features[:2, :], labels[:2]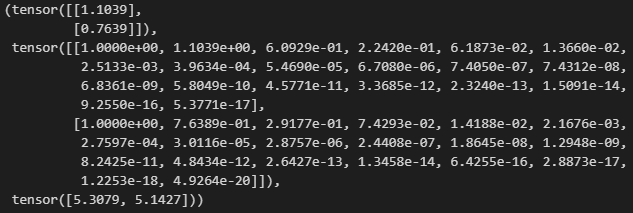
实现一个函数以评估模型在给定数据集上的损失
def evaluate_loss(net, data_iter, loss):
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2)
for X, y in data_iter:
out = net(X)
y = y.reshape(out.shape)
l = loss(out, y)
metric.add(l.sum(), l.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]定义训练函数
def train(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels,
num_epochs=400):
loss = nn.MSELoss()
input_shape = train_features.shape[-1]
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_shape, 1, bias=False))
batch_size = min(10, train_labels.shape[0])
train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features, train_labels.reshape(-1, 1)),
batch_size)
test_iter = d2l.load_array((test_features, test_labels.reshape(-1, 1)),
batch_size, is_train=False)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[1e-3, 1e2],
legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
d2l.train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, trainer)
if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (evaluate_loss(
net, train_iter, loss), evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
print('weight:', net[0].weight.data.numpy())拟合(正态)
train(poly_features[:n_train, :4], poly_features[n_train:, :4],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])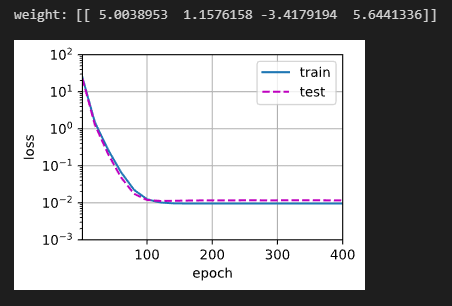
欠拟合
train(poly_features[:n_train, :2], poly_features[n_train:, :2],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:])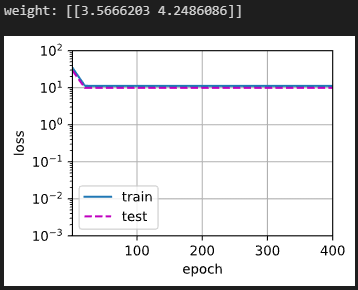
过拟合
train(poly_features[:n_train, :], poly_features[n_train:, :],
labels[:n_train], labels[n_train:], num_epochs=1500)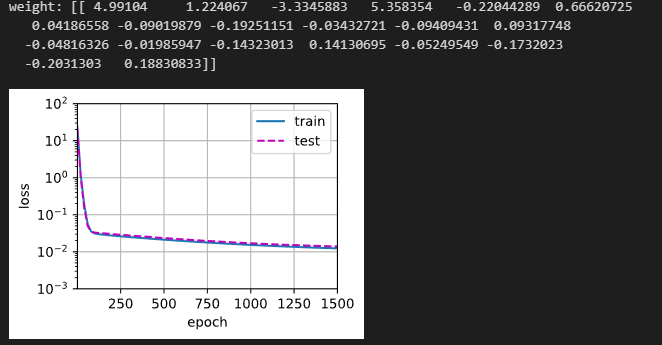
权重衰减
权重衰减是最广泛使用的正则化的技术之一
n_train, n_test, num_inputs, batch_size = 20, 100, 200, 5
true_w, true_b = torch.ones((num_inputs, 1)) * 0.01, 0.05
train_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_train)
train_iter = d2l.load_array(train_data, batch_size)
test_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_test)
test_iter = d2l.load_array(test_data, batch_size, is_train=False)初始化模型参数
def init_params():
w = torch.normal(0, 1, size=(num_inputs, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
return [w, b]定义L2范数惩罚
def l2_penalty(w):
return torch.sum(w.pow(2)) / 2定义训练代码实现
def train(lambd):
w, b = init_params()
net, loss = lambda X: d2l.linreg(X, w, b), d2l.squared_loss
num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[5, num_epochs], legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
with torch.enable_grad():
l = loss(net(X), y) + lambd * l2_penalty(w)
l.sum().backward()
d2l.sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
print('w的L2范数是:', torch.norm(w).item())忽略正则化训练
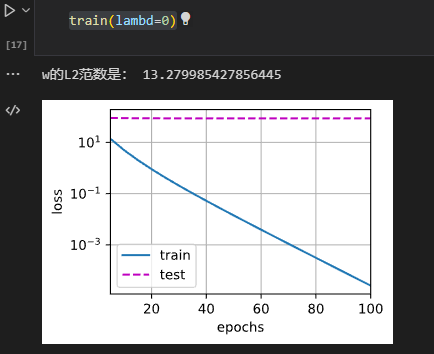
使用权重衰减
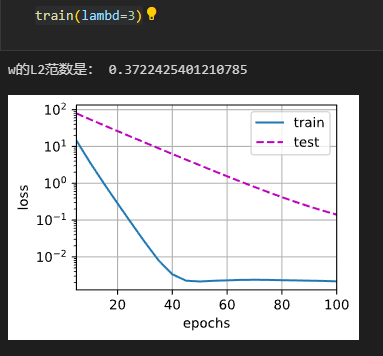
权重衰减的简洁实现
def train_concise(wd):
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
for param in net.parameters():
param.data.normal_()
loss = nn.MSELoss()
num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003
trainer = torch.optim.SGD([{
"params": net[0].weight,
'weight_decay': wd}, {
"params": net[0].bias}], lr=lr)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[5, num_epochs], legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
with torch.enable_grad():
trainer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(X), y)
l.backward()
trainer.step()
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
print('w的L2范数:', net[0].weight.norm().item())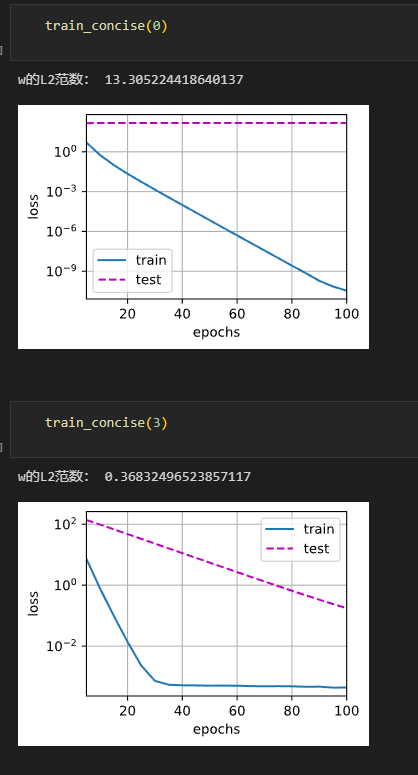
丢弃法
实现drop_out函数
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
from torch import nn
def drop_out(X,dropout):
assert 0 <= dropout <= 1
if dropout == 1:
return torch.zeros_like(X)
if dropout == 0:
return X
mask = (torch.Tensor(X.shape).uniform_(0,1) > dropout).float()
return mask * X /(1.0 - dropout)测试一下
X = torch.arange(16,dtype = torch.float32).reshape((2,8))
print(X)
print(drop_out(X,0.))
print(drop_out(X,0.5))
print(drop_out(X,1.))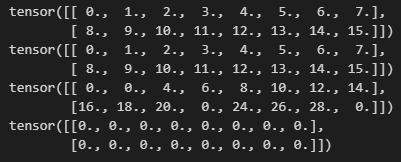
定义具有两个隐藏层的多层感知机,每个隐藏层包含256个单元
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2 = 784, 10, 256, 256
dropout1 = 0.2
dropout2 = 0.5
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2, is_training = True):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.num_inputs = num_inputs
self.training = is_training
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(num_inputs,num_hiddens1)
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(num_hiddens1,num_hiddens2)
self.lin3 = nn.Linear(num_hiddens2,num_outputs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self,X):
H1 = self.relu(self.lin1(X.reshape((-1,self.num_inputs))))
if self.training == True:
H1 = drop_out(H1, dropout1)
H2 = self.relu(self.lin2(H1))
if self.training == True:
H2 = drop_out(H2, dropout2)
return self.lin3(H2)
训练
num_epochs, lr, batch_size = 15, 0.3, 256
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
net = Net(num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2)
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)简洁实现
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 256), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout1), nn.Linear(256, 256), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout2), nn.Linear(256, 10))
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
net.apply(init_weights);训练
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)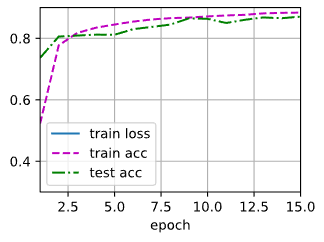
数值稳定性和模型初始化
梯度消失
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
x = torch.arange(-8.0, 8.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.sigmoid(x)
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x))
d2l.plot(x.detach().numpy(), [y.detach().numpy(), x.grad.numpy()],
legend=['sigmoid', 'gradient'], figsize=(4.5, 2.5))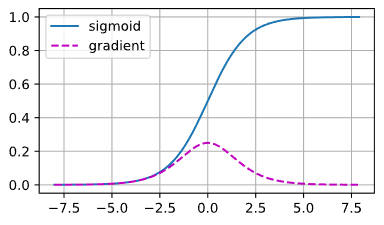
梯度爆炸
M = torch.normal(0, 1, size=(4, 4))
print('一个矩阵 \n', M)
for i in range(100):
M = torch.mm(M, torch.normal(0, 1, size=(4, 4)))
print('乘以100个矩阵后\n', M)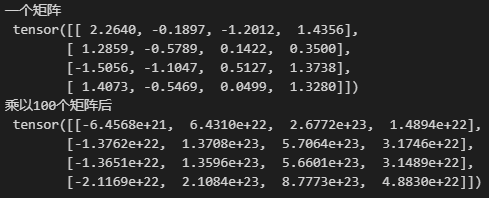







 本文介绍了ReLU、sigmoid和tanh三种常用的激活函数及其导数,展示了它们在神经网络中的作用。接着,通过从零开始和使用nn模块分别实现了多层感知机,并探讨了过拟合、欠拟合以及权重衰减在模型训练中的影响。最后,讨论了丢弃法对缓解梯度消失和爆炸问题的作用。
本文介绍了ReLU、sigmoid和tanh三种常用的激活函数及其导数,展示了它们在神经网络中的作用。接着,通过从零开始和使用nn模块分别实现了多层感知机,并探讨了过拟合、欠拟合以及权重衰减在模型训练中的影响。最后,讨论了丢弃法对缓解梯度消失和爆炸问题的作用。














 986
986

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








