文章目录
创建和递归遍历(扩展先序遍历序列创建二叉链表)
题目描述
从键盘接收扩展先序序列,以二叉链表作为存储结构,建立二叉树。输出这棵二叉树的先序、中序和后序遍历序列。
二叉树结点的data是字符类型数据, 其中#表示空格字符。
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
//二叉链表结点结构
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *Lchild;
struct Node *Rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
//用一级指针来创建
/*BiTNode *CreateBiTree(BiTree root) {
char ch;
ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#') {
root = NULL;
} else {
root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
root->data = ch;
printf("1");
//和与二级指针不同的是
//一级指针要求有返回值,所以一定要接收
root->Lchild = CreateBiTree(root->Lchild);
//有返回值,所以一定要接收
root->Rchild = CreateBiTree(root->Rchild);
}
return root;
}*/
void CreateBiTree(BiTree *root) {
char ch;
ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#') {
*root = NULL;
} else {
*root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
(*root)->data = ch;
//以左子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Lchild));
//以右子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Rchild));
}
}
void PreOrder(BiTree root) {
//printf("进来了");
if (root) {
printf("%c", root->data);
PreOrder(root->Lchild);
PreOrder(root->Rchild);
}
}
void InOrder(BiTree root) {
if (root) {
InOrder(root->Lchild);
printf("%c", root->data);
InOrder(root->Rchild);
}
}
void PostOrder(BiTree root) {
if (root) {
PostOrder(root->Lchild);
PostOrder(root->Rchild);
printf("%c", root->data);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
BiTree root;
//root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
CreateBiTree(&root);
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
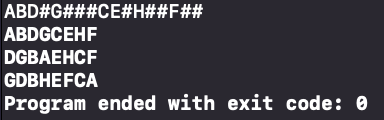
验证结果:
请注意在验证时,一定要输入正确的扩展的先序遍历序列,比如这里的ABD#G###CE#H##F##。随便输一个是不行的,因为它没办法建立起来这棵二叉树
创建和非递归遍历(扩展先序遍历序列创建二叉链表)
先序遍历二叉树的非递归实现:
从根开始,当前结点存在或栈非空,重复以下两步
1.访问根节点,根节点入栈,进入根节点左子树,直至为空
2.如果栈不为空,退栈顶结点,进入其右子树。
中序遍历二叉树非递归实现:
从根开始,当前结点存在或栈非空。重复以下两步
1.入栈,进入左子树,直至左子树为空
2.栈不为空,出栈顶元素,访问出栈结点,并进入其右子树
后序遍历二叉树非递归实现:
首先需要一个q指针,一直保持更新指向刚访问的结点
1.入栈,访问其左子树,重复直至左子树为空
2.如栈非空,取栈顶元素,判断他的右子树是否为空或者右子树是否等于q。
如果右子树不为空或等于q,说明没有右子树或者右子树还没有被访问,出栈,访问,更新q = p(q要一直保持更新为刚才访问的结点), p置空(避免再次访问)否则,进入p右子树.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
//二叉链表结点结构
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *Lchild;
struct Node *Rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
typedef struct Stack {
BiTNode *stack[100];
int top;
}SeqStack;
void CreateBiTree(BiTree *root) {
char ch;
ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#') {
*root = NULL;
} else {
*root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
(*root)->data = ch;
//以左子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Lchild));
//以右子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Rchild));
}
}
void init(SeqStack **s) {
*s = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
(*s)->top = -1;
}
int Empty(SeqStack *s) {
if (s->top == -1) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
void Push(SeqStack *s ,BiTree pNew) {
s->top++;
s->stack[s->top] = pNew;
}
void pop(SeqStack *s, BiTree *p) {
*p = s->stack[s->top];
s->top--;
}
void preOrder(BiTree root) {
SeqStack *s;
BiTree p;
init(&s);
p = root;
while (p != NULL || Empty(s)) {
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%c", p->data);
Push(s, p);
p = p->Lchild;
}
if (Empty(s)) {
pop(s, &p);
p = p->Rchild;
}
}
}
void InOrder1(BiTree root) {
SeqStack *s;
init(&s);
BiTree p;
p = root;
while (p != NULL || Empty(s)) {
while (p != NULL) {
Push(s, p);
p = p->Lchild;
}
if (Empty(s)) {
pop(s, &p);
printf("%c", p->data);
p = p->Rchild;
}
}
}
void top(SeqStack *s, BiTree *p) {
(*p) = s->stack[s->top];
}
void post(BiTree root) {
SeqStack *s;
BiTree p, q;
init(&s);
p = root;
q = NULL;
while (p != NULL || Empty(s)) {
while (p != NULL) {
Push(s, p);
p = p->Lchild;
}
if (Empty(s)) {
top(s, &p);
if (p->Rchild == NULL || p->Rchild == q) {
pop(s, &p);
printf("%c", p->data);
//q时刻记录刚被访问的结点
q = p;
//置空,避免再次被访问
p = NULL;
} else {
p = p->Rchild;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
BiTree root;
//root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
CreateBiTree(&root);
preOrder(root);
printf("\n");
InOrder1(root);
printf("\n");
post(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
运行结果: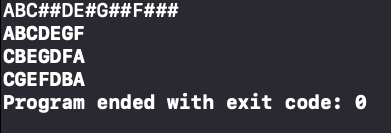
层次遍历(利用队列)
算法思想:
首先根结点入队,当队列非空时,重复如下两步操作
1.队头结点出队,并访问出队结点
2.出队结点的非空左,右孩子依次入队。
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
//二叉链表结点结构
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *Lchild;
struct Node *Rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
typedef struct Queue {
BiTNode *Queue[100];
int front;
int rear;
}SeqQueue;
void CreateBiTree(BiTree *root) {
char ch;
ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#') {
*root = NULL;
} else {
*root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
(*root)->data = ch;
//以左子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Lchild));
//以右子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Rchild));
}
}
void init(SeqQueue **s) {
(*s) = (SeqQueue *)malloc(sizeof(SeqQueue));
(*s)->front = (*s)->rear = -1;
}
void EnterQueue(SeqQueue *s, BiTree root) {
s->rear++;
s->Queue[s->rear] = root;
}
int Empty(SeqQueue *s) {
if (s->front == s->rear) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
void DeleteQueue(SeqQueue *s, BiTree *p) {
s->front++;
*(p) = s->Queue[s->front];
}
void LevelOrder(BiTree root) {
SeqQueue *s;
BiTree p;
init(&s);
EnterQueue(s, root);
while (Empty(s)) {
DeleteQueue(s, &p);
printf("%c", p->data);
if (p->Lchild != NULL) {
EnterQueue(s, p->Lchild);
}
if (p->Rchild != NULL) {
EnterQueue(s, p->Rchild);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
BiTree root;
//root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
CreateBiTree(&root);
LevelOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
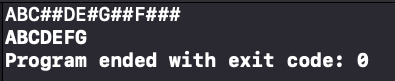
运行结果:
结点个数
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
//二叉链表结点结构
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *Lchild;
struct Node *Rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
void CreateBiTree(BiTree *root) {
char ch;
ch = getchar();
if (ch == '#') {
*root = NULL;
} else {
*root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
(*root)->data = ch;
//以左子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Lchild));
//以右子树域地址为参数,可使被调用函数中建立的结点指针置于该域中
CreateBiTree(&((*root)->Rchild));
}
}
//定义全局变量
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
void InOrder1(BiTree root) {
if (root) {
InOrder1(root->Lchild);
//度为2的结点
if ((root->Lchild != NULL && root->Rchild != NULL)) {
c++;
}
//度为1的结点
if ((root->Lchild == NULL && root->Rchild != NULL) || (root->Lchild != NULL && root->Rchild == NULL)) {
b++;
}
//叶子结点
if (root->Lchild == NULL && root->Rchild == NULL) {
a++;
}
InOrder1(root->Rchild);
}
}
//中序输出叶子结点
void InOrder2(BiTree root) {
if (root) {
InOrder2(root->Lchild);
//叶子结点
if (root->Lchild == NULL && root->Rchild == NULL) {
printf("%c", root->data);
a++;
}
InOrder2(root->Rchild);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
BiTree root;
//root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
CreateBiTree(&root);
InOrder1(root);
printf("%d %d %d\n", a, b, c);
InOrder2(root);
return 0;
}
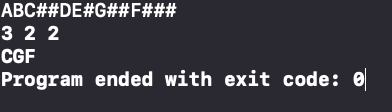
运行结果:
二叉树的最大深度
方法一:递归
int Max(int a, int b) {
if (a > b) {
return a;
} else {
return b;
}
}
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return 1 + Max(left, right);
}
方法二:队列(层序遍历)
#define MAX 1000
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
struct TreeNode *list[MAX];
int count = 0;
int front, rear;
front = rear = 0;
if (root != NULL) {
list[rear % MAX] = root;
rear++;
}
while (front < rear) {
count++;
int j = rear - front;
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
struct TreeNode *t;
t = list[front % MAX];
front++;
if (t->left) {
list[rear % MAX] = t->left;
rear++;
}
if (t->right) {
list[rear % MAX] = t->right;
rear++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
二叉树的最小深度
题目链接
//队列(层次遍历)
总结:相比求最大深度,求最小深度主要是要及时退出循环
#define MAX 1000
int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
struct TreeNode *list[MAX];
int front, rear;
front = rear = 0;
int count = 0;
if (root) {
list[rear % MAX] = root;
rear++;
}
while (front < rear) {
int flag = 0;
count++;
int j = rear - front;
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
struct TreeNode *t;
t = list[front % MAX];
front++;
if (t->left == NULL && t->right == NULL) {
flag = 1;
break;
} else {
if (t->left != NULL) {
list[rear % MAX] = t->left;
rear++;
}
if (t->right != NULL) {
list[rear % MAX] = t->right;
rear++;
}
}
}
if (flag == 1) {
break;
}
}
return count;
}
对称二叉树
题目链接
方法一:递归。
首先判断一个二叉树是否对称是看它的左子树和右子树是否对称,然后左子树和右子树又有相应的左右子树去判断它是否对称。。。依次推导。显然可以用递归解决。
bool isMirror(struct TreeNode *t1, struct TreeNode *t2) {
//递推终止条件
//左右子树为空,表示已经遍历结束。
if (t1 == NULL && t2 == NULL) {
return true;
} else if (t1 == NULL || t2 == NULL) {
//剪支。
//其中一个为空,显然已经不对称了
return false;
} else {
//否则进一步推导它的左右子树。
//&&有短路判断。就是说如果t1->val == t2->val为false。则直接return false;
return ((t1->val == t2->val) && isMirror(t1->left, t2->right) && isMirror(t1->right, t2->left));
}
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root) {
//传入根结点
return isMirror(root, root);
}
方法二:迭代
关于递推,迭代,递归的区别详见这篇博客
//使用队列逐层遍历比较
#define MAX 1000
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root) {
struct TreeNode *list[MAX];
int front, rear;
front = rear = 0;
list[rear % MAX] = root;
rear++;
list[rear % MAX] = root;
rear++;
while (front < rear) {
struct TreeNode *t1;
t1 = list[front % MAX];
front++;
struct TreeNode *t2;
t2 = list[front % MAX];
front++;
if (t1 == NULL && t2 == NULL) {
//如果两个节点均为空,那么它们
//肯定没有左子树和右子树了
//直接进入下一轮循环
continue;
} else if (t1 == NULL || t2 == NULL) {
//其中一个为空,那么肯定不对称了
//直接返回false;
return false;
} else if (t1->val == t2->val) {
//先判断它们的根节点的val是否相等
//如果相等,把它们的左子树和右子树入队列
//注意是交叉入队,因为就是想要比较它们的对称值是否相等
//画个图就知道了
list[(rear++) % MAX] = t1->left;
list[(rear++) % MAX] = t2->right;
list[(rear++) % MAX] = t1->right;
list[(rear++) % MAX] = t2->left;
} else {
//这里t1->val != t2->val
//直接false
return false;
}
}
//如果程序可以走到这里,说明二叉树已经遍历结束
//并且均符合上面分类讨论的情况
//返回true
return true;
}
平衡二叉树
题目链接
这个题是基于求解二叉树的最大深度解决的
这里就是判断他的左右子树的高度差绝对值小于等于1
所以我们可以求得每个左右子树的高度差,然后进行判断。
int Max(int a, int b) {
if (a > b) {
return a;
} else {
return b;
}
}
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return 1 + Max(left, right);
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
if (root == NULL) {
return true;
} else {
int t1 = maxDepth(root->left);
int t2 = maxDepth(root->right);
int t = t1 - t2;
if (abs(t) <= 1) {
return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
翻转二叉树
题目链接
感觉总结二叉树题目是总结递归了
思想:翻转一个二叉树,就是把它的左子树和右子树交换。
然后左子树对应的二叉树又要交换它的左子树和右子树
右子树对应的二叉树又要交换它的左子树和右子树…
以下是我对递归的个人理解:
我感觉递归非常考验一个人的全局意识,
在思考是否要用递归时
你一定不要局限于当前,而应该想它后面的是不是和当前的处理想法是一样的
在实现递归的时候
你又必须要回到当前,想一想当前的代码怎么实现就行。
不要深究后面怎么办
要不然你会觉得这个代码好像又会特别多而很难实现
实际上递归正是帮我们省去了哪些多余代码
交给递归工作栈就行啦
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root){
//递归终止条件
//如果遍历借宿,返回NULL。
//开始回溯过程
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//当前我需要二叉树的左子树
//但是我又希望这个左子树的二叉树它的左子树和二叉树是交换了的
//所以递归调用
struct TreeNode *left = invertTree(root->left);
//同上,当前我需要二叉树的右子树
//但是我也希望这个右子树的二叉树它的左子树和右子树是交换了的
//所以递归调用
struct TreeNode *right = invertTree(root->right);
//下面两行代码,就是把一个二叉树的左子树和右子树对调
root->left = right;
root->right = left;
//你不用但是你的root是否经过这么
//多层递归是否还是起点位置
//因为最后返回的root是经过回溯得到的
//虽然我们前面不停的root->left
//root->right
//但是那是深度搜索的过程
//最后回溯过程root又回到了起点位置
return root;
}
依据先序、中序遍历序列创建二叉树
先感谢这位博主的思路
题目思路来源
虽然总结了好几个二叉树的题目,但是每到一个递归新题的时候总是无处下手。
吐槽自己对递归的理解“一看就懂,一写就懵”
拿到这个题自己也想着递归八九不离十了。
拿这个题来说,按照先序根在第一个的特点,递推:不断得把中序拆分。然后逐层返回。最后得出结果。
题目中用到了C库函数中的strchr.用法可以参考我的这篇博客C/C++常用库函数
关于这个题的分析在代码中已详细给出
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <string.h>
//二叉链表结点结构
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *Lchild;
struct Node *Rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
BiTree CreateBiTree(char *pre, char *in, long n) {
//递归终止条件
//只要遇到递归必不可少。
if (n <= 0) {
return NULL;
}
BiTree root;
root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
//先序序列(根左右)中的第一个元素必为树根结点
root->data = pre[0];
//计算根结点在中序序列中出现的位置
//“拆分”中序序列
char *p = strchr(in, pre[0]);
//“拆分”中序序列后得到左子树的长度
//为了下面的递归(自己调用自己)做准备.
long len = p - in;
//printf("%ld\n", len);
//递归求左子树
//参数一:先序序列(拆分后得到的左子树),
//参数二:中序序列(拆分后得到的左子树)
//参数三:长度
root->Lchild = CreateBiTree(pre + 1, in, len);
//递归求右子树
//同理
root->Rchild = CreateBiTree(pre + len + 1, p + 1, n - len - 1);
return root;
}
void postOrder(BiTree root) {
if (root) {
postOrder(root->Lchild);
postOrder(root->Rchild);
printf("%c", root->data);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
char preStr[100], inStr[100];
BiTree root;
scanf("%s", preStr);
scanf("%s", inStr);
root = CreateBiTree(preStr, inStr, strlen(preStr));
postOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
依据中序、后序遍历序列创建二叉树
由上题可以很容易得到此题。
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <string.h>
//二叉链表结点结构
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *Lchild;
struct Node *Rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
BiTree CreateBiTree(char *in, char *post, long n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return NULL;
}
BiTree root;
root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
root->data = post[n - 1];
char *p;
p = strchr(in, post[n - 1]);
long len = p - in;
//printf("%ld\n", len);
root->Lchild = CreateBiTree(in, post, len);
root->Rchild = CreateBiTree(in + len + 1, post + len, n - len - 1);
return root;
}
void preOrder(BiTree root) {
if (root) {
printf("%c", root->data);
preOrder(root->Lchild);
preOrder(root->Rchild);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
char inStr[100], postStr[100];
BiTree root;
scanf("%s", inStr);
scanf("%s", postStr);
root = CreateBiTree(inStr, postStr, strlen(inStr));
preOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
结点及其所在层次
题目描述
从键盘接收扩展先序序列,以二叉链表作为存储结构,建立二叉树。按先序遍历次序输出各结点的内容及相应的层次数,要求以二元组的形式输出,其所对应的输出结果为:(data,level)
data是二叉树结点数据域值,level是该结点所在的层次。
设根节点在第一层。
输出的元素间不用间隔,()都是英文字符
样例输入 Copy
AB#DG###CE##FH###
样例输出 Copy
(A,1)(B,2)(D,3)(G,4)(C,2)(E,3)(F,3)(H,4)
void PreOrder(BiTree root, int level) {
if (root) {
printf("(%c,%d)", root->data, level);
PreOrder(root->Lchild, level + 1);
PreOrder(root->Rchild, level + 1);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
BiTree root;
//root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
CreateBiTree(&root);
int level = 1;
PreOrder(root, level);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
某层叶子结点个数
题目描述
从键盘接收扩展先序序列,以二叉链表作为存储结构,建立二叉树。并计算指定的第K层的叶子结点个数。设根结点在第一层。
第一行:扩展先序序列
第二行:k的值
样例输入 Copy
ABC##DE#G##F###
3
样例输出 Copy
1
int k, num = 0;
void PreOrder(BiTree root, int level) {
//printf("进来了");
if (root) {
if (level == k && root->Lchild == NULL && root->Rchild == NULL) {
num++;
}
//printf("(%c,%d)", root->data, level);
PreOrder(root->Lchild, level + 1);
PreOrder(root->Rchild, level + 1);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
BiTree root;
//root = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
CreateBiTree(&root);
int level = 1;
scanf("%d", &k);
PreOrder(root, level);
printf("%d", num);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
哈夫曼
题目描述
假设某通信报文的字符集由A,B,C,D,E,F这6个字符组成,它们在报文中出现的频度(频度均为整数值)。
(1)构造一棵哈弗曼树,依次给出各字符编码结果。
(2)给字符串进行编码。
(3)给编码串进行译码。
规定:
构建哈弗曼树时:左子树根结点权值小于等于右子树根结点权值。
生成编码时:左分支标0,右分支标1。
输入
第一行:依次输入6个整数,依次代表A,B,C,D,E,F的频度,用空格隔开。
第二行:待编码的字符串
第三行:待译码的编码串
输出
前6行依次输出各个字符及其对应编码,格式为【字符:编码】(冒号均为英文符号)
第7行:编码串
第8行:译码串
样例输入 Copy
3 4 10 8 6 5
BEE
0010000100111101
样例输出 Copy
A:000
B:001
C:10
D:01
E:111
F:110
001111111
BADBED
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 30
#define M 2 * N - 1
typedef struct {
int index;
int weight;
int Parent, Lchild, Rchild;
}HTNode, HuffmanTree[M + 1];
typedef struct {
HTNode data[1000];
int top;
}SeqStack;
typedef char * Huffmancode[100];
void init(SeqStack **s) {
(*s) = (SeqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
(*s)->top = -1;
}
void push(SeqStack *s, HTNode x) {
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = x;
}
void pop(SeqStack *s, int *p) {
(*p) = s->data[s->top].index;
s->top--;
}
void pop2(SeqStack *s) {
//(*p) = s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
}
int top1(SeqStack *s) {
return s->data[s->top].weight;
}
int top2(SeqStack *s) {
return s->data[s->top - 1].weight;
}
void twoMinSelect(HTNode ht[], int n, int *s1, int *s2) {
SeqStack *s;
init(&s);
HTNode q, p;
q.weight = 999;
p.weight = 999;
push(s, q);
push(s, p);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (ht[i].Parent == 0) {
if (ht[i].weight <= top1(s) && top1(s) >= top2(s)) {
pop2(s);
push(s, ht[i]);
} else if (ht[i].weight <= top1(s) && top1(s) <= top2(s)){
push(s, ht[i]);
} else if (ht[i].weight < top1(s) || ht[i].weight < top2(s)) {
push(s, ht[i]);
}
}
}
if (top1(s) > top2(s)) {
pop(s, s2);
pop(s, s1);
} else {
pop(s, s1);
pop(s, s2);
}
}
//建立哈夫曼树
void CrtHuffmanTree(HuffmanTree ht, int w[], int n) {
int m = 2 * n - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ht[i].index = i;
ht[i].weight = w[i];
ht[i].Parent = 0;
ht[i].Lchild = 0;
ht[i].Rchild = 0;
}
for (int i = n + 1; i <= m; i++) {
ht[i].index = i;
ht[i].weight = 0;
ht[i].Parent = 0;
ht[i].Lchild = 0;
ht[i].Rchild = 0;
}
for (int i = n + 1; i <= m; i++) {
int s1, s2;
twoMinSelect(ht, i - 1, &s1, &s2);
ht[i].weight = ht[s1].weight + ht[s2].weight;
ht[i].Lchild = s1;
ht[i].Rchild = s2;
ht[s1].Parent = i;
ht[s2].Parent = i;
}
}
//哈夫曼编码
void CrtHuffmanCode1(HuffmanTree ht, Huffmancode hc, int n) {
char *cd;
int start;
cd = (char *)malloc(n * sizeof(char));
cd[n - 1] = '\0';
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
start = n - 1;
int c = i;
int p = ht[i].Parent;
while (p != 0) {
--start;
if (ht[p].Lchild == c) {
cd[start] = '0';
} else {
cd[start] = '1';
}
c = p;
p = ht[p].Parent;
}
hc[i] = (char *)malloc((n - start) * sizeof(char));
strcpy(hc[i], &cd[start]);
}
free(cd);
}
//译码
void Output(Huffmancode hc) {
char ch = 65;
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
printf("%c:%s\n", ch, hc[i]);
// if (i != 6) {
// printf("\n");
// }
ch++;
}
}
void secondQuestion(char will[], Huffmancode hc) {
int lenth = 0;
int j = 0;
while (will[j]) {
lenth++;
j++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < lenth; i++) {
for (int j = 65; j <= 71; j++) {
if (will[i] == j) {
printf("%s", hc[j - 64]);
}
}
}
}
//16 5 10 20 3 1
//ABC
//11000110010
void thirdQuestion(HuffmanTree ht, char *third) {
// for (int i = 1; i <= 11; i++) {
// printf("%d:%d %d %d %d\n", i, ht[i].weight, ht[i].Parent, ht[i].Lchild, ht[i].Rchild);
// }
int length = 0;
int j = 0;
while (third[j]) {
length++;
j++;
}
//printf("length:%d\n", length);
int t = 11;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i = k) {
while (1) {
if (ht[t].Lchild == 0 && ht[t].Rchild == 0) {
//下标t与字母之间是有关系的,t-1+'A'即对应字符的ASCII码
printf("%c", t - 1 + 'A');
t = 11;
break;
} else {
if (third[k] == '1') {
t = ht[t].Rchild;
k++;
} else {
t = ht[t].Lchild;
k++;
}
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
int w[100] = {0};
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
scanf("%d", &w[i]);
}
char will[50];
char third[50];
scanf("%s", will);
scanf("%s", third);
HuffmanTree ht;
Huffmancode hc;
CrtHuffmanTree(ht, w, 6);
CrtHuffmanCode1(ht, hc, 6);
Output(hc);
secondQuestion(will, hc);
printf("\n");
thirdQuestion(ht, third);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}





















 333
333











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








