Bean生命周期的管理,可以参考Spring的源码:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的doCreateBean()方法。
什么是Bean的生命周期
Spring其实就是一个管理Bean对象的容器。它负责对象的创建、销毁等等。生命周期指的就是对象从创建开始到销毁的整个过程。生命周期的本质就是在一个时间节点上调用了类上的某个方法。我们需要充分的了解在这个生命线上,都有哪些特殊的时间节点,这样才能够明确代码要写到哪里。我们可能需要在某个特殊的时间点上执行一段特定的代码,这段代码就可以放到放到这个节点上。当生命线走到这里的时候,自然会被调用。
想要了解生命周期就要思考这几个问题:
- Bean对象是什么时候创建的
- Bean对象创建前后调用了哪些方法
- Bean对象是什么时候销毁的
- Bean对象销毁前后调用了哪些方法
生命周期之五步
Bean对象的生命周期可以粗略的分为五步:✅实例化Bean
✅Bean属性赋值
✅初始化Bean
✅使用Bean
✅销毁Bean
流程图大致为:
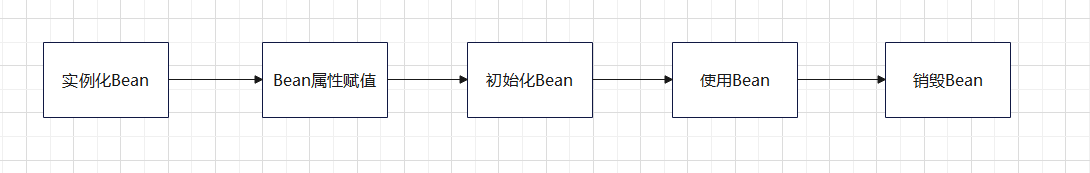
生命周期五步流程图
代码示例
第一步:创建一个Bean,并创建对应的init()和destroy()方法注意:这个init()和destroy()方法需要我们自己写,自己配,实际中这些操作Spring会完成,这里自己写是为了方便测试
package com.powernode.entity;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description:
* Bean的生命周期初略分为五步:
* 第一步:实例化Bean 调用无参数构造方法
* 第二步:给Bean属性赋值 调用set方法
* 第三步:Bean初始化 调用init()方法,
* 第四步:使用Bean
* 第五步:销毁Bean 调用destroy()方法
* 值得注意的是,这个init()和destroy()方法需要我们自己写,自己配,实际中这些操作Spring会完成,这里自己写是为了方便测试
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 11:02
*/
public class User {
private String name;
public User(){
System.out.println("第一步:实例化Bean");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("第二步:给Bean属性赋值");
this.name = name;
}
public void initBean(){
System.out.println("第三步:初始化Bean");
}
public void destroyBean(){
System.out.println("第五步:销毁Bean");
}
}
第二步:实现Spring配置文件,并指定Bean的init-method和destroy-method属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
需要手动指定初始化方法,和销毁方法。
init-method属性指定初始化方法。
destroy-method属性指定销毁方法。
-->
<bean id="userBean" class="com.powernode.entity.User" init-method="initBean" destroy-method="destroyBean">
<property name="name" value="配置Spring"/>
</bean>
</beans>
import com.powernode.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 16:56
*/
public class lifeCycleTest {
@Test
public void FiveBeanTest(){
// 五步生命周期 测试方法
ApplicationContext beans = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lifeCycle-beans.xml");
User userBean = beans.getBean("userBean", User.class);
System.out.println("第四步:使用Bean: " + userBean);
// 只有正常关闭spring容器才会执行销毁方法
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) beans;
context.close();
}
}
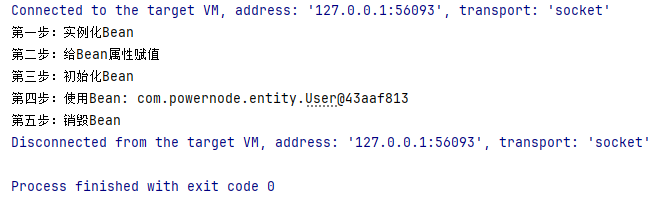
需要注意的是:
- 只有正常关闭Spring容器,bean的销毁方法才会被调用
ClassPathXMLApplicationContext类才有close()方法- 配置文件中的init-method指定初始化方法;destroy-method指定销毁方法
生命周期之七步
生命周期之七步:
- 实例化Bean
- Bean属性赋值
- 执行“Bean后处理器”的before方法
- 初始化Bean
- 执行“Bean后处理器”的after方法
- 使用Bean
- 销毁Bean
相比于五步生命周期,添加了Bean后处理器,节点分别在初始化Bean的前后
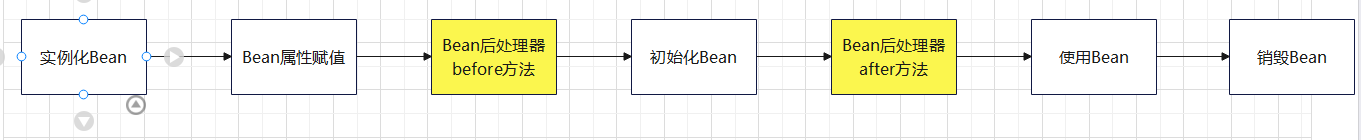
代码示例
package com.powernode.entity;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 17:22
*/
public class Order {
private String name;
public Order(){
System.out.println("第一步:实例化Bean");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("第二步:给Bean属性赋值");
this.name = name;
}
public void initBean(){
System.out.println("第四步:初始化Bean");
}
public void destroyBean(){
System.out.println("第七步:销毁Bean");
}
}
编写一个类实现BeanPostProcessor类,并且重写before()和after()方法
package com.powernode.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 17:23
*/
public class LogBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// AfterInitialization
System.out.println("第五步:执行Bean后处理器的after方法");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//BeforeInitialization
System.out.println("第三步:执行Bean后处理器的before方法");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
在spring.xml文件中配置“Bean后处理器”
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="orderBean" class="com.powernode.entity.Order" init-method="initBean" destroy-method="destroyBean">
<property name="name" value="order配置Spring"/>
</bean>
<!--配置Bean后处理器-->
<!--注意:这个Bean后处理器将作用于整个配置文件中所有的Bean-->
<bean class="com.powernode.entity.LogBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
import com.powernode.entity.Order;
import com.powernode.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 16:56
*/
public class lifeCycleTest {
@Test
public void sevenBeanTest(){
// 七步生命周期 测试方法
ApplicationContext beans = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lifeCycle-beans.xml");
Order orderBean = beans.getBean("orderBean", Order.class);
System.out.println("第六步:使用Bean: " + orderBean);
// 只有正常关闭spring容器才会执行销毁方法
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) beans;
context.close();
}
}
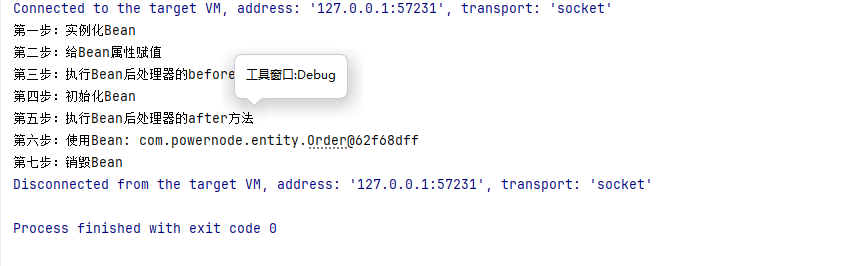
- 在spring.xml文件中配置的**Bean后处理器将作用于当前配置文件中所有的Bean.**
生命周期之十步
> 1. 实例化Bean > 2. Bean属性赋值 > 3. 检查Bean是否实现Aware相关接口,并调用接口方法 > 4. 执行“Bean后处理器”的before方法 > 5. 检查Bean是否实现了InitializingBean接口,并调用接口方法 > 6. 初始化Bean > 7. 执行“Bean后处理器”的after方法 > 8. 使用Bean > 9. 检查Bean是否实现了DisposableBean接口,并调用接口方法 > 10. 销毁Bean >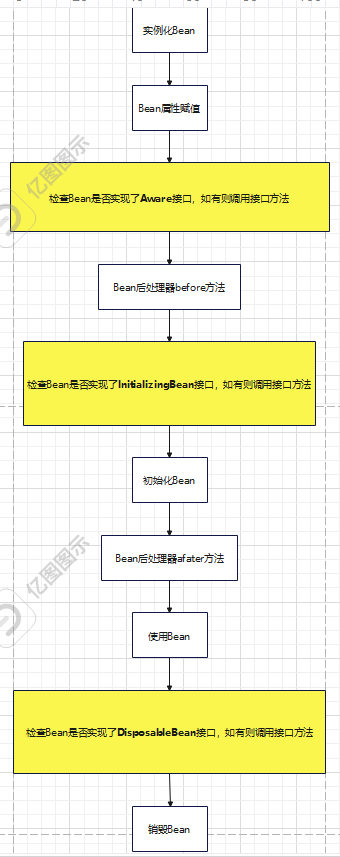
Aware相关接口包括:BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware
- 当Bean实现了`BeanNameAware`,Spring会将Bean的名字传递给Bean. - 当Bean实现了`BeanClassLoaderAware`,Spring会将加载该Bean的类加载器传递给Bean. - 当Bean实现了`BeanFactoryAware`,Spring会将Bean工厂对象传递给Bean.
测试Bean的生命周期之十步,可以让实体类实现5个接口,并实现所有的方法:并实现所有的方法:BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware、InitializingBean、DisposableBean
代码示例
package com.powernode.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 17:22
*/
public class Order implements BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
public Order(){
System.out.println("第一步:实例化Bean");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("第二步:给Bean属性赋值");
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第五步:afterPropertiesSet执行");
}
public void initBean(){
System.out.println("第六步:初始化Bean");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("第三步:Bean的名字:" + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.out.println("第三步:类加载器:" + classLoader);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第三步:Bean工厂:" + beanFactory);
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第九步:DisposableBean destroy");
}
public void destroyBean(){
System.out.println("第十步:销毁Bean");
}
}
package com.powernode.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 17:23
*/
public class LogBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// AfterInitialization
System.out.println("第七步:执行Bean后处理器的after方法");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//BeforeInitialization
System.out.println("第四步:执行Bean后处理器的before方法");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
需要手动指定初始化方法,和销毁方法。
init-method属性指定初始化方法。
destroy-method属性指定销毁方法。
-->
<!--<bean id="userBean" class="com.powernode.entity.User" init-method="initBean" destroy-method="destroyBean">-->
<!-- <property name="name" value="配置Spring"/>-->
<!--</bean>-->
<bean id="orderBean" class="com.powernode.entity.Order" init-method="initBean" destroy-method="destroyBean">
<property name="name" value="order配置Spring"/>
</bean>
<!--配置Bean后处理器-->
<!--注意:这个Bean后处理器将作用于整个配置文件中所有的Bean-->
<bean class="com.powernode.entity.LogBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
import com.powernode.entity.Order;
import com.powernode.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 16:56
*/
public class lifeCycleTest {
@Test
public void tenBeanTest(){
// 十步生命周期 测试方法
ApplicationContext beans = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lifeCycle-beans.xml");
Order orderBean = beans.getBean("orderBean", Order.class);
System.out.println("第八步:使用Bean: " + orderBean);
// 只有正常关闭spring容器才会执行销毁方法
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) beans;
context.close();
}
}
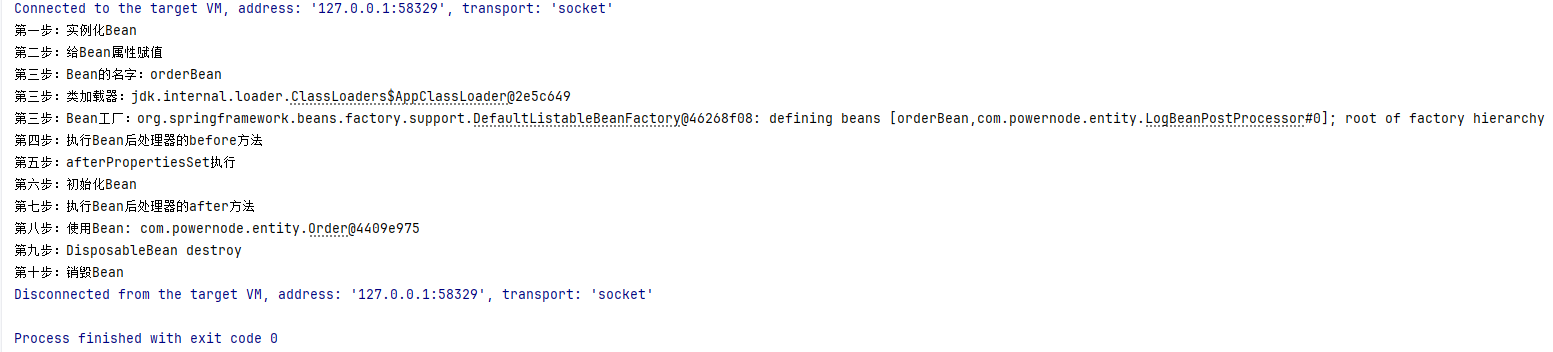
通过测试可以看出:
InitializingBean的方法早于init-method的执行。DisposableBean的方法早于destroy-method的执行。
Bean的作用域不同,生命周期不同
Spring根据Bean的作用域不同来选择管理方法: * 对于singleton作用域的Bean,Spring能够精准的知道该Bean何时被创建,何时完成初始化以及何时被销毁
* 而对于prototype作用域的Bean,Spring只负责创建,当容器创建了Bean的实例后,Bean的实例就交给客户端代码管理,Spring容器将不再跟踪生命周期
package com.powernode.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 17:22
*/
public class Order implements BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
public Order(){
System.out.println("第一步:实例化Bean");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("第二步:给Bean属性赋值");
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第五步:afterPropertiesSet执行");
}
public void initBean(){
System.out.println("第六步:初始化Bean");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("第三步:Bean的名字:" + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
System.out.println("第三步:类加载器:" + classLoader);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第三步:Bean工厂:" + beanFactory);
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第九步:DisposableBean destroy");
}
public void destroyBean(){
System.out.println("第十步:销毁Bean");
}
}
package com.powernode.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 17:23
*/
public class LogBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// AfterInitialization
System.out.println("第七步:执行Bean后处理器的after方法");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//BeforeInitialization
System.out.println("第四步:执行Bean后处理器的before方法");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="orderBean" class="com.powernode.entity.Order" init-method="initBean" destroy-method="destroyBean" scope="prototype">
<property name="name" value="order配置Spring"/>
</bean>
<!--配置Bean后处理器-->
<!--注意:这个Bean后处理器将作用于整个配置文件中所有的Bean-->
<bean class="com.powernode.entity.LogBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
import com.powernode.entity.Order;
import com.powernode.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/25 16:56
*/
public class lifeCycleTest {
@Test
public void tenBeanTest(){
// 十步生命周期 测试方法
ApplicationContext beans = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lifeCycle-beans.xml");
Order orderBean = beans.getBean("orderBean", Order.class);
System.out.println("第八步:使用Bean: " + orderBean);
// 只有正常关闭spring容器才会执行销毁方法
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) beans;
context.close();
}
}
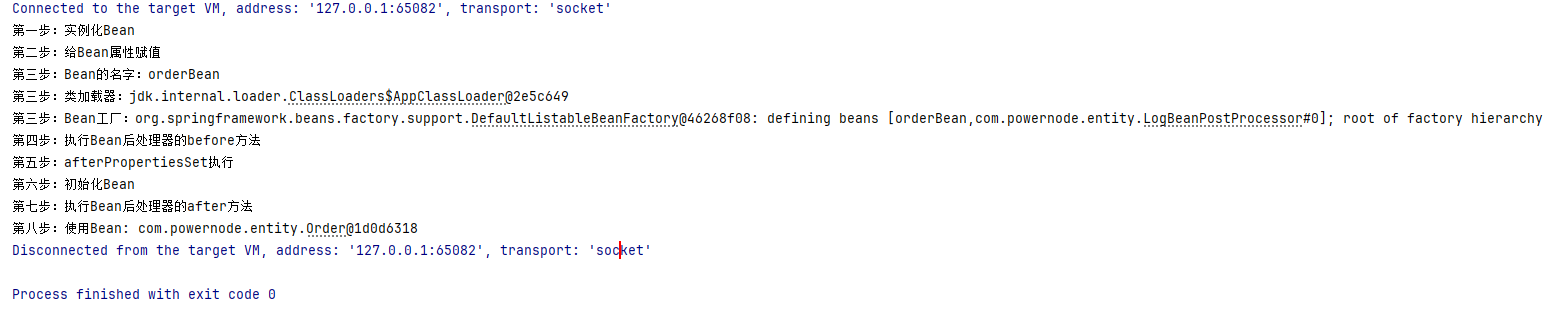
从运行结果可以看到,十步周期到使用Bean就结束了,也就是说Spring对于prototype作用域的Bean后续并没有继续跟踪,不会进行销毁以及销毁前事件的调用
自己new的对象如何让Spring管理
现在有一个Java对象是我们自己new的,然后我们希望这个对象被Spring容器管理,应该实现一下操作。package com.powernode.entity;
public class User {
}
import com.powernode.entity.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
/**
* @Author:
* @Description: TODO
* @DateTime: 2024/9/26 16:40
*/
public class RegisterBeanTest {
@Test
public void registerTest(){
// 自己new的对象
User user = new User();
System.out.println(user);
// 创建 默认列表 BeanFactory 对象
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// 注册Bean
factory.registerSingleton("userBean", user);
User userBean = factory.getBean("userBean", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
Bean的生命周期深度解析
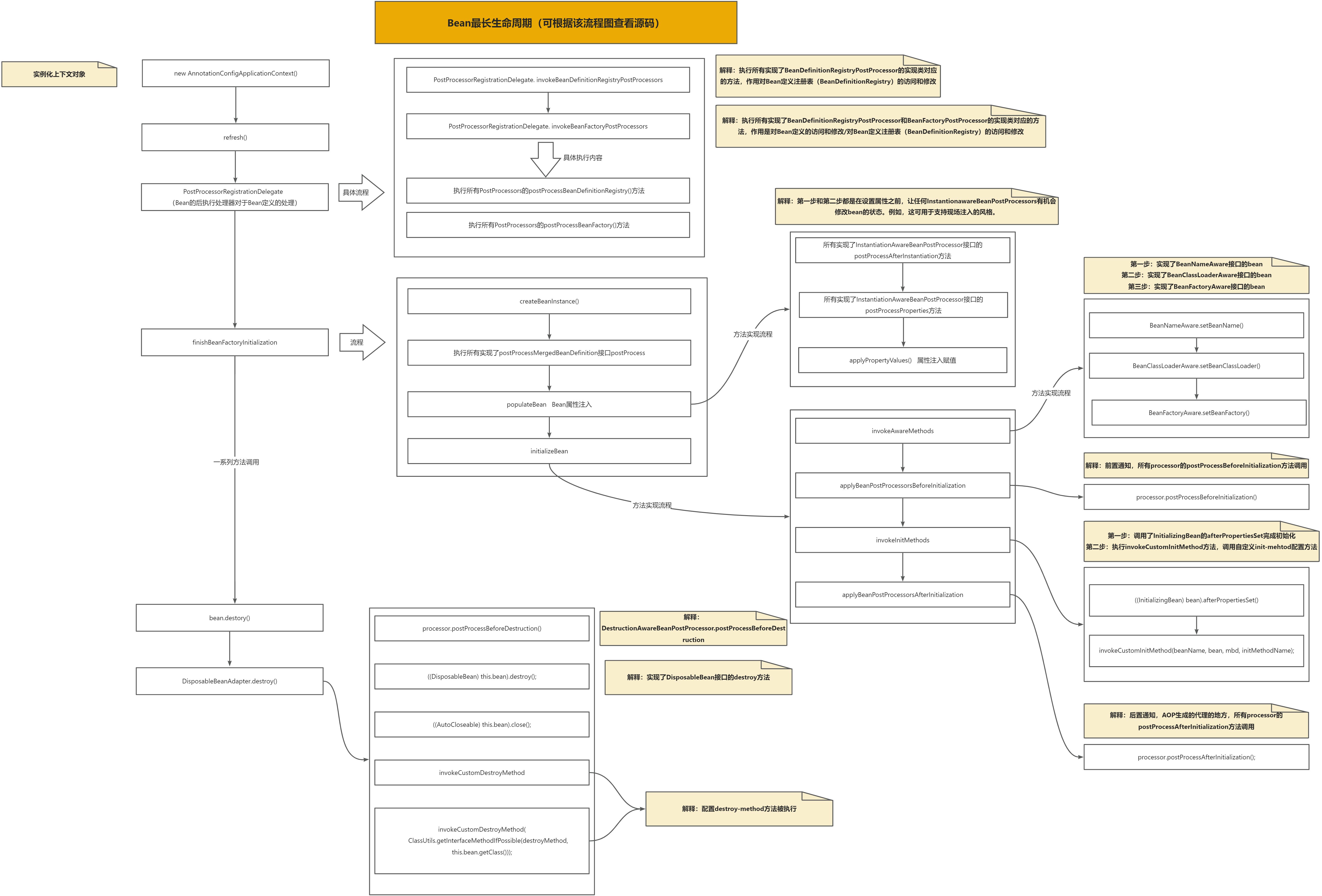由上述流程图可以分出三大部分:PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate、finishBeanFactoryInitialization、destroy
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate:该步骤主要操作就是对Bean定义进行修改
作用:
■ Bean定义的操作,在Bean实例化之前对Bean定义进行修改,包括添加新的Bean定义、修改现有Bean定义的属性或者元数据
■ 优先级排序,对于实现了PriorityOrdered或Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,可以根据它们的优先级顺序来执行
■ 注解的解析和扫描,在此过程中,Spring会解析各种注解(如@Component、@Service、@Repository等),并将对应的类作为Bean定义注册到容器中
■ 自动配置,Spring的自动配置机制也在这个阶段进行,它会根据项目中的依赖和条件来自动配置Bean
将上述生命周期流程的主要步骤简化成以下流程图:
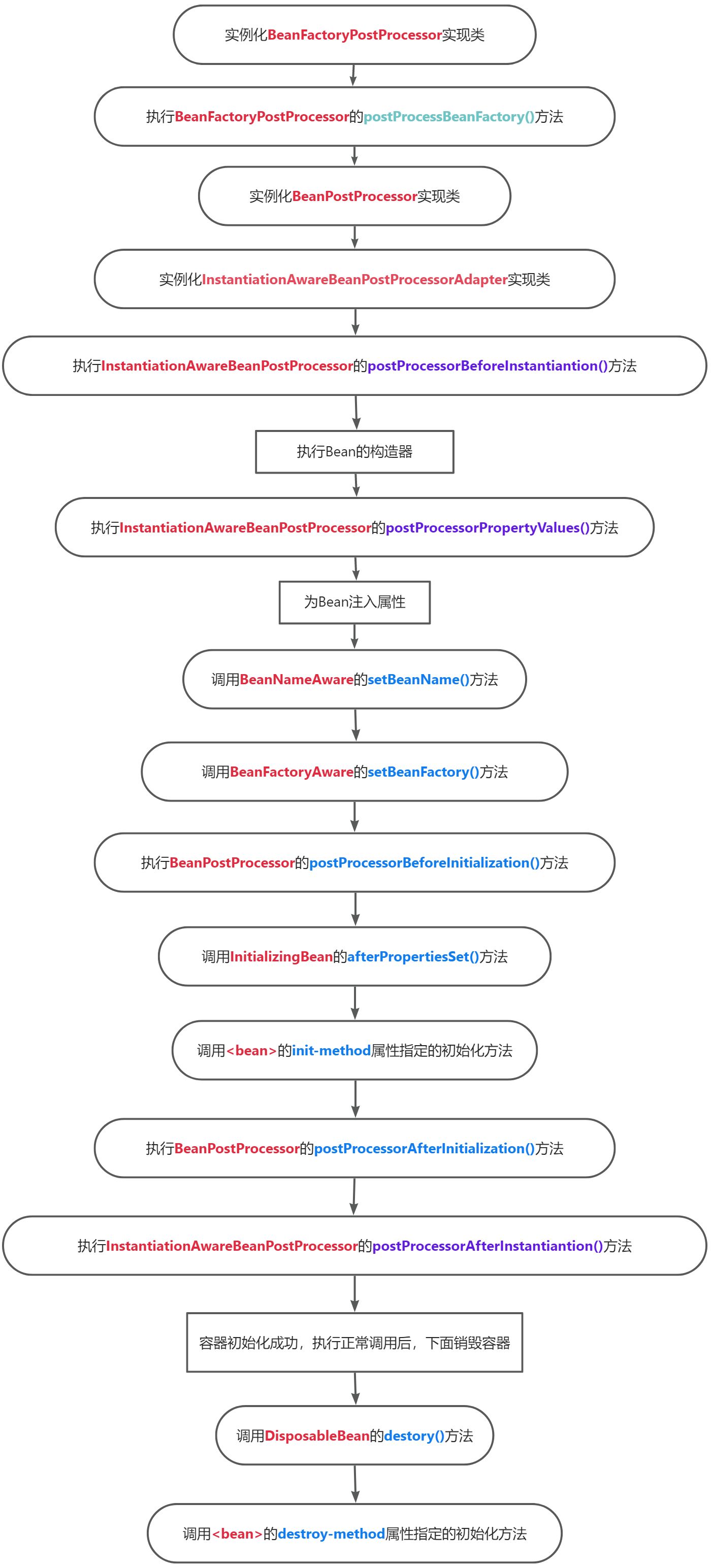





















 4360
4360

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








