简介
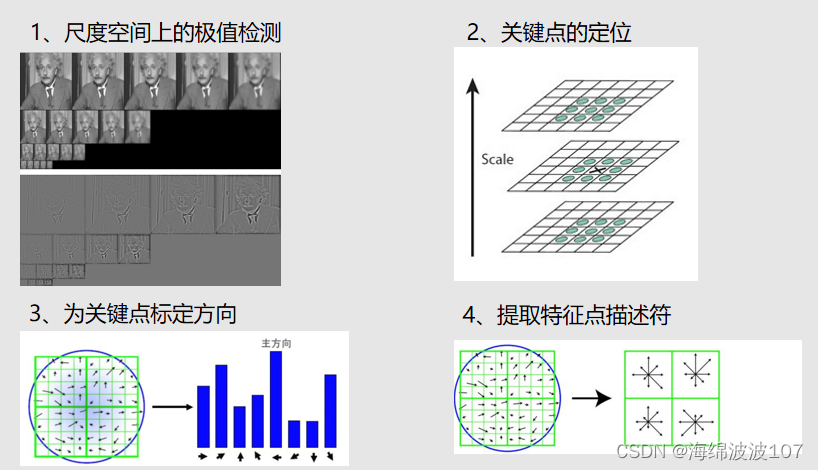
SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)图像匹配是一种在多幅图像之间找出相同特征点(即关键点匹配)的技术。以下是SIFT图像匹配的一般步骤:
- 关键点检测:
对每幅图像,SIFT算法通过高斯差分金字塔来检测潜在的关键点。这些点是在图像尺度空间中亮度极大或极小的点,可能对应于物体的角点、边缘或斑点。
关键点定位:
对这些潜在关键点进行精确定位,并去除低对比度的点以及在边缘附近响应较高的点,因为这些点在匹配过程中可能不稳定。
- 关键点方向赋值:
为每个关键点赋予一个或多个方向,基于其局部图像梯度的方向。这一步是SIFT算法旋转不变性的关键。
- 关键点描述符生成:
在每个关键点周围的区域内,计算局部梯度的方向和大小,并将其转换成一个描述符。描述符通常是一个特征向量,能够在不同的图像之间提供足够的信息进行匹配,同时对于光照、三维视角等变化保持不变性。
- 特征点匹配:
比较不同图像中的关键点描述符,找出相似度最高的一对关键点,并将它们标记为匹配点。常用的相似度度量方法是欧氏距离或余弦相似度。
为了提高匹配的准确性,通常还会使用一个比率测试,例如David Lowe提出的最近邻和次近邻比率测试,用来排除一些错误匹配。
- 匹配优化:
进行一些后处理步骤,如RANSAC(随机抽样一致性算法)来进一步排除错误匹配,以及使用仿射变换或单应性(Homography)矩阵来计算图像间的几何变换。
在进行SIFT图像匹配时,也可以采取一些优化措施来提高效率和准确性,例如使用近似最近邻搜索算法来加速关键点描述符之间的匹配过程,或者采用多核处理和GPU加速等技术来处理大规模数据集。SIFT算法的一个关键优势是其对于图像尺度和旋转的不变性,使其成为许多图像匹配、图像拼接、目标识别和计算机视觉任务中的重要技术。
结果

源代码
代码是在jupyter notebook上运行
特征点匹配
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
from prettytable import PrettyTable
# 检测图像关键点
def sift_detect(img):
sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
return sift.detect(img,None)
# 展示图像
def imshow(img, title=None, dpi=200):
plt.figure(dpi=dpi)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title(title)
plt.imshow(img[...,::-1])
plt.show()
# 无裁剪的旋转
def rotate_bound(image, angle):
# grab the dimensions of the image and then determine the center
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
(cX, cY) = (w // 2, h // 2)
# grab the rotation matrix (applying the negative of the
# angle to rotate clockwise), then grab the sine and cosine
# (i.e., the rotation components of the matrix)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cX, cY), -angle, 1.0)
cos = np.abs(M[0, 0])
sin = np.abs(M[0, 1])
# compute the new bounding dimensions of the image
nW = int((h * sin) + (w * cos))
nH = int((h * cos) + (w * sin))
# adjust the rotation matrix to take into account translation
M[0, 2] += (nW / 2) - cX
M[1, 2] += (nH / 2) - cY
# perform the actual rotation and return the image
return M,cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (nW, nH))
# 计算经线性变换后的点
def apply_matrix(M,point):
point = np.array([point[0],point[1],1]).T
M = np.vstack([M,[0,0,1]])
res = M.dot(point)
return (int(res[0]),int(res[1]))
# 统计匹配的特征点
def count_matched_kp(kp_set,target_kp_set):
d = [(i%3-1,j%3-1) for i in range(3) for j in range(3)]
# d = [(-1, -1), (-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, -1), (0, 0), (0, 1), (1, -1), (1, 0), (1, 1)]
count = 0
for i in target_kp_set:
for j in d:
if (i[0]+j[0],i[1]+j[1]) in kp_set:
count+=1
break
return count
图像拼接
from PIL import Image
class Stitcher:
# 拼接函数
def stitch(self, images, ratio=0.75, reprojThresh=4.0, showMatches=False):
# 获取输入图片
(imageB, imageA) = images
# 检测A、B图片的SIFT关键特征点,并计算特征描述子
(kpsA, featuresA) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageA)
(kpsB, featuresB) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageB)
# 匹配两张图片的所有特征点,返回匹配结果
M = self.matchKeypoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh)
# 如果返回结果为空,没有匹配成功的特征点,退出算法
if M is None:
return None
# 否则,提取匹配结果
# H是3x3视角变换矩阵
(matches, H, status) = M
# 将图片A进行视角变换,result是变换后图片
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, (imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1], imageA.shape[0]))
# 融合
for r in range(result.shape[0]):
left = 0
for c in range(result.shape[1]//2):
if result[r,c].any(): # overlap
if left == 0:
left = c
alpha = (c-left)/(result.shape[1]//2-left)
result[r,c] = imageB[r,c]*(1-alpha) + result[r,c]*alpha
else:
result[r,c] = imageB[r,c]
# 将图片B传入result图片最左端
# result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]] = imageB
# 检测是否需要显示图片匹配
if showMatches:
# 生成匹配图片
vis = self.drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status)
# 返回结果
return (result, vis)
# 返回匹配结果
return result
def detectAndDescribe(self, image):
# 将彩色图片转换成灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 建立SIFT生成器
descriptor = cv2.SIFT_create()
# 检测SIFT特征点,并计算描述子
(kps, features) = descriptor.detectAndCompute(gray, None)
# 将结果转换成NumPy数组
kps = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps])
# 返回特征点集,及对应的描述特征
return kps, features
def matchKeypoints(self, kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh):
# 建立暴力匹配器
matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create("BruteForce")
# 使用KNN检测来自A、B图的SIFT特征匹配对,K=2
rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2)
matches = []
for m in rawMatches:
# 当最近距离跟次近距离的比值小于ratio值时,保留此匹配对
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < m[1].distance * ratio:
# 存储两个点在featuresA, featuresB中的索引值
matches.append((m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx))
# 当筛选后的匹配对大于4时,计算视角变换矩阵
if len(matches) > 4:
# 获取匹配对的点坐标
ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[i] for (_, i) in matches])
ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[i] for (i, _) in matches])
# 计算视角变换矩阵
(H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC, reprojThresh)
# 返回结果
return (matches, H, status)
# 如果匹配对小于4时,返回None
return None
def drawMatches(self, imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status):
# 初始化可视化图片,将A、B图左右连接到一起
(hA, wA) = imageA.shape[:2]
(hB, wB) = imageB.shape[:2]
vis = np.zeros((max(hA, hB), wA + wB, 3), dtype="uint8")
vis[0:hA, 0:wA] = imageA
vis[0:hB, wA:] = imageB
# 联合遍历,画出匹配对
for ((trainIdx, queryIdx), s) in zip(matches, status):
# 当点对匹配成功时,画到可视化图上
if s == 1:
# 画出匹配对
ptA = (int(kpsA[queryIdx][0]), int(kpsA[queryIdx][1]))
ptB = (int(kpsB[trainIdx][0]) + wA, int(kpsB[trainIdx][1]))
cv2.line(vis, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 返回可视化结果
return vis
应用
# 读取拼接图片
imageA = cv2.imread("huo50_3.jpg")
imageB = cv2.imread("huo1.jpg")
# 把图片拼接成全景图
stitcher = Stitcher()
(result, vis) = stitcher.stitch([imageA, imageB], showMatches=True)
imshow(vis,title='Keypoint Matches',dpi=200)
imshow(result, title='Result',dpi=200)
导出图像
cv2.imwrite('room_pingjie.jpg',result)








 本文详细介绍了SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)在图像匹配中的应用,包括关键点检测、精确定位、方向赋值、描述符生成以及特征点匹配的过程,并提供了Python代码示例,展示了如何使用SIFT进行图像拼接和结果可视化。
本文详细介绍了SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)在图像匹配中的应用,包括关键点检测、精确定位、方向赋值、描述符生成以及特征点匹配的过程,并提供了Python代码示例,展示了如何使用SIFT进行图像拼接和结果可视化。















 2575
2575











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










