大整数
1.大整数加法
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iomanip>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define max_n 1000
char str1[max_n], str2[max_n];
int num1[max_n], num2[max_n];
int main() {
memset(str1, 0, sizeof(str1));
memset(str2, 0, sizeof(str2));
memset(num1, 0, sizeof(num2));
memset(num2, 0, sizeof(num2));
scanf("%s%s", str1, str2);
int len1 , len2;
len1 = strlen(str1);
len2 = strlen(str2);
int j = 0;
int max = len1 > len2 ? len1 : len2;//取长度最大的赋值给max
for (int i = len1 - 1 ;i >= 0 ;i--)
num1[j++] = str1[i] - '0';
//到过来存储
j = 0;
for (int i = len2 - 1 ;i >= 0 ;i--)
num2[j++] = str2[i] - '0';
//到过来存储
for (int i = 0 ;i < max; i++) {//以最长的长度为基准
num2[i] += num1[i];
if (num2[i] >= 10) {
num2[i] -= 10;
num2[i + 1] += 1;
}
}
if (num2[max]) printf("%d", num2[max]);
for (int i = max - 1;i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%d", num2[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
代码解析
1.第一种要注意到的就是位数不想等的情况,所以我门要先对齐位数,再去模仿竖式
就用 int max = len1 > len2 ? len1 : len2
2.做完之后将数字到着存在数组中,为了方便思考。
3.之后就是核心思想进位 10位进1, 向下一位进,这就是到这存储的原因
2.大整数减法
思想就是比大整数加法繁琐一点
最主要的一点就是大整数减法是要去借位,去向上一位借1位, 上一位减一位
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string str1, str2, str3;
int aa[1005], bb[1005], cc[1005], la, lb, lc;
int main(){
cin >> str1 >> str2;
la = str1.size();
lb = str2.size();
if(la < lb || ((la == lb) && (str1 < str2))){
str3 = str2;
str2 = str1;
str1 = str3;
cout << "-";
}
la = str1.size();
lb = str2.size();
for(int i = 0; i < la; i++){
aa[i] = str1[la - i -1] - '0';
}
for(int i = 0; i < lb; i++){
bb[i] = str2[lb - i -1] - '0';
}
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < la; i++){
k = aa[i] - bb[i];
if(k < 0){
k += 10;
aa[i + 1] -= 1;
}
cc[i] = k;
}
while(cc[la] == 0) la--;
for(int i = la; i >= 0 ; i--){
cout << cc[i];
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
3.大整数乘法
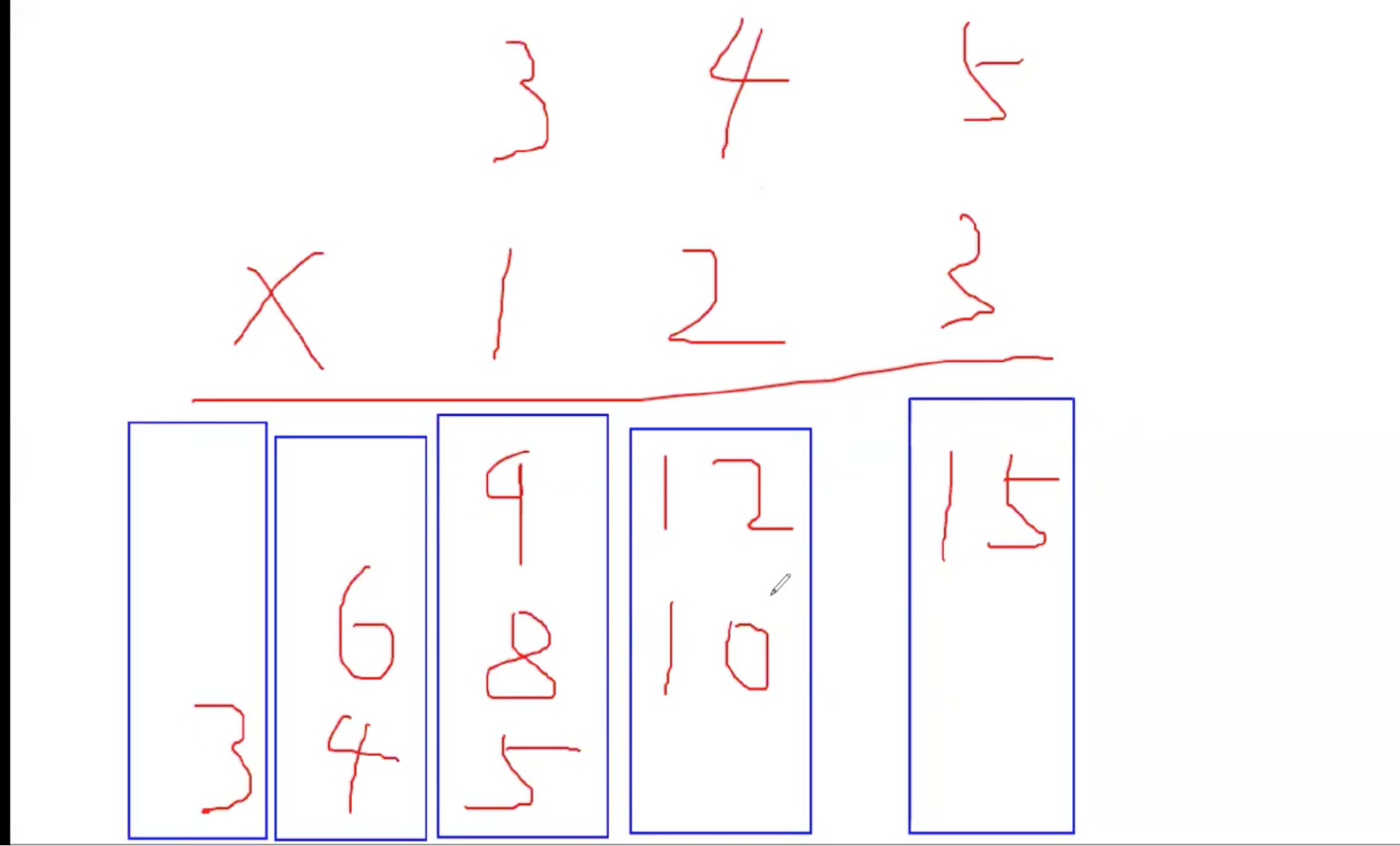
模拟竖式,将乘的结果放在数组中,最后处理一下今进位的问题

数组的0位是长度,倒着存储。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
char num1[105], num2[105];
int num3[105], num4[105], ans[305];
//用数组的0位去存长度可以节省i部分的空间
int main() {
cin >> num1 >> num2;
for (int i = strlen(num1) - 1, j = 1; i >= 0; i--, j++) {
num3[j] = num1[i] - '0';
}
for (int i = strlen(num2) - 1, j = 1; i >= 0; i--, j++) {
num4[j] = num2[i] - '0';
}
num3[0] = strlen(num1);
num4[0] = strlen(num2);
for (int i = 1; i <= num3[0]; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= num4[0]; j++) {
ans[i + j - 1] += num3[i] * num4[j];
}
}
//核心思想
for (int i = 1; i <= num3[0] + num4[0]; i++) {
if (ans[i] >= 10) {
ans[i + 1] += ans[i] / 10;
ans[i] %= 10;
}
if (ans[i] != 0) {
ans[0] = i;
}
}
for (int i = ans[0]; i > 0; i--) {
cout << ans[i];
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
4.大整数除法
1.模拟竖式,每次判断当前缓存是否大于除数
2.若大于则减去一次除数,答案加一 并继续判断
3.若不是则将除数的下一位加入缓存 同时答案进一位 并继续判断
4.直到被除数全部加入缓存 且缓存不大于除数
5.此时答案即为商 缓存即为余数























 967
967











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








