常见的四则混合运算表达式,中缀表达式便于人的理解,但后序表达式更方便计算机的运算(如二叉树运算树、堆栈的方法计算)。本文主要谈论的重点是将算术表达式的“中序表达式”转换为“后序表达式”,并根据后序表达式得到算数表达式的值。
一、中序表达式-->后序表达式(堆栈)
1、举例:
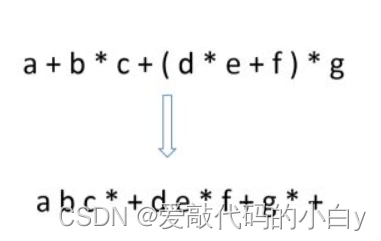
2、具体实现的算法步骤(中序->后序(infix->postfix)):
2.1)从左到右读取中序表达式infix_express中的每个字符;
2.2)如果读入的字符为操作数(a~z/A~Z),则直接输出到后序法表达式postfix_express中;
2.3)如果遇到'(',则弹出堆栈内的运算符,知道弹出到一个')',两者抵消;
'('的优先级在堆栈中,比任何运算符都小;但在堆栈外却是优先级最高的运算符;
2.4)将准备进入堆栈中的“外部运算符”与“栈顶的运算符”进行优先级比较,高于则外部运算符压入栈中;低于或等于则将栈中的元素逐个从栈顶弹出,直到外部运算符的优先级高于栈顶的运算符或栈为空时,将外部运算符压入栈;
2.5)读取完中序表达式后,如果堆栈不为空,则将其内部的运算符从栈顶逐个弹出并写在postfix_express的尾部;
注:(部分运算符)在栈中的优先级的排序:'^'、'*' '/'、'+' '-'、'('等;
3、代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include<stack> // use std::stack for Stack operations
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/* C++ implementation to convert infix expression to postfix*/
//Function to return precedence of operators
int precede(char c)
{
if (c == '^') { return 3; }
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') { return 2; }
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') { return 1; }
else if (c == '(' ) { return -1; }
else { return -1; }
}
// convert infix expression to postfix expression
string infixToPostfix(string str)
{
std::stack<char> stack_operator; // 用来存放运算符
stack_operator.push('#'); // 栈空的标识符
int len = str.length(); // 输入的中序表达式的长度
string output_postfix; // 用来存放输出的后序表达式postfix
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (str[i] != ' ') // 消除字符串中,空格的影响
{
// If the scanned character is an operand(操作数), add it to output string
if ((str[i] >= 'a' && str[i] <= 'z') || (str[i] >= 'A' && str[i] <= 'Z'))
{
output_postfix += str[i];
}
// If the scanned character is an '(', push it to the stack
else if (str[i] == '(')
{
stack_operator.push('(');
}
// If the scanned character is an ')', pop and to output string from the stack until an ‘(‘ is encountered.
else if (str[i] == ')')
{
while (stack_operator.top() != '#' && stack_operator.top() != '(')
{
char ch = stack_operator.top();
stack_operator.pop();
output_postfix += ch;
}
// 此种情况是,(一个操作数),故直接将栈中的'('弹出
if (stack_operator.top() == '(')
{
stack_operator.pop();
}
}
// If an operator is scanned
else
{
while (stack_operator.top() != '#' && precede(str[i]) <= precede(stack_operator.top()))
{
char ch = stack_operator.top();
stack_operator.pop();
output_postfix += ch;
}
stack_operator.push(str[i]);
}
}
}
// Pop all the remaining elements from the stack
while (stack_operator.top() != '#')
{
char ch = stack_operator.top();
stack_operator.pop();
output_postfix += ch;
}
return output_postfix;
}
int main()
{
string infix_express = "a+b*c/h+((d^i)*e+f)*g";
cout << "infix:" << infix_express << endl;
string postfix_express = infixToPostfix(infix_express);
cout << "postfix:" << postfix_express << endl;
return 0;
}二、将中序表达式转换成后序表达式,并计算结果
代码分析:先利用前面提到的将中序表达式转换为后序表达式;接下来,后序表达式可以直接在计算机上运算,使用循环读取表达式中的每个字符并转换成整型压入栈中,当读到运算符时从栈顶pop两个整型数字,运算后重新将结果压入栈中,知道循环结束,输出结果;
#include <iostream>
#include<stack> // use std::stack for Stack operations
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int precede(char c)
{
if (c == '^') { return 3; }
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') { return 2; }
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') { return 1; }
else { return -1; }
}
string infixToPostfix(string str)
{
std::stack<char> stack_operator; // 用来存放运算符
stack_operator.push('#'); // 栈空的标识符
int len = str.length(); // 输入的中序表达式的长度
string output_postfix; // 用来存放输出的后序表达式postfix
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
// If the scanned character is an operand(操作数), add it to output string
if (str[i] != ' ')
{
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
{
output_postfix += str[i];
}
// If the scanned character is an '(', push it to the stack
else if (str[i] == '(')
{
stack_operator.push('(');
}
// If the scanned character is an ')', pop and to output string from the stack until an ‘(‘ is encountered.
else if (str[i] == ')')
{
while (stack_operator.top() != '#' && stack_operator.top() != '(')
{
char ch = stack_operator.top();
stack_operator.pop();
output_postfix += ch;
}
// 此种情况是,(一个操作数),故直接将栈中的'('弹出
if (stack_operator.top() == '(')
{
stack_operator.pop();
}
}
// If an operator is scanned
else
{
while (stack_operator.top() != '#' && precede(str[i]) <= precede(stack_operator.top()))
{
char ch = stack_operator.top();
stack_operator.pop();
output_postfix += ch;
}
stack_operator.push(str[i]);
}
}
}
// Pop all the remaining elements from the stack
while (stack_operator.top() != '#')
{
char ch = stack_operator.top();
stack_operator.pop();
output_postfix += ch;
}
return output_postfix;
}
int calcPostfix(string str)
{
std::stack<int> stack_operand; // 用来存放操作数
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (str[i] != ' ')
{
if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
{
stack_operand.push((int)str[i] - 48); // 将字符型数字,转换为整型数字
}
else
{
int data1 = stack_operand.top();
stack_operand.pop();
int data2 = stack_operand.top();
stack_operand.pop();
if (str[i] == '+')
{
stack_operand.push(data1 + data2);
}
else if (str[i] == '-')
{
stack_operand.push(data1 - data2);
}
else if (str[i] == '*')
{
stack_operand.push(data1 * data2);
}
else if (str[i] == '/')
{
stack_operand.push((int)data1 / data2);
}
else if (str[i] == '^')
{
stack_operand.push(pow(data2, data1));
}
}
}
}
return stack_operand.top();
}
void test_calcPostfix()
{
string infix_express = "2*(3^2 + 4) + 5/6";
string postfix_express = infixToPostfix(infix_express);
cout << "postfix:" << postfix_express << endl;
int result = calcPostfix(postfix_express);
cout << result << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_calcPostfix();
return 0;
}三、中序表达式-->后序表达式(二叉树运算树)
将中序表达式按照运算符的优先级,建立一棵二叉运算树binary expression tree;之后按照二叉树的特性进行前、中、后序的遍历,即可得到前、中、后序表达式。
注意:二叉运算树的树叶一定是操作数;内部节点一定是运算符;
代码分析:①create()函数:用来将存放在一维数组中中序排列的二叉运算树的结点,通过该函数用链表表示法,将其转换为链表的形式存储;为了便于在一维数组中找到父节点对应的子节点,故在数组开头加入了空字符,这样从索引值1开始遍历数组:左子节点是父节点索引的2倍、右子节点是父节点索引的2倍加1;②通过postOrder()、inOrder()、preOrder()三个函数来遍历二叉运算树;③通过GetResult()、condition(),两个函数来完成算术表达式的运算;
注意:这种写法,必须将二叉运算树变成满二叉树,缺省值用0代替;
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
struct Node // 二叉树节点的声明
{
int data; // 节点数据
Node *left; // 指向左子树的指针
Node *right; // 指向右子树的指针
};
// create将二叉树的数组表示法(中序表达式)转换成 链表表示法
Node* create(char sequence[100], int index, int ArraySize)
{
if (sequence[index] == 0 || index >= ArraySize) { return NULL; } // 作为出口条件
else
{
Node* tempNode = new Node;
tempNode->data = (int)sequence[index];
tempNode->left = NULL;
tempNode->right = NULL;
// 建立左子树
tempNode->left = create(sequence, 2 * index, ArraySize);
// 建立右子树
tempNode->right = create(sequence, 2 * index + 1, ArraySize);
return tempNode;
}
}
// 前序遍历
void preOrder(Node* node)
{
if (node != NULL)
{
cout << setw(1) << (char)node->data;
preOrder(node->left);
preOrder(node->right);
}
}
// 中序遍历
void inOrder(Node* node)
{
if (node != NULL)
{
inOrder(node->left);
cout << setw(1) << (char)node->data;
inOrder(node->right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
void postOrder(Node* node)
{
if (node != NULL)
{
postOrder(node->left);
postOrder(node->right);
cout << setw(1) << (char)node->data;
}
}
// 判断表达式如何运算的方法
int condition(char operator_char, int num1, int num2)
{
switch (operator_char)
{
case '*': return (num1 * num2); // 乘法请返回num1 * num2
case '/': return (num1 / num2); // 除法请返回num1 / num2
case '+': return (num1 + num2); // 加法请返回num1 + num2
case '-': return (num1 - num2); // 减法请返回num1 - num2
case '%': return (num1 % num2); // 取余数法请返回num1 % num2
}
return -1; // 输入其他操作符表示错误
}
// 传入根节点,用来计算此二叉运算树的值
int GetResult(Node* node)
{
int firstNumber = 0;
int secondNumber = 0;
// 递归调用的出口条件:即node是二叉运算树的叶子节点时
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
{
return node->data - 48; // 将数字字符 转换为 整型数字,并返回给firstNumber
}
else
{
firstNumber = GetResult(node->left); // 计算左子树表达式的值
secondNumber = GetResult(node->right); // 计算右子树表达式的值
return condition((char)node->data, firstNumber, secondNumber);
}
}
int main()
{
// 建立二棵二叉查找树,分别用来表示两个算数表达式
char information1[] = { ' ','+','*','%','6','3','9','5' };
Node* rootNode1 = new Node;
rootNode1 = create(information1, 1, 8);
cout << "中序表达式: "; inOrder(rootNode1); cout << endl;
cout << "前序表达式: "; preOrder(rootNode1); cout << endl;
cout << "后序表达式: "; postOrder(rootNode1); cout << endl;
cout << "此二叉运算树,计算后得到的结果: " << setw(1) << GetResult(rootNode1) << endl;
cout << endl;
char information2[] = { ' ','+','+','+','*','%','/','*','1','2','3','2','6','3','2','2' };
Node* rootNode2 = new Node;
rootNode2 = create(information2, 1, 16);
cout << "中序表达式: "; inOrder(rootNode2); cout << endl;
cout << "前序表达式: "; preOrder(rootNode2); cout << endl;
cout << "后序表达式: "; postOrder(rootNode2); cout << endl;
cout << "此二叉运算树,计算后得到的结果: " << setw(1) << GetResult(rootNode2) << endl;
delete rootNode1; rootNode1 = nullptr;
delete rootNode2; rootNode2 = nullptr;
system("pause");
return 0;
}





















 4178
4178











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










