1. 定义 & 组成
- 一般直接把进程实体称为进程,但是严格来说进程实体强调静态,而进程强调动态。
- PCB(Process Control Block)是进程存在的唯一标志。
- 进程的创建 & 撤销,实质上就是进程实体中 PCB 的创建 & 撤销。
- 进程是OS进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位。

- OS 通过 PCB 管理进程,因此 PCB 中应该包含 OS 对其进行管理所需的各种信息
- PID(Process identifier):不重复,相当于进程的身份证

- 组成:PCB & 程序段 & 数据段

2. 进程的组织
- 前面是说的进程的内部,而这里是说的进程的外部——多个进程之间的问题。
- 链接 & 索引 ==》 队列 & 索引表

- 链接方式:
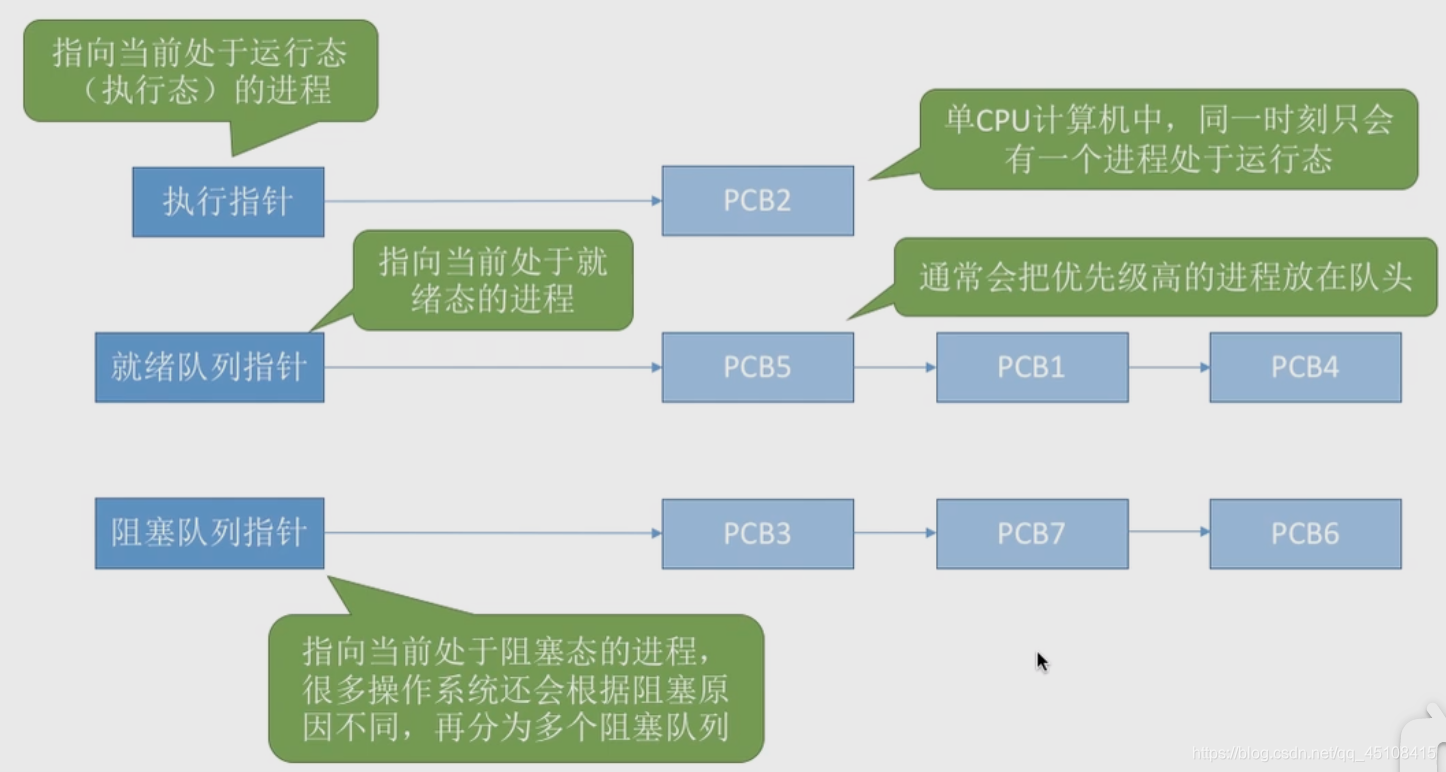
- 索引方式:

3. 特征
- 动态性:最基本特征
- 异步性:由此衍生出了进程同步机制

1、2、3 总结导图

4. 状态
- 五种状态:运行、就绪、阻塞、创建、终止
- 这里看看定义就好,主要还是理解下面的转换部分


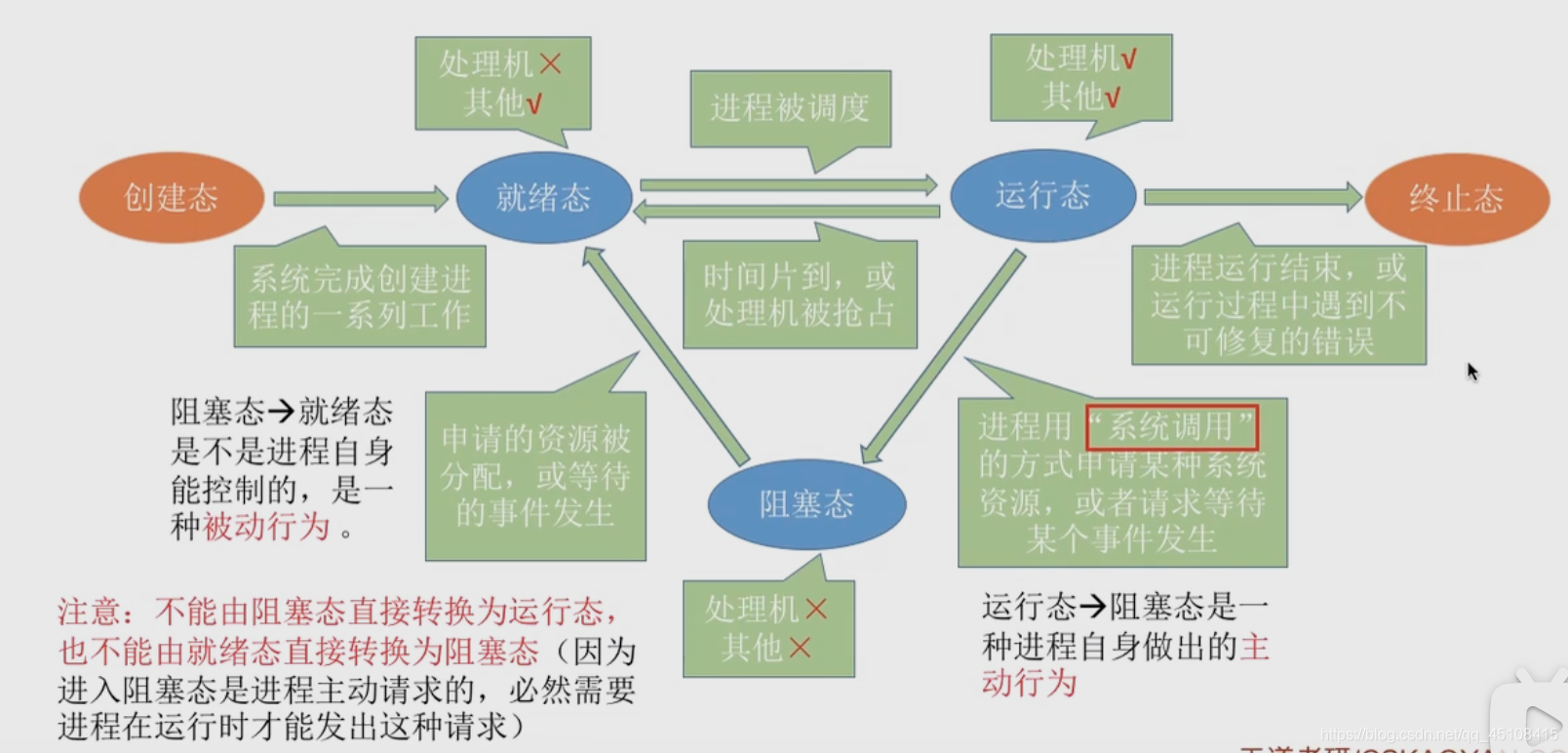
5. 转换
- 很重要的图噢~可以多动手画几遍
- 注意:就绪态不能直接到阻塞态,阻塞态也不能直接返回到运行态
- 运行态到阻塞态是进程主动的,这是为了申请资源导致的
- 阻塞态时拥有的资源最少
4、5 总结导图


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








