实验环境: Ubuntu 20.04 LTS,内核版本 5.4.34。
一、实验准备
编译和调试 ARM64 环境,必须安装交叉编译工具链和跨平台版 gdb
sudo apt-get install gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu
sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev build-essential git bison flex libssl-dev
sudo apt install gdb-multiarch
需要为 ARM64 新建一个内核编译配置文件,对这个新配置文件进行修改
make defconfig ARCH=arm64
make menuconfig ARCH=arm64
选择如下编译配置
Kernel hacking --->
Compile-time checks and compiler options --->
[*] Compile the kernel with debug info
[*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging
[*] Kernel debugging
Kernel Features ---->
[] Randomize the address of the kernel image
在终端提前 export 交叉编译选项再 make(否则编译的还是 x86 的内核)
export ARCH=arm64
export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
make Image -j$(nproc) # 这里指定target为Image,只编译kernel不会编译modules,加快编译速度
编译 busybox 之前也要 export 交叉编译选项
export ARCH=arm64
export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
make Image -j$(nproc) # 这里指定target为Image,只编译kernel不会编译modules,加快编译速度
制作内存根系统
wget https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.36.0.tar.bz2
tar -jxvf busybox-1.36.0.tar.bz2
cd busybox-1.36.0
设置编译选项
export ARCH=arm64
export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
make menuconfig
Settings --->
[*] Build static binary (no shared libs)
make -j$(nproc) && make install
二、使用内嵌汇编触发 time/gettimeofday 系统调用
使用内嵌汇编触发 gettimeofday 的用户态 C 语言示例代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
int main()
{
time_t tt;
struct timeval tv;
struct tm *t;
#if 0
gettimeofday(&tv,NULL); // 使用库函数的方式触发系统调用
#else
asm volatile( // 使用内嵌汇编的方式触发系统调用
"add x0, x29, 16\n\t" //X0寄存器用于传递参数&tv
"mov x1, #0x0\n\t" //X1寄存器用于传递参数NULL
"mov x8, #0xa9\n\t" //使用X8传递系统调用号169
"svc #0x0\n\t" //触发系统调用
);
#endif
tt = tv.tv_sec; //tv是保存获取时间结果的结构体
t = localtime(&tt); //将世纪秒转换成对应的年月日时分秒
printf("time: %d/%d/%d %d:%d:%d\n",
t->tm_year + 1900,
t->tm_mon,
t->tm_mday,
t->tm_hour,
t->tm_min,
t->tm_sec);
return 0;
}
将上述代码保存为 test.c,运行以下命令将其编译为 ARM64 下的可执行文件。
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o test test.c -static
在 VSCode 中启动调试,首先在窗口左下角的断点设置处新增断点 __arm64_sys_gettimeofday(32 位 ARM 下是 sys_gettimeofday,注意不要搞错了),再在终端中执行 test
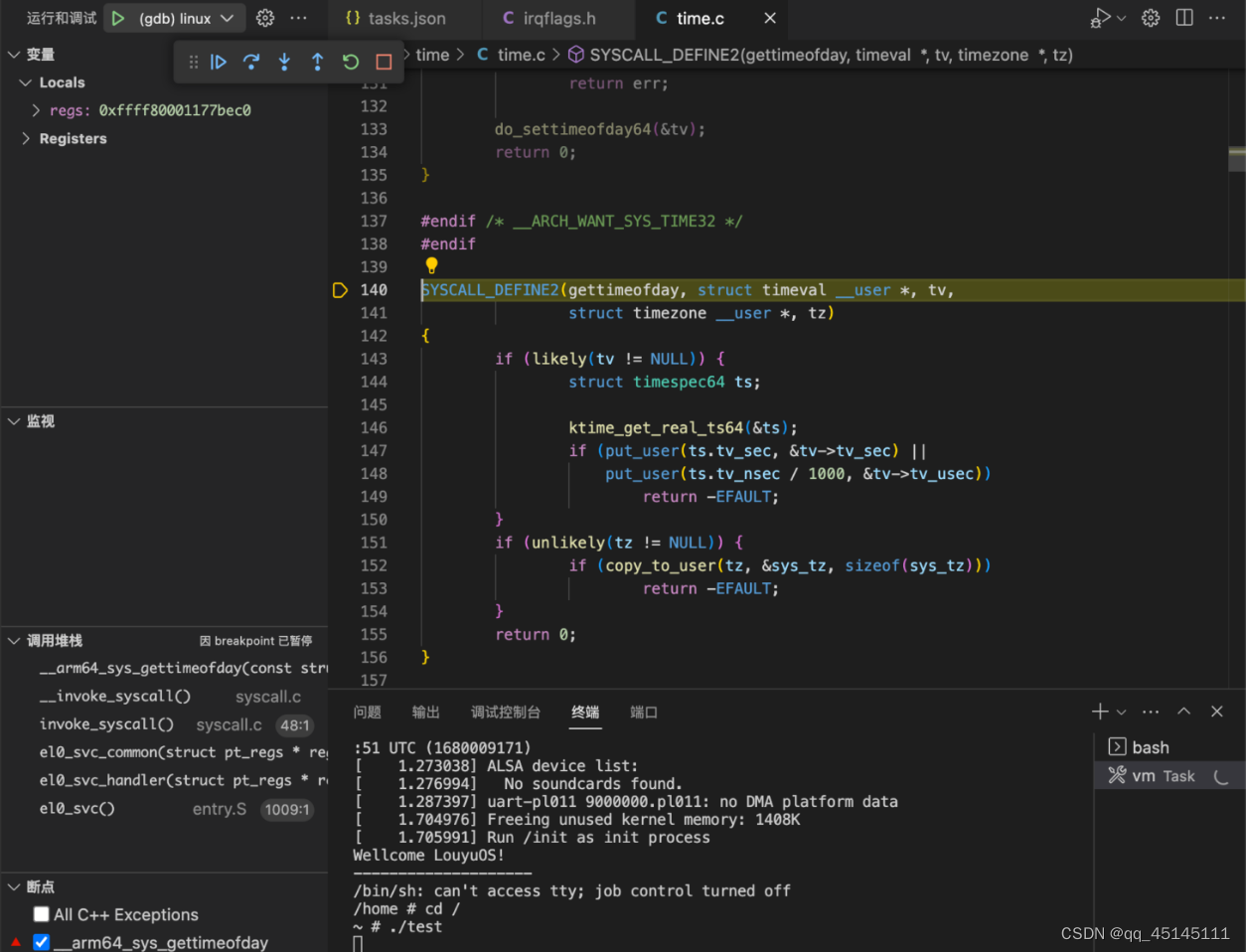
三、分析 time/gettimeofday 系统调用的执行过程
ARM64 架构下 Linux 系统调用由同步异常 svc 指令触发,当用户态(EL0 级)程序调用库函数 gettimeofday() 从而触发系统调用的时候,先把系统调用的参数依次放入 X0-X5 这 6 个寄存器(Linux 系统调用最多有 6 个参数,ARM64 函数调用参数可以使用 X0-X7 这 8 个寄存器),然后把系统调用号放在 X8 寄存器里,最后执行 svc 指令,CPU 即进入内核态(EL1 级)。
以 svc 指令对应的 el0_sync 为例,el0_sync 处的内核汇编代码首先做的就是保存异常发生时程序的执行现场(保存现场,即栈、通用寄存器等),然后根据异常发生的原因(ESR_EL1 寄存器中的内容)跳转到 el0_svc,el0_svc 会调用 el0_svc_handler、el0_svc_common 函数,将 X8 寄存器(regs->regs[8])中存放的系统调用号传递给 invoke_syscall 函数。
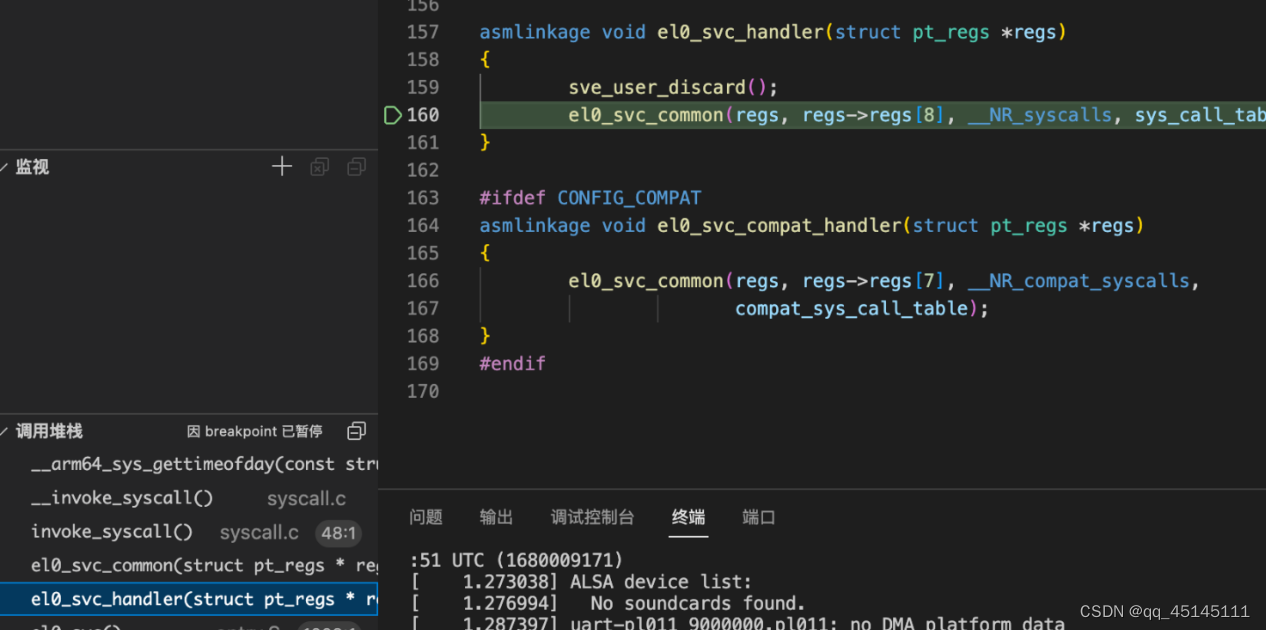
接着执行 invoke_syscall 函数,将通用寄存器中的内容传入 syscall_fn()

系统调用内核处理函数执行完成后,会将系统调用的返回值存放在 X0 寄存器中。
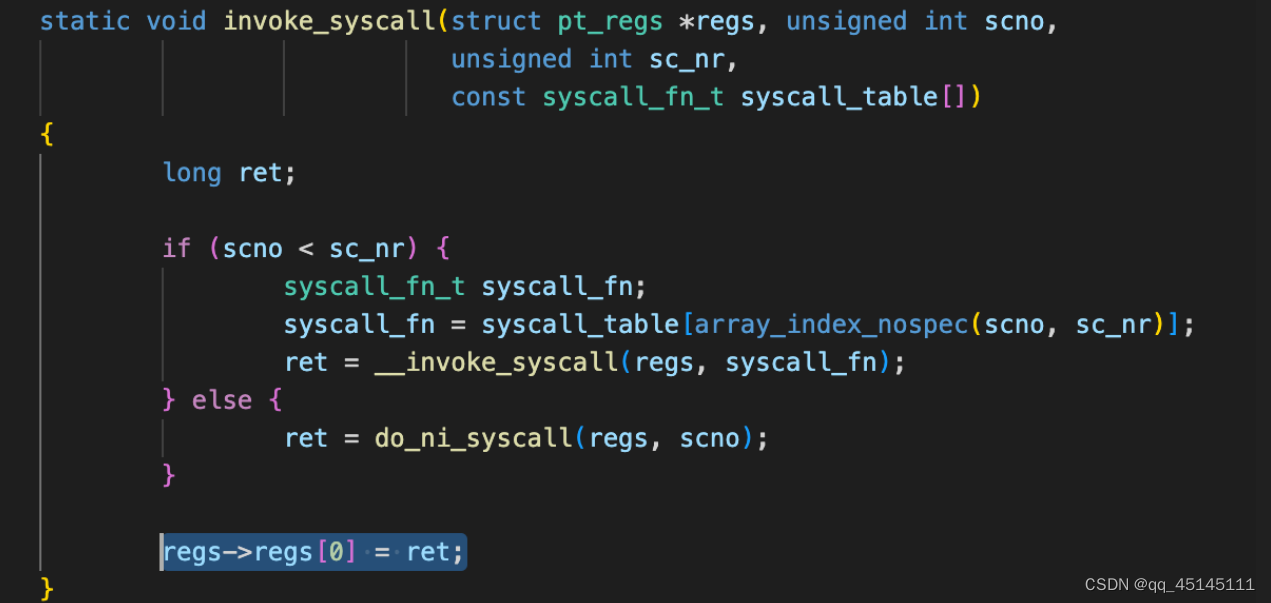
系统调用返回前,需要恢复异常发生时程序的执行现场(恢复现场),其中就包括恢复 ELR_EL1 和 SPSR_EL1 的值。最后内核调用异常返回指令 eret,CPU 把 ELR_EL1 写回 PC,把 SPSR_EL1 写回 PSTATE,返回用户态继续执行用户态程序。





















 225
225











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








