CS144实验记录(二)lab1
实验编译说明
- 在sponge目录下有CMakeLists.txt文件,用来生成编译所需的Makefile文件。
- cmake后会生成很多编译的中间文件以及makefile文件,所以一般不会在CMakeLists.txt所在的目录中使用cmake,而是使用
mkdir build新建一个新的目录build,专门用来编译。 - 使用
cd build进入build目录,在build目录下使用cmake ..命令,..表明CMakeList.txt在build的上一层目录,将CMakeLists.txt文件转化为编译所需要的makefile文件。 - 生成了Makefile文件后,就可以使用
make命令编译代码(可以使用make -jn来指定使用n个核来并行编译,提高编译的速度)。编译成功后,在build目录下使用make check_lab1来测试我们lab1的代码。
一共有如下几种编译选项可供选择:
Release- optimizationsDebug- debug symbols and-OgRelASan- release build with ASan and UBSanRelTSan- release build with ThreadSanDebugASan- debug build with ASan and UBSanDebugTSan- debug build with ThreadSan
当编译时出现 segmentation fault,可以在build目录下使用cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelASan开启编译器的“sanitizers”,在编译时可以检测到内存错误和未定义的行为。如果需要调试,也可以使用cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug开启调试模式,在gdb中有更好的调试信息。
cmake切换模式时必须将之前的编译文件删除,使用make clean将之前make命令生成的.o文件或可执行文件删除。再使用make命令重新编译,使用make check_lab1测试。(不知道cmake是否会将之前的Makefile覆盖,最好使用rm -rf build命令删除build目录,也就是之前的Makefile文件,再使用cmake切换模式,重新生成Makefile文件,再使用make命令重新编译)
在本实验中,为避免每次切换编译模式时都需要make clean或rm -rf build,我选择将不同的模式在不同的目录下编译。不再是一个build目录,而是一个Debug目录和一个Release目录还有一个RelASan目录。
Overview
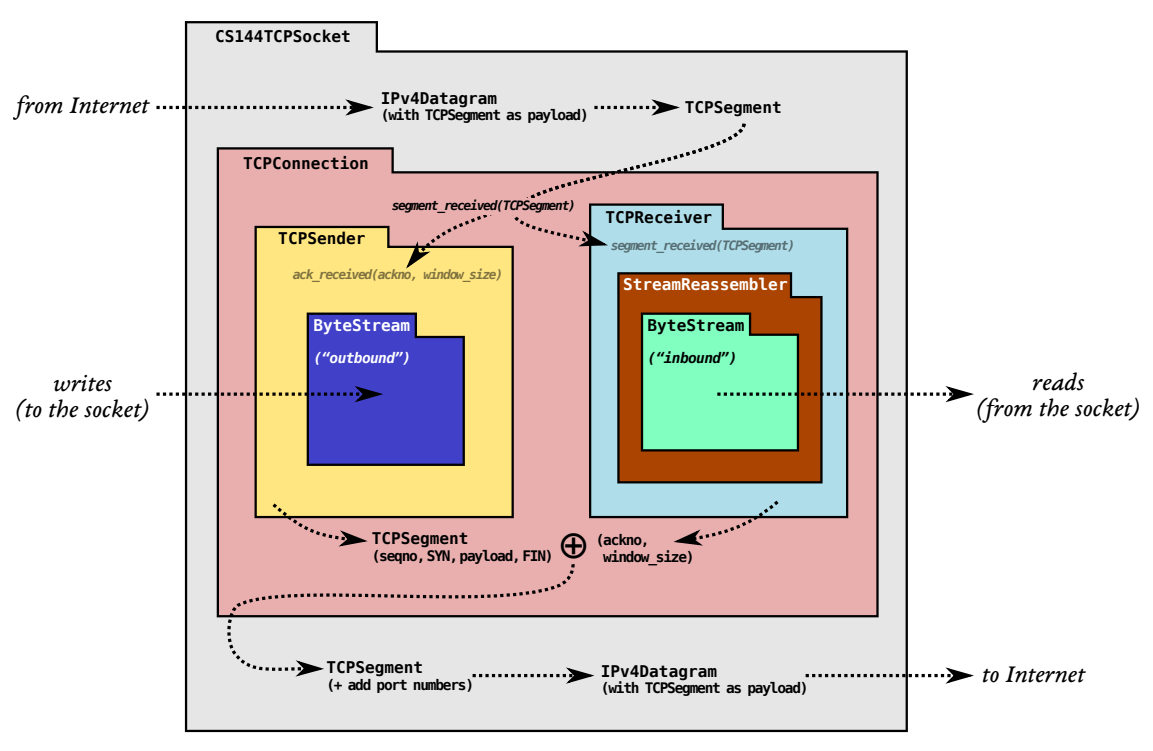
IPv4的数据报通过IP层后,提取出TCP报文段,交付给TCP层,每个TCP连接在双方主机的本地都有一对TCPreceiver和TCPsender:
- TCPreceiver负责接收对方发送的TCPpacket中的segment部分(包括序列号,载荷等)。由收到的上一个packet的序列号和载荷才能确定发送给对方的ack号和接收窗口的大小,所以TCPreceiver还负责发送ackno和window_size。
- TCPsender负责接收对方发送的TCPpacket中的ack号和接收窗口大小(即接收缓冲区的空余部分)。由收到的上一个packet的ack号和接收窗口的大小才能确定发送给对方的packet的序列号以及大小,所以TCPsender还负责发送segment(包括序列号和载荷)。
由TCPreceiver发送的接收窗口大小以及ack号和TCPsender发送的segment组成TCPpacket,交付给网络层形成IPv4数据报,发送出去。(接收窗口即接收缓冲区的空闲空间的大小)
TCPReceiver接收端收到的是一个个的TCP数据段(segment),它们有可能并不按照发送端发出的顺序排列,还有可能发生丢失、重叠或者重复。而ByteStream在输入端写入的字节会以相同的顺序从输出端读出来,所以我们需要确保最终存入ByteStream的是正确的字节流。即我们此次lab要实现的StreamReassembler一个流重组器(stream reassembler),可以将带索引的字节流碎片重组成有序的字节流,将收到的报文段按情况送入 ByteStream ,或丢弃,或暂存(在合适的时候重组送入 ByteStream)。
- 对方发送的segment由receiver接收,通过
StreamReassembler重组成有序的字节流,再写入ByteStream,然后应用层通过运输层提供的层间接口socket从receiver的ByteStream中读取。 - 应用层通过socket将字节流写入sender中的ByteStream,再由TCPsender从ByteStream中读取出来,发送给对方。
也就是说ByteStream不只是接收缓冲区,还是发送缓冲区。
Putting substrings in sequence
StreamReassembler将接收子字符串,由一串字节组成,以及该字符串在字节流中的第一个字节的索引。StreamReassembler最多可以存储capacity个字节,capacity包括已重组的字节(即在ByteStream中的字节)和已接收但是未重组的字节。

每个字节流碎片都通过索引、长度、内容三要素进行描述。接收到并且重组完的字节流应当被送入指定的字节流(byte stream)对象_output中,还有部分容量用于存储不与_output连续的子串,一旦连续自然也需要写入_output。**以上的两部分容量合起来就是capacity。**也就是说,这两部分中任意一部分最大容量不超过capacity。
提供的接口:
// A class that assembles a series of excerpts from a byte stream (possibly out of order,possibly overlapping) into an in-order byte stream.
class StreamReassembler {
private:
ByteStream _output; //ByteStream对象,存放重组完有序的字节流,等待应用层的读取
size_t _capacity; //StreamReassembler的容量
public:
//构造一个StreamReassembler对象,容量为capacity,capacity包括已重组的字节(即在ByteStream中的字节)和已接收但是未重组的字节。
StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity);
//! 接收一个子字符串并将任何新的连续字节写入流中,同时保持在“capacity”的内存限制内。超过capacity的字节会被直接丢弃
//data:接收的子串
//index:表示 `data` 中第一个字节在字节流中的索引
//eof:`data` 的最后一个字节是否是整个流中的最后一个字节
void push_substring(const std::string &data, const uint64_t index, const bool eof);
//访问重组的字节流ByteStream
const ByteStream &stream_out() const { return _output; }
ByteStream &stream_out() { return _output; }
//已接收但尚未重组的子串中的字节数
//如果某个索引处的字节已被push了多次,它应该只计数一次。
size_t unassembled_bytes() const;
//内部状态是否为空(BYteStream除外)?
//如果没有子字符串等待重组,则返回 `true`
bool empty() const;
};
**当receiver收到子串时,调用push_substring方法,该方法或将收到的子串送入StreamReassembler的缓冲区中,或送入ByteStream缓冲区中,或丢弃。**它将忽略会导致 StreamReassembler 超出其“容量”的字符串的部分(在实际操作中,不是按照容量来判断,而是按照收到子串的index与first unacceptable的大小来判断)。StreamReassembler接收到的字节应该尽快送入ByteStream中,一个字节没有被送入ByteStream的唯一情况就是在它之前有一个字节还没有被送入。提供给push_substring()方法的子串可能会有重叠。注意!StreamReassembler的缓冲区中也不允许有重叠的字符串!只允许存在不连续的字符串(如果对方不停发送相同的字符串,很快就会超过容量)
StreamReassembler收到的子串可能出现的情况:
- 重复, 比如你发了一个包 “ab” index = 0 然后又发了一个包 “ab” index = 0, 这就是重复
- 重叠, 比如你发了一个包 “abcd” index = 1, 然后又发了一个 “bcdef”, index = 2, 这就是重叠
- 乱序, 比如你下一个期待收到的index 为2, 但是收到一个包 “def” index = 4, 这就是乱序
- 丢包, 就是包丢了没收到,需要重发, 这个不是这个实验需要考虑的问题,我们只负责处理收到的包
StreamReassembler中需要_next_index字段,记录此时与ByteStream连续的子串的索引是多少, _next_index的初始值为0 ,还需要 _eof字段来记录是否已经收到过有 EOF 标识的段。当receiver收到子串时,调用push_substring方法,该方法需要做的是:
-
对收到的不为空的子串进行剪切:
- 如果该子串索引大于等于first unacceptable(
_next_index+remaining_capacity()),则直接丢弃。直接结束函数。 - 如果该子串最后字符的索引(
index + length - 1)小于_next_index,则直接丢弃。直接结束函数。 - 如果该子串的索引小于
_next_index,最后字符的索引大于等于first unacceptable,则切除两边的部分,保留子串中间的部分,改变子串的索引为_next_index。 - 如果该子串的索引小于first unacceptable,最后字符的索引大于等于first unacceptable,则切除大于等于first unacceptable的子串部分。
- 如果该子串的索引小于
_next_index,最后字符的索引大于等于_next_index,则切除小于_next_index的子串部分,改变该子串的索引为_next_index。还需要接收该子串的eof信号。 - 如果该子串的索引大于等于
_next_index,最后字符的索引小于first unacceptable,则不需要切除。只需要接收该子串的eof信号。
- 如果该子串索引大于等于first unacceptable(
-
将第一步切除剩下的子串(称为S)再去重后加入StreamReassembler的缓冲区:
-
遍历StreamReassembler的缓冲区中的每一个子串,如果有重叠,就将缓冲区中的该子串(称为other)与子串S合并,将缓冲区中的子串移除出去。这一步的重叠与第一步类似,有四种情况:
- S是other的一部分,完全重叠。将other的中间切除,前后与S拼接
- 重叠的部分在other的后半部分,S的前半部分
- 重叠的部分在other的前半部分,S的后半部分
- other是S的一部分,完全重叠,那么S不需要改变,other直接从缓冲区中移除
合并的新的子串S继续与剩下的子串对比是否有重叠,如此往复直到出现一个子串没有重叠,结束循环。将S加入缓冲区。
-
-
如果StreamReassembler的缓冲区为空且
_eof为真时,调用ByteStream的end_input,结束函数。否则从StreamReassembler的缓冲区中取出最小索引的子串:- 如果该子串的索引大于
_next_index,那么直接结束函数,等待下一个接收的子串 - 如果该子串的索引等于
_next_index,那么调用ByteStream中的write函数,将子串写入ByteStream中。更改_next_index(_next_index+=子串长度),同时将它从StreamReassembler中的缓冲区中移除。再重复第三步。
- 如果该子串的索引大于
因此选择set作为StreamReassembler缓冲区的数据结构,将处理的segment封装成一个类,包含data、index、eof三个字段,按照报文段的 index 大小对比重载 < 运算符。
初步实现:
stream_reassembler.hh文件:
#include "byte_stream.hh"
#include <cstdint>
#include <string>
#include <set>
class StreamReassembler {
private:
//ByteStream的缓冲区,已经重组的连续segment,等待应用层读取
ByteStream _output; //!< The reassembled in-order byte stream
//StreamReassembler的缓冲区,等待重组的segment,初始化为空
std::set<segment>_segs_to_be_reassembled = {};
size_t _capacity; //!< The maximum number of bytes
//此时ByteStream需要的子串索引,即与ByteStream连续的子串的索引,初始化为0
size_t _next_index=0;
bool _eof=false;
class segment{
public:
size_t index;
std::string data;
bool eof;
bool operator<(const segment s)const {return index < s.index; }
};
bool _cut(segment &s);
//处理重叠的子串
void _handle_overlap(segment s);
//合并重叠的子串,返回被合并后新的segment
segment _merge_seg(segment s,segment other);
void _push_into_bytestream();
public:
StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity);
void push_substring(const std::string &data, const uint64_t index, const bool eof);
const ByteStream &stream_out() const { return _output; }
ByteStream &stream_out() { return _output; }
size_t unassembled_bytes() const;
bool empty() const;
};
stream_reassembler.cc文件:
#include "stream_reassembler.hh"
using namespace std;
StreamReassembler::StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity) : _output(capacity), _capacity(capacity) {}
//或将收到的子串送入StreamReassembler的缓冲区中,或送入ByteStream缓冲区中,或丢弃
void StreamReassembler::push_substring(const string &data, const size_t index, const bool eof) {
segment seg={index,data,eof};
//如果收到的字符串为空,不需要对它进行任何处理,只需要接收它的eof信息即可
if(data.length()==0){
if(eof==true)_eof=eof;
}else{
//对收到的segment进行剪切,符合可接受的范围
if(_cut(seg)==false) return;
//将剪切剩下的segment去重后再加入StreamReassembler的缓冲区
_handle_overlap(seg);
//将StreamReassembler中与ByteStream中的子串连续的segment写入ByteStream中
_push_into_bytestream();
}
if(_segs_to_be_reassembled.empty() == true && _eof == true)
_output.end_input();
}
//传入segment,进行剪切,当segment的索引超出了范围,直接结束,返回false,剪切失败。
bool
StreamReassembler::_cut(segment &s){
size_t index=s.index;
size_t first_unacceptable=_next_index+_output.remaining_capacity();
size_t length=s.data.length();
//最后一个字符的索引位置
size_t last_index = index + length - 1;
//接收的字符串不在可接受范围之内,直接结束函数
if(index>=first_unacceptable) return false;
else if(last_index <_next_index) return false;
else if(index < _next_index && last_index >= first_unacceptable){
s.data = s.data.substr(_next_index - index,first_unacceptable - _next_index);
s.index = _next_index;
}
else if(index<first_unacceptable && last_index >= first_unacceptable){
s.data=s.data.substr(0,first_unacceptable - index);
}
else if(index<_next_index && last_index >=_next_index){
s.data = s.data.substr(_next_index - index,last_index - _next_index + 1);
s.index = _next_index;
if(s.eof==true)_eof=true;
}
else if(index >= _next_index && last_index < first_unacceptable)
if(s.eof == true) _eof = true;
return true;
}
//将剪切剩下的segment去重后再加入StreamReassembler的缓冲区
void StreamReassembler::_handle_overlap(segment s){
if(_segs_to_be_reassembled.empty() == true){
_segs_to_be_reassembled.insert(s);
return;
}
for(auto it=_segs_to_be_reassembled.begin();it != _segs_to_be_reassembled.end();){
//S与缓冲区中的子串重叠的情况,合并S与子串,将该子串从缓冲区中移除
if(( s.index >= it->index && s.index <= it->index + it->data.length() - 1) ||
(it->index >= s.index && it->index <= s.index +s.data.length() - 1)){
s = _merge_seg(s,*it);
//在修改了容器容量后更新迭代器!
it = _segs_to_be_reassembled.erase(it);
}else it++;
}
_segs_to_be_reassembled.insert(s);
}
void StreamReassembler::_push_into_bytestream(){
if(_segs_to_be_reassembled.empty() == true)return;
auto smallest_seg= _segs_to_be_reassembled.begin();
if(smallest_seg->index > _next_index)return;
if(smallest_seg->index == _next_index){
_output.write(smallest_seg->data);
_next_index += smallest_seg->data.length();
_segs_to_be_reassembled.erase(smallest_seg);
}
_push_into_bytestream();
}
//合并重叠的子串
StreamReassembler::segment
StreamReassembler::_merge_seg(segment s,segment other){
size_t s_left = s.index;
size_t s_right = s_left + s.data.length() -1;
size_t other_left = other.index;
size_t other_right = other_left +other.data.length() -1;
size_t overlap_left_index= s_left >other_left ?s_left :other_left;
size_t overlap_right_index= s_right < other_right ? s_right :other_right;
//S是other的一部分,完全重叠
if(s_left >= other_left && s_right <= other_right){
string other_front = other.data.substr(0,overlap_left_index - other_left);
string other_back = other.data.substr(overlap_right_index - other_left + 1,other_right - overlap_right_index);
s.data = other_front + s.data + other_back;
s.index = other.index;
}
//重叠的部分在other的后半部分,S的前半部分
else if(s_left >= other_left && s_left <= other_right ){
//切割other
other.data = other.data.substr(0,overlap_left_index -other_left );
s.data = other.data + s.data;
s.index = other.index;
}
//重叠的部分在other的前半部分,S的后半部分
else if(s_right >= other_left && s_right <= other_right){
//切割other
other.data = other.data.substr(overlap_right_index - other_left + 1,other_right - overlap_right_index);
s.data = s.data + other.data;
}
//如果other是S的一部分,完全重叠,那么S不需要改变,other直接从缓冲区中移除
return s;
}
size_t StreamReassembler::unassembled_bytes() const {
size_t unassembled_bytes = 0;
for(auto it = _segs_to_be_reassembled.begin();it != _segs_to_be_reassembled.end();it++){
unassembled_bytes += it->data.length();
}
return unassembled_bytes;
}
bool StreamReassembler::empty() const {
return unassembled_bytes() == 0;
}
调试方法:
在Debug模式下对出错的测试文件使用gdb,找到出错位置
fsm_stream_reassembler_single中:
在gdb调试过程中出现<value optimized out>,表明gcc编译器认为这个变量是多余的,在编译中将这个变量优化掉了。如果想要去掉优化,在编译时使用-g参数。
gdb调试非常难用,经常到处乱跳,经过胡神的推荐,我改用了lldb。
经过调试,首先发现的问题是:没有考虑接收的字符串为空的情况。如果收到的字符串为空,不需要对它进行任何处理,只需要接收它的eof信息即可。
问题二:非常智障,C++的substr和java的substring是不一样的!C++的substr是从指定位置开始,截取n个字符,而java的substring是一个前闭后开区间。全部都要重新修改!
问题三:在改变容器的循环程序内没有更新迭代器:我们在调用insert 和erase后都必须更新迭代器,因为两者都会使迭代器失效!
说出来也不怕丢人,做这个lab又是复习C++、又是复习计网、又是调试,居然花了我一个星期的时间,特别是调试程序,这么几个智障的bug,找了几天。唉,只能说是太失败了。。。。。。






















 510
510











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








