1.集合体系图
我们常用的集合主要有List,Map,set,以及ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector,HashSet,TreeSet,HashMap等,其体系结构图如下:
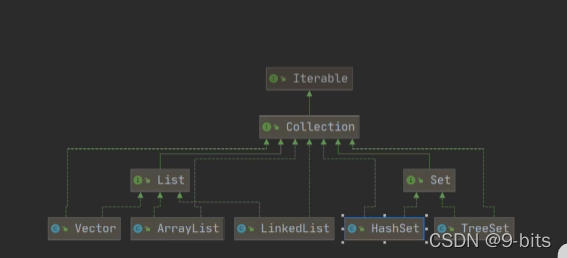
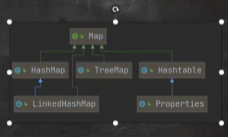
事实上,实现了List,Set,Map的集合远不止这些,更多的可以去看相关API.
2.Collections接口中的方法
相关方法的参数和返回值如下图:
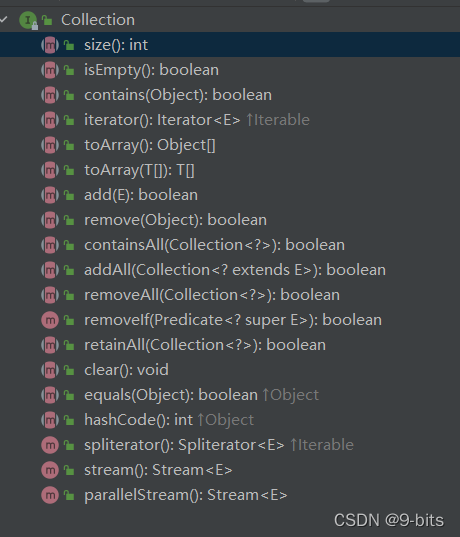
我们经常用到的是add,remove,addAll,contains,Iterator等方法。
3.Iterator接口
Iterator是一个迭代器类型,主要用于遍历集合。其中最重要的是两个方法,hasNext()和next()。这两个方法在不同类型的集合中有不同的实现方式,但目的都是相同的,hasNext主要用于判断迭代器指向的内容的下一个是否为空,next()主要获取迭代器指向的内容,下面展示ArrarList中实现的Iterator:
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
可以看到相关方法均已被重写。
4.遍历集合
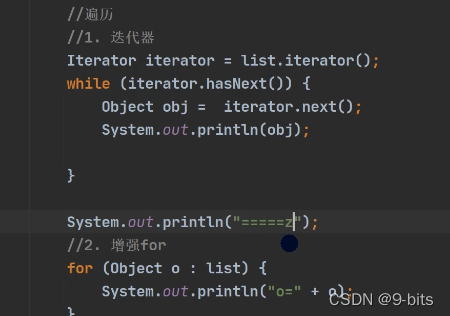
有三种方式遍历集合:
1.迭代器遍历
2.增强for循环
3.普通for循环
欢迎关注,后期有更精彩的内容呦。





















 246
246











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








