一、程序及函数
1.引导脚本ex1.m
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 1: Linear Regression
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% linear exercise. You will need to complete the following functions
% in this exericse:
%
% warmUpExercise.m
% plotData.m
% gradientDescent.m
% computeCost.m
% gradientDescentMulti.m
% computeCostMulti.m
% featureNormalize.m
% normalEqn.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
% x refers to the population size in 10,000s
% y refers to the profit in $10,000s
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% ==================== Part 1: Basic Function ====================
% Complete warmUpExercise.m
fprintf('Running warmUpExercise ... \n');
fprintf('5x5 Identity Matrix: \n');
warmUpExercise()
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ======================= Part 2: Plotting =======================
fprintf('Plotting Data ...\n')
data = load('ex1data1.txt');
X = data(:, 1);
y = data(:, 2);
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% Plot Data
% Note: You have to complete the code in plotData.m
plotData(X, y);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% =================== Part 3: Cost and Gradient descent ===================
X = [ones(m, 1), data(:,1)]; % Add a column of ones to x
theta = zeros(2, 1); % initialize fitting parameters
% Some gradient descent settings
iterations = 3000;
alpha = 0.01;
fprintf('\nTesting the cost function ...\n')
% compute and display initial cost
J = computeCost(X, y, theta);
fprintf('With theta = [0 ; 0]\nCost computed = %f\n', J);
fprintf('Expected cost value (approx) 32.07\n');
% further testing of the cost function
J = computeCost(X, y, [-1 ; 2]);
fprintf('\nWith theta = [-1 ; 2]\nCost computed = %f\n', J);
fprintf('Expected cost value (approx) 54.24\n');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
fprintf('\nRunning Gradient Descent ...\n')
% run gradient descent
[theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, iterations);
iteration = zeros(1,iterations);
for i = 1 : iterations
iteration(i) = i;
end
% print theta to screen
fprintf('Theta found by gradient descent:\n');
fprintf('%f\n', theta);
fprintf('Expected theta values (approx)\n');
fprintf(' -3.6303\n 1.1664\n\n');
% Plot the linear fit
hold on; % keep previous plot visible
plot(X(:,2), X*theta, '-')
legend('Training data', 'Linear regression')
hold off % don't overlay any more plots on this figure
% Predict values for population sizes of 35,000 and 70,000
predict1 = [1, 3.5] *theta;
fprintf('For population = 35,000, we predict a profit of %f\n',...
predict1*10000);
predict2 = [1, 7] * theta;
fprintf('For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of %f\n',...
predict2*10000);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============= Part 4: Visualizing J(theta_0, theta_1) =============
fprintf('Visualizing J(theta_0, theta_1) ...\n')
% Grid over which we will calculate J
theta0_vals = linspace(-10, 10, 100);
theta1_vals = linspace(-1, 4, 100);
% initialize J_vals to a matrix of 0's
J_vals = zeros(length(theta0_vals), length(theta1_vals));
% Fill out J_vals
for i = 1:length(theta0_vals)
for j = 1:length(theta1_vals)
t = [theta0_vals(i); theta1_vals(j)];
J_vals(i,j) = computeCost(X, y, t);
end
end
% Because of the way meshgrids work in the surf command, we need to
% transpose J_vals before calling surf, or else the axes will be flipped
J_vals = J_vals';
% Surface plot
figure;
surf(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals)
xlabel('\theta_0'); ylabel('\theta_1');
% Contour plot
figure;
% Plot J_vals as 15 contours spaced logarithmically between 0.01 and 100
contour(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals, logspace(-2, 3, 20))
xlabel('\theta_0'); ylabel('\theta_1');
hold on;
plot(theta(1), theta(2), 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 2);
% 绘制损失随迭代次数变化的折线图
figure;
plot(iteration,J_history,'-b','linewidth',2);
set(gca,'YLim',[4,7]);%X轴的数据显示范围
xlabel('迭代次数'); ylabel('Cost');
2.warmUpExercise.m
function A = warmUpExercise()
%WARMUPEXERCISE Example function in octave
% A = WARMUPEXERCISE() is an example function that returns the 5x5 identity matrix
A = [];
% ============= YOUR CODE HERE ==============
% Instructions: Return the 5x5 identity matrix
% In octave, we return values by defining which variables
% represent the return values (at the top of the file)
% and then set them accordingly.
A = eye(5);
% ===========================================
end
3.plotData.m
function plotData(x, y)
%PLOTDATA Plots the data points x and y into a new figure
% PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points and gives the figure axes labels of
% population and profit.
figure; % open a new figure window
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Plot the training data into a figure using the
% "figure" and "plot" commands. Set the axes labels using
% the "xlabel" and "ylabel" commands. Assume the
% population and revenue data have been passed in
% as the x and y arguments of this function.
%
% Hint: You can use the 'rx' option with plot to have the markers
% appear as red crosses. Furthermore, you can make the
% markers larger by using plot(..., 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10);
plot(x, y, 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10); % Plot the data
ylabel('Profit in $10,000s'); % Set the y?axis label
xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s'); % Set the x?axis label
% ============================================================
end
4.computeCost.m
function J = computeCost(X, y, theta)
%COMPUTECOST Compute cost for linear regression
% J = COMPUTECOST(X, y, theta) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for linear regression to fit the data points in X and y
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta
% You should set J to the cost.
% 初始化累加和
sum = 0;
for i = 1 : m
sum = sum + (dot(theta,X(i,:)) - y(i)).^2;
end
J = 1/(2*m) * sum;
% ========================================================================
end
5.gradientDescent.m
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters)
%GRADIENTDESCENT Performs gradient descent to learn theta
% theta = GRADIENTDESCENT(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) updates theta by
% taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1);
for iter = 1:num_iters
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Perform a single gradient step on the parameter vector
% theta.
%
% Hint: While debugging, it can be useful to print out the values
% of the cost function (computeCost) and gradient here.
% 初始化当前的累加和
sum0 = 0;
sum1 = 0;
for j = 1 : m
sum0 = sum0 + (dot(theta,X(j,:)') - y(j)) * X(j,1);
sum1 = sum1 + (dot(theta,X(j,:)') - y(j)) * X(j,2);
end
% 同时更新theta0和theta1
theta(1,1) = theta(1,1) - alpha * 1/m * sum0;
theta(2,1) = theta(2,1) - alpha * 1/m * sum1;
% ============================================================
% Save the cost J in every iteration
% 调用函数计算更新完theta后的损失
J_history(iter) = computeCost(X, y, theta);
end
end
二、运行结果



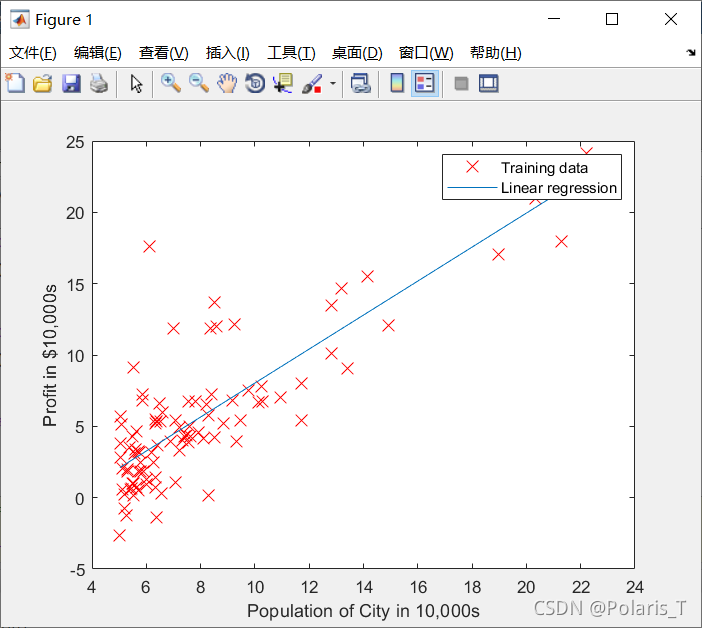











 这篇博客介绍了线性回归的实现过程,包括数据预处理、梯度下降算法的运用以及成本函数的计算。作者通过编程练习,展示了如何在MATLAB中完成这些任务,如初始化参数、绘制数据点、计算成本以及进行梯度下降优化。此外,还展示了成本函数随着参数变化的可视化结果。
这篇博客介绍了线性回归的实现过程,包括数据预处理、梯度下降算法的运用以及成本函数的计算。作者通过编程练习,展示了如何在MATLAB中完成这些任务,如初始化参数、绘制数据点、计算成本以及进行梯度下降优化。此外,还展示了成本函数随着参数变化的可视化结果。

















 720
720

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










