二叉树专题
- 二叉树
- 二叉树的理论基础
- 4.二叉树的递归遍历
- 5.二叉树的迭代遍历(基础必须掌握)
- 二叉树的统一迭代法
- 6.二叉数的层序遍历
- 7.反转二叉树
- N叉树的前后序遍历(n叉树没有中序遍历)
- 8.对称二叉树
- 9.二叉树的最大深度
- 10.完全二叉树的节点个数
- 11.平衡二叉树
- 13.二叉树的所有路径
- 14.左叶子之和
- 15.找树左下角的指
- 17.路径总和
- 18.由俩个遍历序列构建二叉树
- 19.最大的二叉树
- 20.合并二叉树
- 21. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 22.验证二叉搜索树
- 23.中序遍历团灭系列二叉搜索树问题
- 24.二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 25.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 26.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 27.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 28.修剪二叉搜素树
- 29.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
- 30.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
今天刷完了二叉树专题,
二叉树
二叉树的理论基础

1.满二叉树
满二叉树:如果一棵二叉树只有度为0的结点和度为2的结点,并且度为0的结点在同一层上,则这棵二叉树为满二叉树。
2.完全二叉树
完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2^(h-1) 个节点。

3.二叉搜索树
前面介绍的树,都没有数值的,而二叉搜索树是有数值的了,二叉搜索树是一个有序树。
若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
4.二叉树的递归遍历
//前序遍历:根左右
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode *cur,vector<int>&res){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
res.push_back(cur->val);
traversal(cur->left,res);
traversal(cur->right,res);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>result;
traversal(root,result);
return result;
}
};
//中序遍历:左右根
class Solution {
public:
void Inorder(TreeNode *cur,vector<int>&res){
if(cur==nullptr) return ;
Inorder(cur->left,res);
res.push_back(cur->val);
Inorder(cur->right,res);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>ans;
Inorder(root,ans);
return ans;
}
};
//后序遍历:左右根
class Solution {
public :
void Order(TreeNode *cur,vector<int>&res){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
Order(cur->left,res);
Order(cur->right,res);
res.push_back(cur->val);
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>ans;
Order(root,ans);
return ans;
}
};
5.二叉树的迭代遍历(基础必须掌握)
//二叉树的前序遍历:根左右
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
//只掌握递归写法完全不够,还需掌握迭代写法(很基础)
//利用栈实现树的前序遍历
vector<int>res;
if(root==nullptr){
return res;
}
stack<TreeNode *>st;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()){
TreeNode *node =st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if(node->right) st.push(node->right); //因为是栈,所以是先进栈右节点
if(node->left) st.push(node->left); //
}
return res;
}
};
//二叉树的中序遍历:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
//中序遍历:左根右
vector<int>res;
stack<TreeNode *>st;
while(root!=nullptr||!st.empty()){
while(root!=nullptr){
st.push(root);
root=root->left;
}
root=st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(root->val);
root=root->right;
}
return res;
}
};
//二叉树的后序遍历:先序遍历是中左右,后续遍历是左右中,那么我们只需要调整一下先序遍历的代码顺序,就变成中右左的遍历顺序,然后在反转result数组,输出的结果顺序就是左右中了
//后序遍历:左右根
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>res;
if(root==nullptr){
return res;
}
stack<TreeNode*>st;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()){
TreeNode *node=st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left) st.push(node->left);
if(node->right) st.push(node->right);
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
二叉树的统一迭代法
6.二叉数的层序遍历
BFS 的使用场景总结:层序遍历、最短路径问题
可以参考这篇点赞2k+的题解:链接: link
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
//层序遍历的模板
class Solution {
public:
//使用一个队列
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*>que;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
vector<vector<int>>res;
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
vector<int>vec;
//这里一定要使用固定大小的size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size()是不断变化的
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode *node=que.front();//front访问第一个元素,back访问最后一个元素
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(vec);
}
return res;
}
};
//递归法实现
class Solution {
public:
void order(TreeNode* cur, vector<vector<int>>& result, int depth)
{
if (cur == nullptr) return;
if (result.size() == depth) result.push_back(vector<int>());
result[depth].push_back(cur->val);
order(cur->left, result, depth + 1);
order(cur->right, result, depth + 1);
}
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
int depth = 0;
order(root, result, depth);
return result;
}
};
- 二叉树的层序遍历 II
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
//返回其节点值 自底向上的层序遍历:二叉树的遍历的逆序
queue<TreeNode *>que;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
vector<vector<int>>res;
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
vector<int>vec;
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode *node=que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(vec);
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
199.二叉树的右视图
//bfs:O(N),o(N)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
//使用层序遍历,并只保留每层最后一个节点的值
queue<TreeNode *>que;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
vector<int>res;
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode *node=que.front();
que.pop();
if(i==(size-1)) res.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
//DFS:我们按照 「根结点 -> 右子树 -> 左子树」 的顺序访问,就可以保证每层都是最先访问最右边的节点的。(与先序遍历 「根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树」 正好相反,先序遍历每层最先访问的是最左边的节点)
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(TreeNode *root,vector<int>&res,int depth){
if(root==nullptr){
return ;
}
//先访问当前节点,再递归的访问右子树和左子树
if(depth==res.size()){
/*如果当前节点所在的深度还没有出现再res里,
说明在该深度下当前节点是第一个被访问的节点,因此将当前节点加入res中
*/
res.push_back(root->val);
}
dfs(root->right,res,depth+1);
dfs(root->left,res,depth+1);
}
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>res;
dfs(root,res,0);
return res;
}
};
7.反转二叉树
//递归法
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return nullptr;
TreeNode *rightTree=root->right;
root->right=invertTree(root->left);
root->left=invertTree(rightTree);
return root;
}
};
//
N叉树的前后序遍历(n叉树没有中序遍历)
1.n叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {
public:
void helper(Node *cur,vector<int>&res){
if(cur==nullptr) return ;
res.push_back(cur->val);
for(auto ch:cur->children){
helper(ch,res);
}
}
vector<int> preorder(Node* root) {
vector<int>res;
helper(root,res);
return res;
}
};
2.n叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {
public:
void helper(Node *cur,vector<int>&res){
if(cur==nullptr) return ;
for(auto ch:cur->children){
helper(ch,res);
}
res.push_back(cur->val);
}
vector<int> postorder(Node* root) {
vector<int>res;
helper(root,res);
return res;
}
};
8.对称二叉树
101.对称二叉树
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)return true;
return dfs(root->left,root->right);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode *left,TreeNode *right){
if(left==nullptr&&right==nullptr){
return true;
}
if(left==nullptr||right==nullptr||left->val!=right->val){
return false;
}
return dfs(left->left,right->right)&&dfs(left->right,right->left);
}
};
相似题目:
100.相同的树
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
//如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的
if(p==nullptr&&q==nullptr) return true;
if(p==nullptr||q==nullptr||p->val!=q->val) return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
};
572.另一棵树的子树
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
/*
首先判断一个树是否是另一棵树的子树,很明显想到可以用递归,但是两棵树完全相同也可以看做一棵树是另一棵树的子树。
所以自然而然想到用一个判断两棵树是否相同的递归函数。
*/
if(subRoot==nullptr) return true;
if(root==nullptr) return false;
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root->right,subRoot)||isSameTree(root,subRoot);
}
bool isSameTree(TreeNode *s,TreeNode *t){
if(s==nullptr&&t==nullptr) return true;
if(s==nullptr||t==nullptr) return false;
if(s->val!=t->val) return false;
return isSameTree(s->left,t->left)&&isSameTree(s->right,t->right);
}
};
9.二叉树的最大深度
111.二叉树的最小深度
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode *cur){
if(cur==nullptr) return 0;
int leftDepth=getDepth(cur->left);
int rightDepth=getDepth(cur->right);
if(cur->left==nullptr&&cur->right!=nullptr){
return 1+rightDepth;
}
if(cur->right==nullptr&&cur->left!=nullptr){
return 1+leftDepth;
}
int res=1+min(leftDepth,rightDepth);
return res;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};
精简一下代码:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
int m1=minDepth(root->left);
int m2=minDepth(root->right);
//1.如果左孩子和右孩子有为空的情况,直接返回m1+m2+1
//2.如果都不为空,返回较小深度+1
return root->left==nullptr||root->right==nullptr?m1+m2+1:min(m1,m2)+1;
}
};
10.完全二叉树的节点个数
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
//层序遍历:迭代法
queue<TreeNode*>que;
int count=0;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode *node=que.front();
que.pop();
count++;
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return count;
}
};
//递归法
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
return 1+countNodes(root->left)+countNodes(root->right);
}
};
11.平衡二叉树
lass Solution {
public:
//一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1
int getDepth(TreeNode *cur){
if(cur==nullptr) return 0;
int leftHeight=getDepth(cur->left);
if(leftHeight==-1) return -1;
int rightHeight=getDepth(cur->right);
if(rightHeight==-1) return -1;
return abs(leftHeight-rightHeight)>1?-1:1+max(leftHeight,rightHeight);
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root)==-1? false:true;
}
};
13.二叉树的所有路径
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(TreeNode *cur,string path,vector<string>&res){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
//to_string 函数:将数字常量转换为字符串,返回值为转换完毕的字符串
path+=to_string(cur->val);
if(cur->left==nullptr&&cur->right==nullptr){
res.push_back(path);
}else{
path+="->";
dfs(cur->left,path,res);
dfs(cur->right,path,res);
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string>res;
string path;
dfs(root,path,res);
return res;
}
};
14.左叶子之和
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
//首先要注意是判断左叶子,不是二叉树左侧节点
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
int res=0;
if(root->left!=nullptr&&root->left->left==nullptr&&root->left->right==nullptr){
res+=root->left->val;
}
return res+sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left)+sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
}
};
15.找树左下角的指
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
//层序遍历:只需记录最后一行,第一个节点的数值就可以
queue<TreeNode *>que;
int res;
if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;++i){
TreeNode *node=que.front();
que.pop();
if(i==0) res=node->val;//记录最后一行的第一个节点的数值
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
//层序遍历,从右往左添加结点,最后访问的一个结点即为最后一层最左边的。
queue<TreeNode *>que;
int res;
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
auto p=que.front();
que.pop();
if(p->right) que.push(p->right);
if(p->left) que.push(p->left);
res=p->val;
}
return res;
}
};
17.路径总和
112.路径总和
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
//递归法:dfs
if(root==nullptr) return false;//经典先判空
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr){
return root->val-targetSum==0;
}
return hasPathSum(root->left,targetSum-root->val)||hasPathSum(root->right,targetSum-root->val);
}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
//广度优先遍历,记录从根节点到当前节点的路径和
if(root==nullptr) return false;
queue<TreeNode*>que_node;
queue<int>que_val;
que_node.push(root);
que_val.push(root->val);
while(!que_node.empty()){
TreeNode *node=que_node.front();
int tmp=que_val.front();
que_node.pop();
que_val.pop();
if(node->left==nullptr&&node->right==nullptr){
if(tmp==targetSum){
return true;
}
}
if(node->left!=nullptr){
que_node.push(node->left);
que_val.push(node->left->val+tmp);
}
if(node->right!=nullptr){
que_node.push(node->right);
que_val.push(node->right->val+tmp);
}
}
return false;
}
};
113.路径之和2
class Solution {
public:
//[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]],看到这种输出结果,肯定需要一个一维数组一个二维数组
//dfs:我们可以采用深度优先搜索的方式,枚举每一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
//当我们遍历到叶子节点,且此时路径和恰为目标和时,我们就找到了一条满足条件的路径。
vector<vector<int>>res;
vector<int>path;
void dfs(TreeNode *root,int targetSum){
if(root==nullptr) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
targetSum-=root->val;
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr&&targetSum==0){
res.push_back(path);
}
dfs(root->left,targetSum);
dfs(root->right,targetSum);
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root,targetSum);
return res;
}
};
//bfs
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
unordered_map<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> parent;
void getPath(TreeNode* node) {
vector<int> tmp;
while (node != nullptr) {
tmp.emplace_back(node->val);
node = parent[node];
}
reverse(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
ret.emplace_back(tmp);
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return ret;
}
queue<TreeNode*> que_node;
queue<int> que_sum;
que_node.emplace(root);
que_sum.emplace(0);
while (!que_node.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = que_node.front();
que_node.pop();
int rec = que_sum.front() + node->val;
que_sum.pop();
if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) {
if (rec == targetSum) {
getPath(node);
}
} else {
if (node->left != nullptr) {
parent[node->left] = node;
que_node.emplace(node->left);
que_sum.emplace(rec);
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
parent[node->right] = node;
que_node.emplace(node->right);
que_sum.emplace(rec);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
1026.节点与其祖先之间的最大差值
class Solution {
public:
int ans=0;
void dfs(TreeNode *cur,int mx,int mn){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
// 虽然题目要求「不同节点」,但是相同节点的差值为 0,不会影响最大差值
// 所以先更新 mn 和 mx,再计算差值也是可以的
// 在这种情况下,一定满足 mn <= node.val <= mx
mx=max(mx,cur->val);
mn=min(mn,cur->val);
ans=max(ans,max(cur->val-mn,mx-cur->val));
dfs(cur->left,mx,mn);
dfs(cur->right,mx,mn);
}
int maxAncestorDiff(TreeNode* root) {
//维护最大值,最小值即可。
dfs(root,root->val,root->val);
return ans;
}
};
18.由俩个遍历序列构建二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *dfs(vector<int>&inorder,vector<int>&postorder){
if(postorder.size()==0) return nullptr;
//后序遍历数组的最后一个元素,就是当前的中间节点
int rootValue=postorder[postorder.size()-1];
TreeNode *root=new TreeNode(rootValue);
if(postorder.size()==1) return root;
//找到中序遍历的切割点·
int index;
for(index=0;index<inorder.size();++index){
if(inorder[index]==rootValue) break;
}
//切割中序数组
//左闭右开区间:[o,index)[index,size]
vector<int>leftInorder(inorder.begin(),inorder.begin()+index);
vector<int>rightInorder(inorder.begin()+index+1,inorder.end());
postorder.resize(postorder.size()-1);
//切割后序数组
vector<int>leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin()+leftInorder.size());
vector<int>rightPostorder(postorder.begin()+leftInorder.size(),postorder.end());
root->left=dfs(leftInorder,leftPostorder);
root->right=dfs(rightInorder,rightPostorder);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
/* 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树,;理论清楚,那么代码怎么写呢?
第一步:如果数组的大小为0的话,说明是空节点
第二步:如果不为空,取后序遍历最后一个元素作为节点元素
第三步:找到后序数组的最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组
第五步:切割后序数组,切割成后序左数组和后序右数组
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
*/
if(inorder.size()==0||postorder.size()==0) return nullptr;
return dfs(inorder,postorder);
}
};
19.最大的二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *dfs(vector<int>&nums,int left,int right){
if(left>=right) return nullptr;
int index=left;
for(int i=left+1;i<right;++i){
if(nums[i]>nums[index]) index=i;
}
TreeNode *root=new TreeNode(nums[index]);
root->left=dfs(nums,left,index);
root->right=dfs(nums,index+1,right);
return root;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
return dfs(nums,0,nums.size());
}
};
20.合并二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if(root1==nullptr) return root2;
if(root2==nullptr) return root1;
auto merge=new TreeNode(root1->val+root2->val);
merge->left=mergeTrees(root1->left,root2->left);
merge->right=mergeTrees(root1->right,root2->right);
return merge;
}
};
21. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
//一个适用于各种二叉树的方法,运行速度比较慢
if(root==nullptr){
return nullptr;
}
if(root->val==val) return root;
TreeNode *node_left=searchBST(root->left,val);
TreeNode *node_right=searchBST(root->right,val);
if(node_left!=nullptr) return node_left;
if(node_right!=nullptr) return node_right;
return nullptr;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
//迭代
while(root!=nullptr&&root->val!=val){
root=root->val<val? root->right:root->left;
}
return root;
}
};
22.验证二叉搜索树
//
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>res;
void dfs(TreeNode *root){
if(root==nullptr) return;
dfs(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right);
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
//二叉搜索树中序遍历为递增序列
if(root==nullptr) return true;
dfs(root);
for(int i=1;i<res.size();++i){
if(res[i]<=res[i-1]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
优化代码
class Solution {
public:
long pre=LONG_MIN;//注意数据范围
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
//验证是否为二叉搜索树:中序遍历为升序
if(root==nullptr) return true;
//访问左子树
if(!isValidBST(root->left)){
return false;
}
//访问根节点
if(root->val<=pre){
return false;
}
pre=root->val;
return isValidBST(root->right);
}
};
23.中序遍历团灭系列二叉搜索树问题
中序遍历团灭系列二叉搜索树问题
二叉搜索树一个很重要的性质:中序遍历为升序序列
1.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>res;
int ans=INT_MAX;
void Inorder(TreeNode *root){
if(root==nullptr) return;
Inorder(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
Inorder(root->right);
}
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
//注意是二叉搜索树,二叉搜索树可是有序的。
if(root==nullptr) return 0;
Inorder(root);
for(int i=1;i<res.size();++i){
ans=min(ans,res[i]-res[i-1]);
}
return ans;
}
};
- 二叉搜索树中第k小的元素
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>res;
void Inorder(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
Inorder(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
Inorder(root->right);
}
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
Inorder(root);
sort(res.begin(),res.end());
//使用了sort,使时间复杂度大大增加,可在中序遍历初处理
return res[res.size()-k];
}
};
优化:倒叙中序遍历,第k个就是所需结果
class Solution {
public:
int res;
void dfs(TreeNode *root,int &k){
if(root==NULL) return;
dfs(root->right,k);
if(--k==0) res=root->val;
dfs(root->left,k);
}
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
dfs(root,k);
return res;
}
};
3.二叉搜索树中的众数
c++的语法还不是很熟悉啊
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>res;
unordered_map<int,int>map;
void dfs(TreeNode *root,unordered_map<int,int>& map){
if(root==nullptr) return ;
dfs(root->left,map);
map[root->val]++;
dfs(root->right,map);
}
bool static cmp(const pair<int,int>&a,const pair<int,int>&b){
return a.second>b.second;
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return res;
dfs(root,map);
vector<pair<int,int>>vec(map.begin(),map.end());
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),cmp);//给频率排个序
res.push_back(vec[0].first);
for(int i=1;i<vec.size();++i){
if(vec[i].second==vec[0].second) res.push_back(vec[i].first);
else break;
}
return res;
}
};
优化:中序遍历二叉搜索树是一个有序数组,给出一个有序数组,求最大频率的元素集合。
class Solution {
private:
int count;
int maxCount;
TreeNode *pre;
vector<int>res;
void dfs(TreeNode *cur){
if(cur==nullptr) return;
dfs(cur->left);//左
if(pre==nullptr){//第一个节点
count=1;
}else if(pre->val==cur->val){//与前一个节点数值相同
count++;
}else{//与前一个节点数值不同
count=1;
}
pre=cur;//更新上一个节点
if(count==maxCount){//如果和最大值相同,放入res中
res.push_back(cur->val);
}
if(count>maxCount){//如果计数大于最大值
maxCount=count;
res.clear();
res.push_back(cur->val);
}
dfs(cur->right);
}
public:
//中序遍历二叉搜索树是一个有序数组,给出一个有序数组,求最大频率的元素集合。
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
int count=0; //记录元素出现的次数
int maxCount=0;
TreeNode *pre=nullptr;//记录前一个节点
res.clear();
dfs(root);
return res;
}
};
24.二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
if(root == p || root == q)
return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == NULL)
return right;
if(right == NULL)
return left;
if(left && right) // p和q在两侧
return root;
return NULL; // 必须有返回值
}
};
25.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
方法一,参考 236,二叉树迭代最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root==NULL||root==p||root==q) return root;
TreeNode *left=lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
TreeNode *right=lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
if(left&&right) return root;
if(left==NULL) return right;
return left;
}
};
26.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(root==nullptr){
TreeNode *node=new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if(val<root->val){
root->left=insertIntoBST(root->left,val);
}
if(val>root->val){
root->right=insertIntoBST(root->right,val);
}
return root;
}
};
27.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
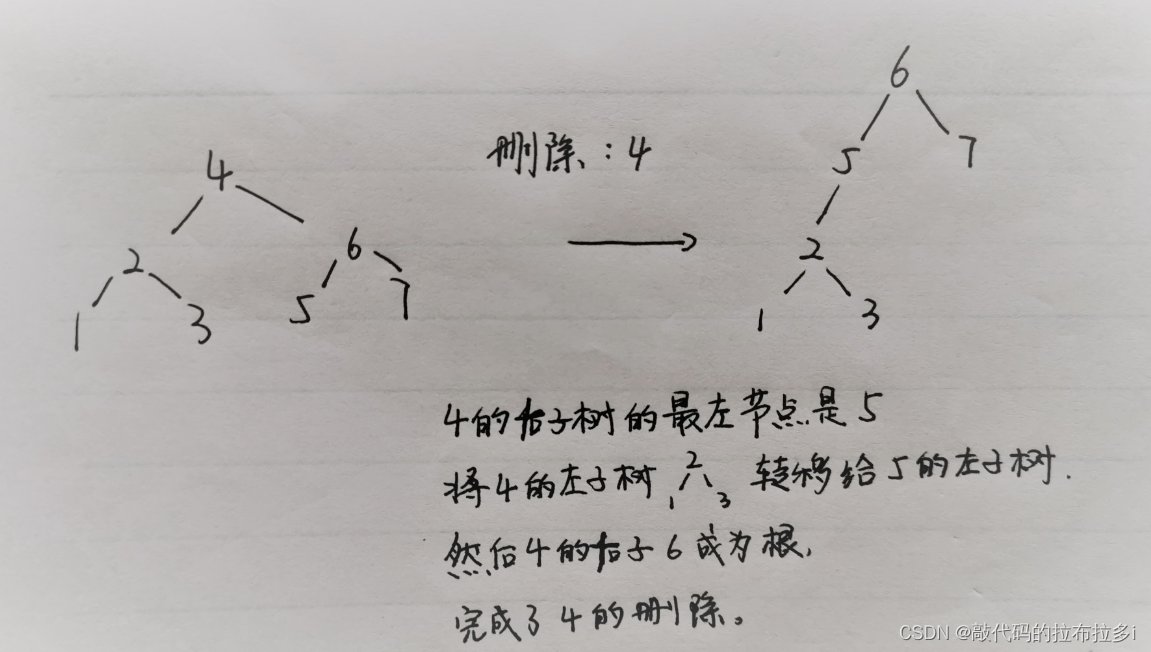
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
/*根据二叉搜索树的性质:(主要把删除)
如果目标节点大于当前节点值,则去右子树中删除;
如果目标节点小于当前节点值,则去左子树中删除;
如果目标节点就是当前节点,分为以下三种情况:
其无左子:其右子顶替其位置,删除了该节点;
其无右子:其左子顶替其位置,删除了该节点;
其左右子节点都有:其左子树转移到其右子树的最左节点的左子树上,然后右子树顶替其位置,由此删除了该节点。
*/
if(root==nullptr) return nullptr;
if(key>root->val) root->right=deleteNode(root->right,key);
else if(key<root->val) root->left=deleteNode(root->left,key);
else{
if(!root->left) return root->right; //情况一,欲删除节点无左子
if(!root->right) return root->left;//情况二,欲删除节点无右子
TreeNode *node=root->right; //情况三,欲删除节点左右子都有
while(node->left){ //寻找欲删除节点右子树的最左节点
node=node->left;
}
node->left=root->left; //将欲删除节点的左子树成为其右子树的最左节点的左子树
root=root->right; //将欲删除节点的右子顶替其位置,节点被删除
}
return root;
}
};
28.修剪二叉搜素树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
/*一下代码不可行,因为有些节点不能直接删除
if(root==nullptr||root->val<low||root->val>high) return nullptr;
root->left=trimBST(root->left,low,high);
root->right=trimBST(root->right,low,high);
return root;
*/
if(root==nullptr) return nullptr;
if(root->val<low){//注意是二叉搜索树
TreeNode *right=trimBST(root->right,low,high);
return right;
}
if(root->val>high){
TreeNode *left=trimBST(root->left,low,high);
return left;
}
root->left=trimBST(root->left,low,high);
root->right=trimBST(root->right,low,high);
return root;
}
};
29.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode * dfs(vector<int>&nums,int left,int right){
if(left>right) return nullptr;
//总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点
int mid=left+((right-left)/2);
TreeNode *node=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
node->left=dfs(nums,left,mid-1);
node->right=dfs(nums,mid+1,right);
return node;
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
//中序遍历二叉搜素树是有序数组,分割
TreeNode*root=dfs(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
return root;
}
};
30.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
lc 538和lc1038
class Solution {
public:
//从图中可以看出累加顺序是右中左
int pre=0;//记录前一个节点的值
void dfs(TreeNode *root){
if(root==nullptr) return;
dfs(root->right);
root->val+=pre;
pre=root->val;
dfs(root->left);
}
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr) return nullptr;
dfs(root);
return root;
}
};





















 958
958











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








