问题描述
24点游戏是经典的纸牌益智游戏。
常见游戏规则:
从扑克中每次取出4张牌。使用加减乘除,第一个能得出24者为赢。(其中,J代表11,Q代表12,K代表13,A代表1),按照要求编程解决24点游戏。
基本要求: 随机生成4个代表扑克牌牌面的数字字母,程序自动列出所有可能算出24的表达式,用擅长的语言(C/C++/Java或其他均可)实现程序解决问题。
1.程序风格良好(使用自定义注释模板)
2.列出表达式无重复。
内容
算法分析
1.函数random_number()随机生成4个1~13范围内的整数;
2.poke()函数将生成的四个随机整数以扑克牌的形式输出(A,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,J,Q,K);
3.fun()函数进行两个数的四则运算;
4.calculate()函数计算所有情况;
5.timer()函数实现计时器功能;
6.player()函数就是玩家进行游戏:
玩家初始生命值为3,分数为0,若随机生成的四个数可以组成24并且玩家能写出其中一种表达式则可得十分,若四张牌无法完成24点或者玩家未在规定的时间内完成,则生命值减1,减到0游戏结束。
概要设计
流程图:

代码如下:
"""
@author: CheYuHang
@software: PyCharm
@file: puke.py
@time: 2021/5/9 12:35
"""
import random
import time
def random_number():
"""
随机生成四个整数
:return:
"""
y = []
for i in range(4):
y.append(random.randint(1,13))
return y
# def fun(k,l,i):
# """
# 两个数据之间的运算
# :param k:
# :param l:
# :param i:
# :return:
# """
# if i==0:
# tem = k+l
# return tem
# elif i==1:
# tem = k-l
# return tem
# elif i==2:
# tem = k*l
# return tem
# elif i==3:
# if l==0:
# return
# else:
# tem = k/l
# return tem
def fun(k, l, i):
"""
两个数据之间的运算
:param k:
:param l:
:param i:
:return:
"""
if i==0:
if (type(k) is int or type(k) is float) and (type(l) is int or type(l) is float):
tem = k + l
return tem
else:
return
elif i==1:
if (type(k) is int or type(k) is float) and (type(l) is int or type(l) is float):
tem = k - l
return tem
else:
return
elif i==2:
if (type(k) is int or type(k) is float) and (type(l) is int or type(l) is float):
tem = k * l
return tem
else:
return
elif i==3:
if (type(k) is int or type(k) is float) and (type(l) is int or type(l) is float):
if l != 0:
tem = k / l
return tem
else:
return
else:
return
def poker(y):
"""
将生成的随机数以扑克牌的形式输出
:param y:
:return:
"""
y1 = y.copy()
while 1 in y1 or 11 in y1 or 12 in y1 or 13 in y1:
if 1 in y1:
z = y1.index(1)
y1.remove(1)
y1.insert(z, 'A')
if 11 in y1:
z = y1.index(11)
y1.remove(11)
y1.insert(z, 'J')
if 12 in y1:
z = y1.index(12)
y1.remove(12)
y1.insert(z, 'Q')
if 13 in y1:
z = y1.index(13)
y1.remove(13)
y1.insert(z, 'K')
continue
# if 1 in y1:
# z = y1.index(1)
# y1.remove(1)
# y1.insert(z, 'A')
# if 11 in y1:
# z = y1.index(11)
# y1.remove(11)
# y1.insert(z, 'J')
# if 12 in y1:
# z = y1.index(12)
# y1.remove(12)
# y1.insert(z, 'Q')
# if 13 in y1:
# z = y1.index(13)
# y1.remove(13)
# y1.insert(z, 'K')
print("随机抽取的四张牌为:", y1[0], y1[1], y1[2], y1[3])
# y = random_number()
# print(y)
# y = [7, 1, 11, 6]
# x = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
def calculate(y):
"""
计算,求出符合题目要求的
:return:
"""
result_list = []
result_list2 = []
temp = 0
temp1 = 0
temp2 = 0
for i in range(0,4):
for j in range(0,4):
for k in range(0,4):
for l in range(0,4):
if i == j or i == k or i == l or j == k or j == l or k == l:
continue
else:
for n in range(0,4):
for m in range(0,4):
for p in range(0,4):
for q in range(0,6):
result = 0
if q == 0:
temp1 = fun(y[i], y[j], n)
temp1 = fun(temp1, y[k], m)
result = fun(temp1, y[l], p)
if result==24:
result_list.append(
"(({0}{1}{2}){3}{4}){5}{6}=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
result_list2.append(
"(({0}{1}{2}){3}{4}){5}{6}".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
# print("(({0}{1}{2}){3}{4}){5}{6}=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
# x[p], y[l]))
temp += 1
#break
continue
elif q == 1:
temp1 = fun(y[i], y[j], n)
temp2 = fun(y[k], y[l], p)
result = fun(temp1, temp2, m)
if result == 24:
result_list.append(
"({0}{1}{2}){3}({4}{5}{6})=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
result_list2.append(
"({0}{1}{2}){3}({4}{5}{6})".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
# print("({0}{1}{2}){3}({4}{5}{6})=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
# x[p], y[l]))
temp += 1
#break
continue
elif q == 2:
temp1 = fun(y[j], y[k], m)
temp1 = fun(y[i], temp1, n)
result = fun(temp1, y[l], p)
if result == 24:
result_list.append(
"({0}{1}({2}{3}{4})){5}{6}=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
result_list2.append(
"({0}{1}({2}{3}{4})){5}{6}".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
# print("({0}{1}({2}{3}{4})){5}{6}=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
# x[p], y[l]))
temp += 1
# break
continue
# elif q==3:
# temp1 = fun(y[k], y[l], m)
# temp2 = fun(y[i], y[j], p)
# result = fun(temp1, temp2, n)
# if result == 24:
#
# print("({0}{1}{2}){3}({4}{5}{6})=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
# x[p], y[l]))
# temp += 1
# break
elif q == 3:
temp1 = fun(y[j], y[k], m)
temp1 = fun(temp1, y[l], p)
result = fun(y[i], temp1, n)
if result == 24:
result_list.append(
"{0}{1}(({2}{3}{4}){5}{6})=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
result_list2.append(
"{0}{1}(({2}{3}{4}){5}{6})".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
# print("{0}{1}(({2}{3}{4}){5}{6})=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
# x[p], y[l]))
temp += 1
#break
continue
elif q == 4:
temp1 = fun(y[k], y[l], p)
temp1 = fun(y[j], temp1, m)
result = fun(y[i], temp1, n)
if result == 24:
result_list.append(
"{0}{1}({2}{3}({4}{5}{6}))=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
result_list2.append(
"{0}{1}({2}{3}({4}{5}{6}))".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
x[p], y[l]))
# print("{0}{1}({2}{3}({4}{5}{6}))=24".format(y[i], x[n], y[j], x[m], y[k],
# x[p], y[l]))
temp += 1
#break
continue
return temp, result_list, result_list2
# if temp == 0:
# print("这四张牌无法完成24点游戏")
# else:
# print()
def timer():
"""
计时器
:return:
"""
return time.perf_counter()
def player():
"""
玩家进行游戏
:return:
"""
hit_point = 3
score = 0
print("==================================================")
print("== 24点游戏 ==")
print("==游戏玩家开始时的血量为:{0} ==".format(hit_point))
print("==游戏玩家开始时的分数为:{0} ==".format(score))
print("==是否开始游戏:Y or N ==")
print("==================================================")
use = input()
while use == 'Y':
y = random_number()
poker(y)
result, result_list, result_list2 = calculate(y)
if result == 0:
print("这四个数无法完成24点游戏,生命值扣一")
hit_point -= 1
if hit_point !=0:
print("你当前的生命值为:{0} 是否继续:Y/N".format(hit_point))
use = input()
else:
print("生命值为0,游戏结束")
break
# break
continue
elif result != 0:
print("请玩家输入正确表达式:(A为1,J为11,Q为12,K为13)")
# for i in result_list:
# print(i)
start_time = timer()
player_expression = input()
end_time = timer()
if end_time-start_time <= 10:
if player_expression in result_list2:
print("回答正确,加十分")
score += 10
print("这四张牌所有的组合为:")
for i in result_list:
print("{0}".format(i))
print("是否继续:Y/N")
use = input()
else:
print("回答错误:生命值扣一")
hit_point -= 1
if hit_point != 0:
print("你当前的生命值为:{0} 得分为{1}".format(hit_point, score))
print("这四张牌所有的组合为:")
for i in result_list:
print("{0}".format(i))
print("是否继续:Y/N")
use = input()
else:
print("生命值为0,游戏结束")
break
# print("这四张牌所有的组合为:")
# for i in result_list:
# print("{0}".format(i))
# print("是否继续:Y/N")
# use = input()
else:
print("未在规定时间内答完,生命值减一")
hit_point -= 1
print("是否继续:Y/N")
use = input()
continue
# continue
print("你最后的生命值为:{0};最终得分为:{1}".format(hit_point, score))
# y = random_number()
# # y = [5,9,3,7]
# x = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
# poker(y)
# calculate(y)
x = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
player()
测试
测试的时候出现这个错误:unsupported operand type(s) for +: ‘NoneType’ and ‘int’
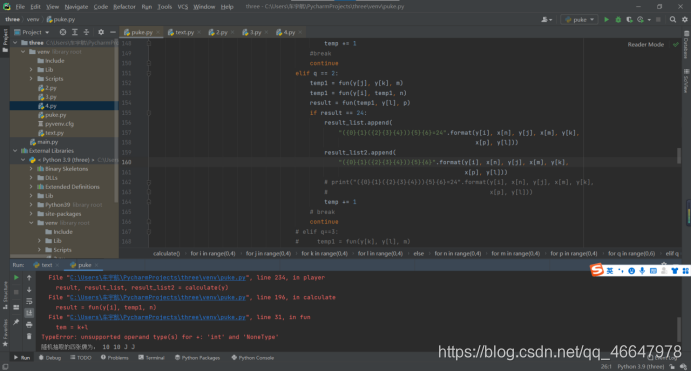
将fun()函数进行了修改:

调试
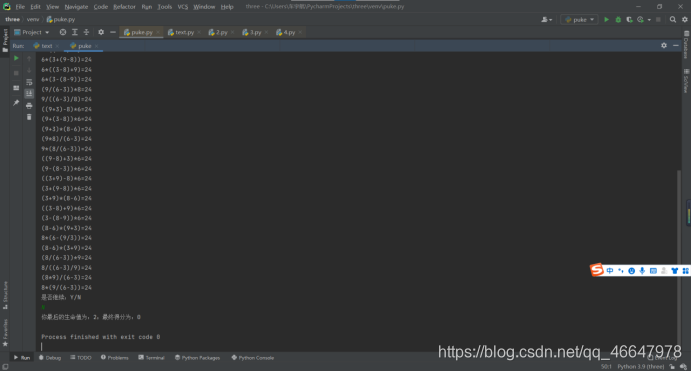
运行程序:出现游戏页面

玩家输入Y进行游戏,这时,会自动生成四张扑克,电脑自动判断这四个数是否可以完成24点游戏,若可以完成,则需要玩家在规定的时间内完成一个表达式的输入,若输入合理,则得10分并输出所有可能的表达式,若输入不合理或者未在规定时间内完成,则扣1点生命值,如果生命值为0或者玩家不继续进行游戏,则游戏结束:



玩家未在规定时间内完成:

第二次测试:

心得体会
在做的过程中,比较难得就是这四个随机数和四个运算符能有多少种排列组合,最后在比较下,使用括号对四个数进行分类比较合适(共四种情况)。
在处理那个异常的情况下,在网上找资源,以及查阅资料,将那个异常解决了,这个是最花费时间的。








 本文详细介绍了一款经典纸牌游戏——24点游戏的算法实现过程,包括随机数生成、四则运算处理、组合计算及游戏逻辑实现,并附带完整的Python代码示例。
本文详细介绍了一款经典纸牌游戏——24点游戏的算法实现过程,包括随机数生成、四则运算处理、组合计算及游戏逻辑实现,并附带完整的Python代码示例。
















 1955
1955

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








