并行化数据挖掘算法设计
数据挖掘算法
选用Naive-Bayes 进行简单的数据挖掘,采用IRIS数据集进行训练以及测试,实现了串行的NB算法以及Map-Reduce的并行的NB算法。
Navie Bayes 思想
设每个数据样本用一个n维特征向量来描述n个属性的值,即:X={x1,x2,…,xn},假定有m个类,分别用Y1, Y2,…,Ym表示
给定一个未分类的数据样本X,若朴素贝叶斯分类将未知的样本X分配给类Yi,则一定有P(Yi|X)>P(Yj|X), 1≤j≤m,j≠i
根据贝叶斯定理P(Yi|X)=P(X|Yi)*P(Yi)/P(X),由于P(X)对于所有类为常数,概率P(Yi|X)可转化为概率P(X|Yi)P(Yi)
如果训练数据集中有很多具有相关性的属性,计算P(X|Yi)将非常复杂,为此,通常假设各属性是互相独立的,这样P(X|Yi) 的计算可简化为求P(x1|Yi),P(x2|Yi),…,P(xn|Yi)之积;而每个P(xj|Yi)可以从训练数据集近似求得
据此,对一个未知类别的样本X,可以先分别计算出X属于每一个类别Yi的概率P(X|Yi)P(Yi),然后选择其中概率最大的Yi作为其类别
数据集选取
使用IRIS数据集进行训练以及测试,Iris数据集是常用的分类实验数据集,由Fisher, 1936收集整理。Iris也称鸢尾花卉数据集,是一类多重变量分析的数据集。数据集包含150个数据样本,分为3类,每类50个数据,每个数据包含4个属性。可通过花萼长度,花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度4个属性预测鸢尾花卉属于(Setosa,Versicolour,Virginica)三个种类中的哪一类。
类别:三种
Iris Setosa,Iris Versicolour,Iris Virginica
属性数:四
sepal length(花萼长度)sepal width(花萼宽度)petal length(花瓣长度)petal width(花瓣宽度)
总数据集:共150项数据
训练数据集:选取三个类别每个50条里面的40条进行训练
测试数据集:选取总数据集 - 测试数据集 的 数据集,共三十条进行测试,计算准确率
串行化NB的实现
基础数据结构
conf保存基础的输入输出信息,HashMap freq保存对应的 某个统计量的频数
add 是更新HashMap的方法
// 加载conf
private static NaiveBayesConf NBConf = new NaiveBayesConf();
// 保存频数
public static HashMap<String,Integer> freq = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// add
public static void add(String key){
// 不存在则初始化为1
if(freq.get(key) == null)
freq.put(key, new Integer(1));
else{
// 频数++
int temp = freq.get(key).intValue() + 1;
freq.put(key,new Integer(temp));
}
}
Train
对于输入的每一行,实际上统计了P(Yi) 以及 P(Xj | Yi)的频数
/* Input line
* Output key:sum value:count
* key:classStr value:count
* key:classStr#deminNo#deminVal value:count
*/
public static void train(String trainFile) throws Exception{
FileInputStream filein = new FileInputStream(trainFile);
BufferedReader bufin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(filein));
// sum用来count 某分类结果的频数
int sum = 0;
String line;
// 逐行扫描训练数据集
while ((line = bufin.readLine()) != null) {
sum++;
String[] vals = line.split("\t");
// add 类别
add(vals[0]);
//add 类别#属性编号#属性值
for(int i = 1;i < vals.length;i++){
String temp = new String();
temp += vals[0] + "#" + (i - 1) + "#" + vals[i];
add(temp);
}
}
freq.put("sum",new Integer(sum));
bufin.close();
filein.close();
}
Test
输入属性,测试P(Yi | xi) 取最大的作为类别
public void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
double pyi,px_yi,pxj_yi;
double maxp = 0;
int idx = -1;
int sum,sub;
Integer integer = nBTData.freq.get("sum");
if(integer == null)
sum = 0;
else
sum = integer.intValue();
String[] vals = value.toString().split(" ");
for(int i = 0;i < nBConf.class_num;i++){
px_yi = 1;
String class_name = nBConf.classNames.get(i);
integer = nBTData.freq.get(class_name);
if(integer == null){
sub = 0;
pyi = 0;
}
else{
sub = integer.intValue();
pyi = (double)sub / sum;
}
for(int j = 1;j < vals.length;j++){
String temp = class_name + "#" + (j - 1) + "#" + vals[j];
integer = nBTData.freq.get(temp);
if (integer == null) pxj_yi = 0;
else pxj_yi = (double)integer.intValue() / sub;
px_yi = px_yi * pxj_yi;
}
if(px_yi * pyi > maxp){
maxp = px_yi * pyi;
idx = i;
}
}
context.write(new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(vals[0])), new Text("" + idx));
}
getAccuracy
计算准确率 读入测试结果
public static void getAccuarcy(String outfile, String answerfile) throws Exception{
FileInputStream filetest = new FileInputStream(outfile);
BufferedReader tests = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(filetest));
FileInputStream fileans = new FileInputStream(answerfile);
BufferedReader answers = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fileans));
String test;
String answer;
// 读取测试的结果 和 标准结果比对
int sum = 0;
while ((test = tests.readLine()) != null && (answer = answers.readLine()) != null) {
String[] testval = test.split("\t");
String[] ansval = answer.split(" ");
int testnum = Integer.parseInt(testval[1]);
int ansnum = Integer.parseInt(ansval[1]);
// System.out.println("test:"+ testnum + " answer:"+ ansnum + "\n");
if(testnum == ansnum)
sum++;
}
System.out.println("Accuarcy: " + sum / 30.0);
}
并行化NB实现
Train
train里面Map 主要是统计 类#属性#属性值 更新HashMap
Reducer类 主要是统计 类#属性#属性值 的count之和 写入中间结果 用于测试
Test
map是在给定xi 下计算P(Yi | Xi) 并且选取最大的write
reduce 是把Map传来的<key=行号,value = 类别> 写入文件
结果
准确率方面
即使是小数据集,150条,仍然可以得到不错的结果,测得准确率在
Accuarcy: 0.7666666666666667
success!
76.67% 左右
对比结果
对比串行化以及并行化最后的输出结果,diff比较,完全一样
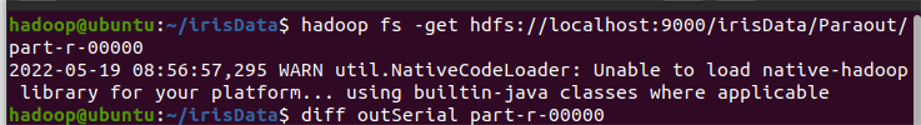

效率方面
注意:默认map 以及 reduce task 都是1个。所以实际上的MapReduce的NB也是并行的,需要手动设置MapTask个数以及ReduceTask个数,来并行,而最关键的则是MapTask个数
又考虑到数据量太小,所以把TrainData分别复制50、100次,这样就有50、100个MapTask,然后同时对比串行化,测试时间对比
| Train数据量 | MapTask个数 | 并行化时间 | 串行化时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12000 | 100 |  |  |
| 6000 | 50 |  |  |
测时间
- long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间
- doSomeThing(); //测试的代码段
- long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间
- System.out.println("程序运行时间: "+(end-start)+“ms”);

























 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










